Hyper-local delivery focuses on delivering goods directly from a nearby source to the customer, reducing transit time and enhancing customer satisfaction through rapid service. Warehouse consolidation involves centralizing inventory in fewer locations to streamline operations, reduce storage costs, and optimize freight efficiencies. Explore the benefits and challenges of both strategies to determine the best logistics solution for your business needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between hyper-local delivery and warehouse consolidation is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing last-mile delivery costs. Hyper-local delivery focuses on rapid shipments within a small geographic area, enhancing customer satisfaction with faster order fulfillment. Warehouse consolidation strategically aggregates inventory to minimize storage expenses and streamline order processing across multiple locations. This knowledge enables businesses to tailor logistics strategies for improved operational performance and cost savings.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Hyper-Local Delivery | Warehouse Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
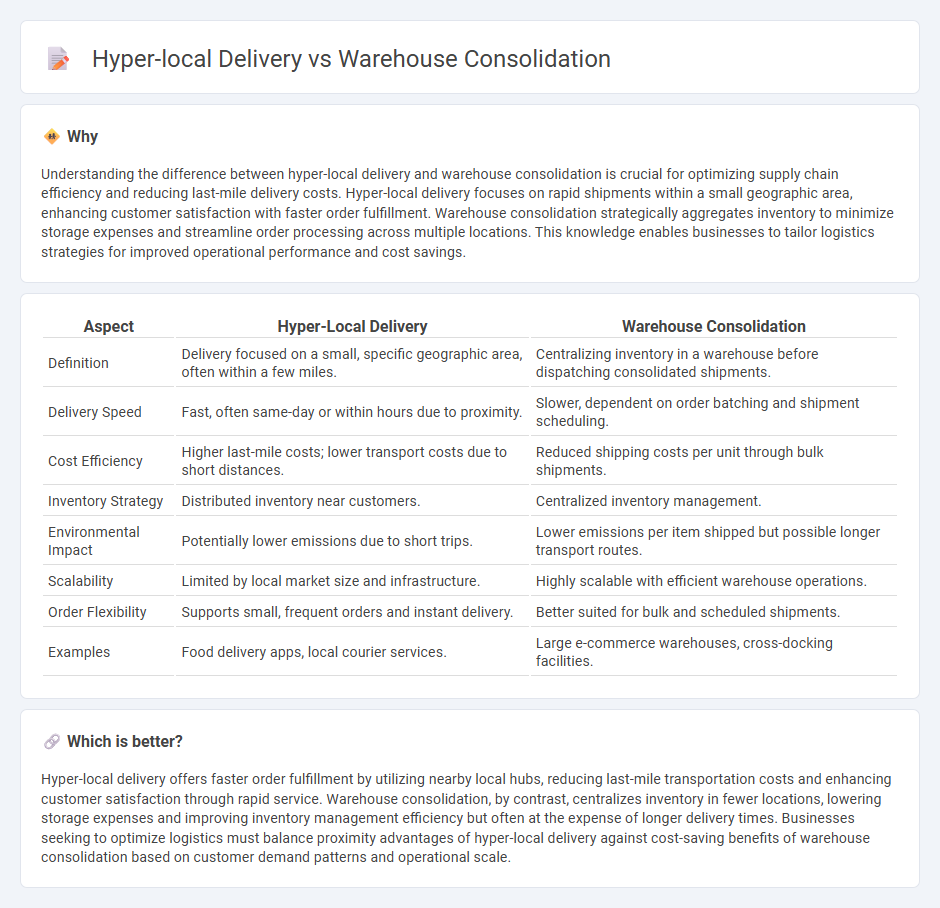
| Definition | Delivery focused on a small, specific geographic area, often within a few miles. | Centralizing inventory in a warehouse before dispatching consolidated shipments. |
| Delivery Speed | Fast, often same-day or within hours due to proximity. | Slower, dependent on order batching and shipment scheduling. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher last-mile costs; lower transport costs due to short distances. | Reduced shipping costs per unit through bulk shipments. |
| Inventory Strategy | Distributed inventory near customers. | Centralized inventory management. |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially lower emissions due to short trips. | Lower emissions per item shipped but possible longer transport routes. |
| Scalability | Limited by local market size and infrastructure. | Highly scalable with efficient warehouse operations. |
| Order Flexibility | Supports small, frequent orders and instant delivery. | Better suited for bulk and scheduled shipments. |
| Examples | Food delivery apps, local courier services. | Large e-commerce warehouses, cross-docking facilities. |
Which is better?
Hyper-local delivery offers faster order fulfillment by utilizing nearby local hubs, reducing last-mile transportation costs and enhancing customer satisfaction through rapid service. Warehouse consolidation, by contrast, centralizes inventory in fewer locations, lowering storage expenses and improving inventory management efficiency but often at the expense of longer delivery times. Businesses seeking to optimize logistics must balance proximity advantages of hyper-local delivery against cost-saving benefits of warehouse consolidation based on customer demand patterns and operational scale.
Connection
Hyper-local delivery leverages warehouse consolidation by streamlining inventory storage closer to end consumers, reducing last-mile transportation costs and delivery times. Consolidated warehouses enable faster order processing and increased inventory accuracy, enhancing the efficiency of hyper-local distribution networks. This connection supports sustainable logistics practices by minimizing carbon emissions and optimizing resource allocation in urban supply chains.
Key Terms
Centralized Distribution
Centralized distribution relies on warehouse consolidation to streamline inventory management and reduce operational costs by storing products in a single, strategic location. This approach contrasts with hyper-local delivery, which prioritizes multiple small fulfillment centers closer to consumers to enable faster last-mile delivery. Explore more to understand how centralized warehouses can optimize supply chain efficiency and meet evolving consumer demands.
Last-Mile Delivery
Warehouse consolidation improves last-mile delivery efficiency by centralizing inventory in fewer, larger warehouses, reducing operational costs but potentially increasing delivery distances and time. Hyper-local delivery leverages multiple small, strategically placed fulfillment centers closer to customers, enabling faster, more flexible deliveries while managing higher inventory and logistics complexity. Explore deeper insights into optimizing last-mile delivery strategies by comparing warehouse consolidation and hyper-local delivery models.
Inventory Pooling
Warehouse consolidation optimizes inventory pooling by centralizing stock in fewer, larger facilities, reducing overhead and improving stock visibility across regions. Hyper-local delivery relies on decentralized inventory to enable rapid fulfillment from multiple small warehouses or stores within close proximity to customers, enhancing speed and flexibility. Explore the benefits of inventory pooling strategies in balancing efficiency and delivery speed for your supply chain needs.
Source and External Links
Warehouse Consolidation [Key Benefits + Automated Solutions] - Warehouse consolidation is the process of combining multiple warehouse locations into one centralized facility, helping to reduce shipping fees, transportation costs, and dispatch numbers by grouping shipments from suppliers in the same region for more efficient delivery.
Making the Case for Warehouse Consolidation - Consolidating warehouses centralizes operations and can save costs, improve inventory control, and increase capacity in less space by using automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) that maximize vertical space and streamline processes.
Consolidated Warehouse: What It Is, Process, and Benefits - A consolidated warehouse is a third-party logistics facility that combines individual orders from several suppliers into grouped shipments, enabling cost savings by reducing transportation and material handling, as well as allowing more frequent shipments and improving customer satisfaction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com