Empathy mapping focuses on understanding customers' emotions, thoughts, and needs to improve user experience, while root cause analysis identifies underlying problems in processes to prevent issues and enhance performance. Both techniques are essential in management for creating effective solutions and driving organizational success. Explore how combining empathy mapping with root cause analysis can transform your management strategies.
Why it is important
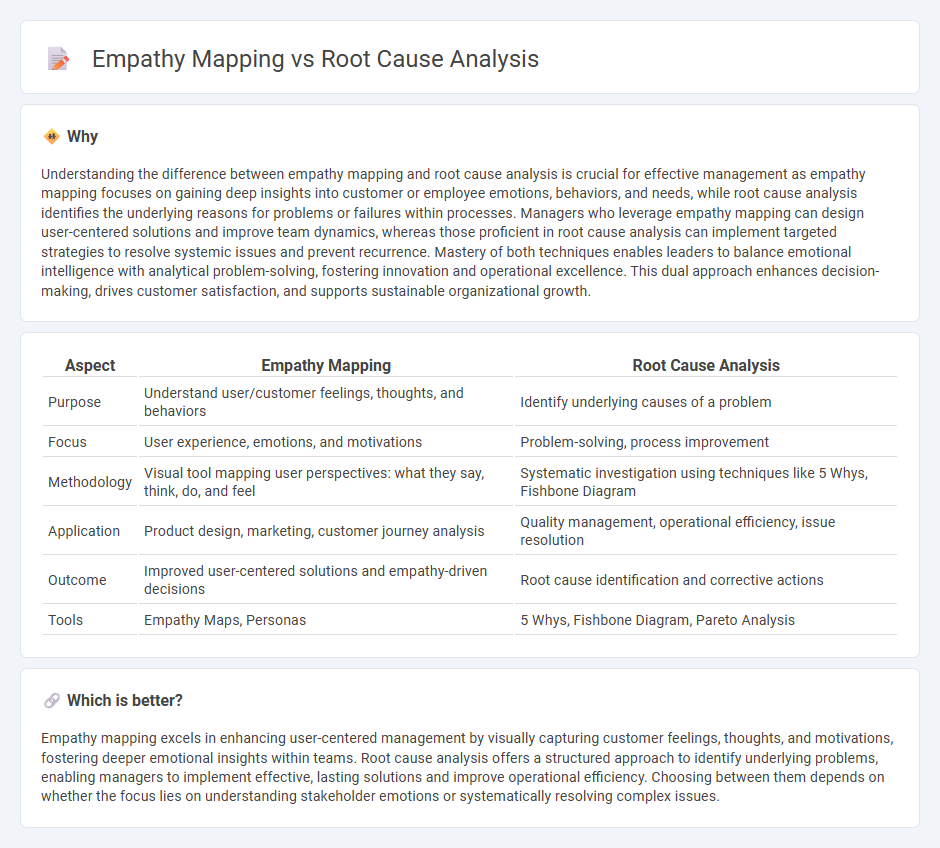
Understanding the difference between empathy mapping and root cause analysis is crucial for effective management as empathy mapping focuses on gaining deep insights into customer or employee emotions, behaviors, and needs, while root cause analysis identifies the underlying reasons for problems or failures within processes. Managers who leverage empathy mapping can design user-centered solutions and improve team dynamics, whereas those proficient in root cause analysis can implement targeted strategies to resolve systemic issues and prevent recurrence. Mastery of both techniques enables leaders to balance emotional intelligence with analytical problem-solving, fostering innovation and operational excellence. This dual approach enhances decision-making, drives customer satisfaction, and supports sustainable organizational growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Empathy Mapping | Root Cause Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Understand user/customer feelings, thoughts, and behaviors | Identify underlying causes of a problem |
| Focus | User experience, emotions, and motivations | Problem-solving, process improvement |
| Methodology | Visual tool mapping user perspectives: what they say, think, do, and feel | Systematic investigation using techniques like 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram |
| Application | Product design, marketing, customer journey analysis | Quality management, operational efficiency, issue resolution |
| Outcome | Improved user-centered solutions and empathy-driven decisions | Root cause identification and corrective actions |
| Tools | Empathy Maps, Personas | 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, Pareto Analysis |
Which is better?
Empathy mapping excels in enhancing user-centered management by visually capturing customer feelings, thoughts, and motivations, fostering deeper emotional insights within teams. Root cause analysis offers a structured approach to identify underlying problems, enabling managers to implement effective, lasting solutions and improve operational efficiency. Choosing between them depends on whether the focus lies on understanding stakeholder emotions or systematically resolving complex issues.
Connection
Empathy mapping enhances root cause analysis by providing deep insights into customer emotions, behaviors, and pain points, revealing the underlying reasons behind problems. This combined approach allows management to identify not only the symptoms but also the emotional and experiential factors driving issues. Integrating empathy mapping with root cause analysis leads to more effective problem-solving and customer-centered strategies.
Key Terms
**Root Cause Analysis:**
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies the underlying causes of problems by systematically examining processes and events to prevent recurrence. It often uses tools like the 5 Whys, Fishbone diagrams, and fault tree analysis to dissect complex issues and improve decision-making. Explore detailed methodologies and practical applications to master Root Cause Analysis.
Five Whys
Root cause analysis, particularly the Five Whys technique, systematically uncovers the underlying causes of a problem by repeatedly asking "why" to go beyond surface symptoms. Empathy mapping centers on understanding customer experiences, feelings, and motivations to identify needs and pain points rather than causal roots. Explore how integrating Five Whys with empathy mapping can deepen insights and improve problem-solving effectiveness.
Fishbone Diagram
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is a key tool in root cause analysis used to systematically identify potential causes of a problem by categorizing them into major branches like Methods, Machines, Materials, and People. Empathy mapping, in contrast, centers on understanding user experiences and emotions by charting what users say, think, feel, and do, making it less about problem causation and more about human-centered insights. Explore how the Fishbone Diagram can effectively isolate root causes for process improvement and quality control.
Source and External Links
Root Cause Analysis Explained: Definition, Examples, and Methods - Root cause analysis (RCA) is the process of discovering the root causes of problems by asking iterative "why" questions, such as in the 5 Whys method, to identify appropriate solutions and prevent recurrence of issues.
Root Cause Analysis: A Quick Guide - ProjectManager - Root cause analysis uses problem-solving techniques like the "Five Whys" to systematically dig deeper into issues, helping teams uncover underlying causes of failures in processes or projects.
What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)? - ASQ - Root cause analysis encompasses a range of approaches and techniques such as causal factor analysis, change analysis, and barrier analysis to methodically identify the causes behind problems and prevent them in the future.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com