Reverse mentoring pairs younger employees with senior leaders, fostering knowledge exchange on technology and fresh perspectives to enhance leadership agility. Peer mentoring involves colleagues at similar career stages supporting each other's skill development and problem-solving through shared experiences. Explore the benefits and applications of both mentoring styles to optimize organizational growth.
Why it is important
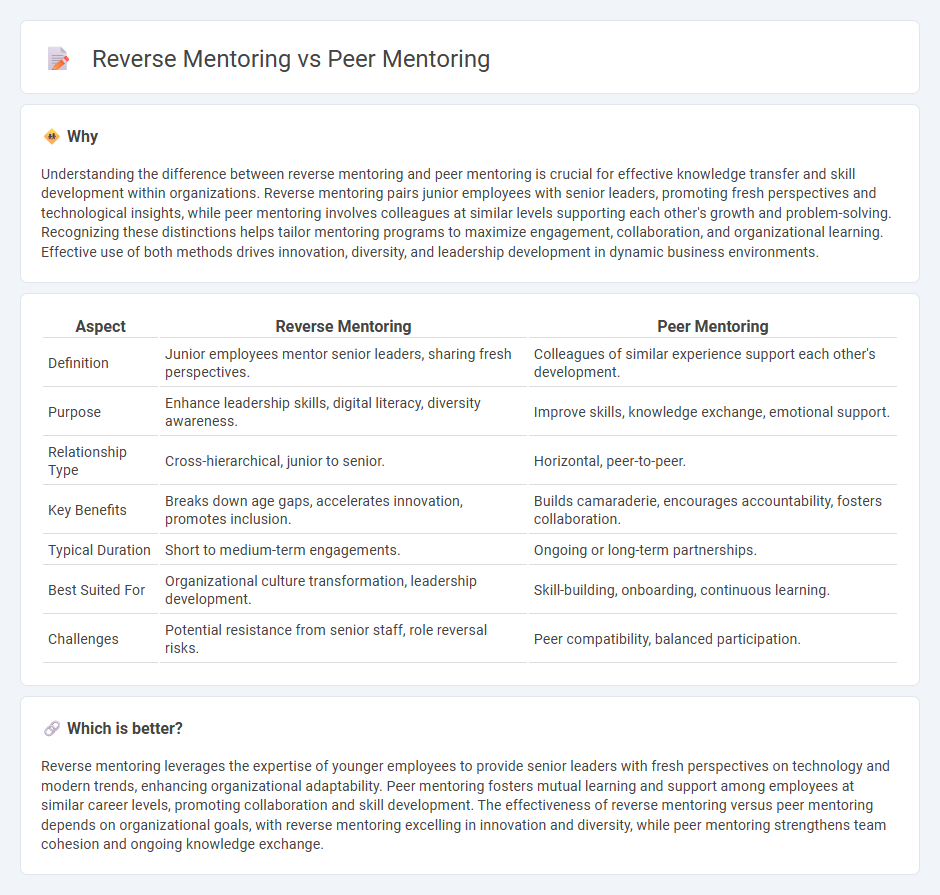
Understanding the difference between reverse mentoring and peer mentoring is crucial for effective knowledge transfer and skill development within organizations. Reverse mentoring pairs junior employees with senior leaders, promoting fresh perspectives and technological insights, while peer mentoring involves colleagues at similar levels supporting each other's growth and problem-solving. Recognizing these distinctions helps tailor mentoring programs to maximize engagement, collaboration, and organizational learning. Effective use of both methods drives innovation, diversity, and leadership development in dynamic business environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Mentoring | Peer Mentoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Junior employees mentor senior leaders, sharing fresh perspectives. | Colleagues of similar experience support each other's development. |
| Purpose | Enhance leadership skills, digital literacy, diversity awareness. | Improve skills, knowledge exchange, emotional support. |
| Relationship Type | Cross-hierarchical, junior to senior. | Horizontal, peer-to-peer. |
| Key Benefits | Breaks down age gaps, accelerates innovation, promotes inclusion. | Builds camaraderie, encourages accountability, fosters collaboration. |
| Typical Duration | Short to medium-term engagements. | Ongoing or long-term partnerships. |
| Best Suited For | Organizational culture transformation, leadership development. | Skill-building, onboarding, continuous learning. |
| Challenges | Potential resistance from senior staff, role reversal risks. | Peer compatibility, balanced participation. |
Which is better?
Reverse mentoring leverages the expertise of younger employees to provide senior leaders with fresh perspectives on technology and modern trends, enhancing organizational adaptability. Peer mentoring fosters mutual learning and support among employees at similar career levels, promoting collaboration and skill development. The effectiveness of reverse mentoring versus peer mentoring depends on organizational goals, with reverse mentoring excelling in innovation and diversity, while peer mentoring strengthens team cohesion and ongoing knowledge exchange.
Connection
Reverse mentoring and peer mentoring both foster knowledge exchange and skill development by leveraging different levels of experience within an organization. Reverse mentoring pairs junior employees with senior leaders to share fresh perspectives and digital skills, while peer mentoring connects colleagues at similar levels to enhance collaboration and professional growth. Together, these approaches create a dynamic learning environment that drives innovation and strengthens organizational culture.
Key Terms
Experience Sharing
Peer mentoring involves individuals with similar experience levels exchanging knowledge and skills to enhance professional growth, fostering mutual development in a collaborative environment. Reverse mentoring pairs junior employees with senior leaders, enabling the sharing of fresh perspectives and up-to-date expertise, particularly in areas like technology and digital trends. Discover how both approaches can transform your organization's culture and skill set by exploring their unique benefits in experience sharing.
Knowledge Transfer
Peer mentoring facilitates knowledge transfer by promoting shared learning between colleagues of similar experience, enabling skill development and problem-solving through mutual support. Reverse mentoring enhances knowledge exchange by allowing younger or less experienced employees to share digital skills and fresh perspectives with senior leaders, fostering innovation and adaptability. Explore further to understand how these mentoring approaches optimize organizational knowledge flow.
Mutual Learning
Peer mentoring fosters a collaborative environment where individuals with similar experience levels exchange skills and knowledge to enhance personal and professional growth. Reverse mentoring flips traditional roles, enabling younger or less experienced employees to share fresh perspectives and digital expertise with senior staff, driving innovation and inclusivity. Explore deeper insights on how mutual learning through these mentoring approaches boosts organizational success.
Source and External Links
Peer mentoring - Peer mentoring is a form of mentorship that involves a person with experience supporting someone new to a similar experience, often used in educational settings or for lifestyle changes.
Peer Mentor Programs: What They Are and How to Start One - This article discusses the concept of peer mentoring programs as lateral relationships where mentors and mentees are close in age or experience, facilitating a collaborative learning environment.
What is a Peer Mentor, and How Does Peer Mentoring Work? - Peer mentoring is described as a process where two individuals at similar stages in their careers or life experiences work together to support each other's growth and development.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com