Robotic process automation (RPA) enhances efficiency in logistics by streamlining repetitive tasks such as inventory tracking and shipment scheduling, whereas in supply chain management (SCM), RPA optimizes end-to-end processes including procurement, demand forecasting, and supplier coordination. The integration of RPA in logistics focuses on operational speed and accuracy, while SCM leverages automation to improve strategic decision-making and overall supply chain agility. Explore how RPA transforms both logistics and SCM to unlock operational excellence and competitive advantage.
Why it is important
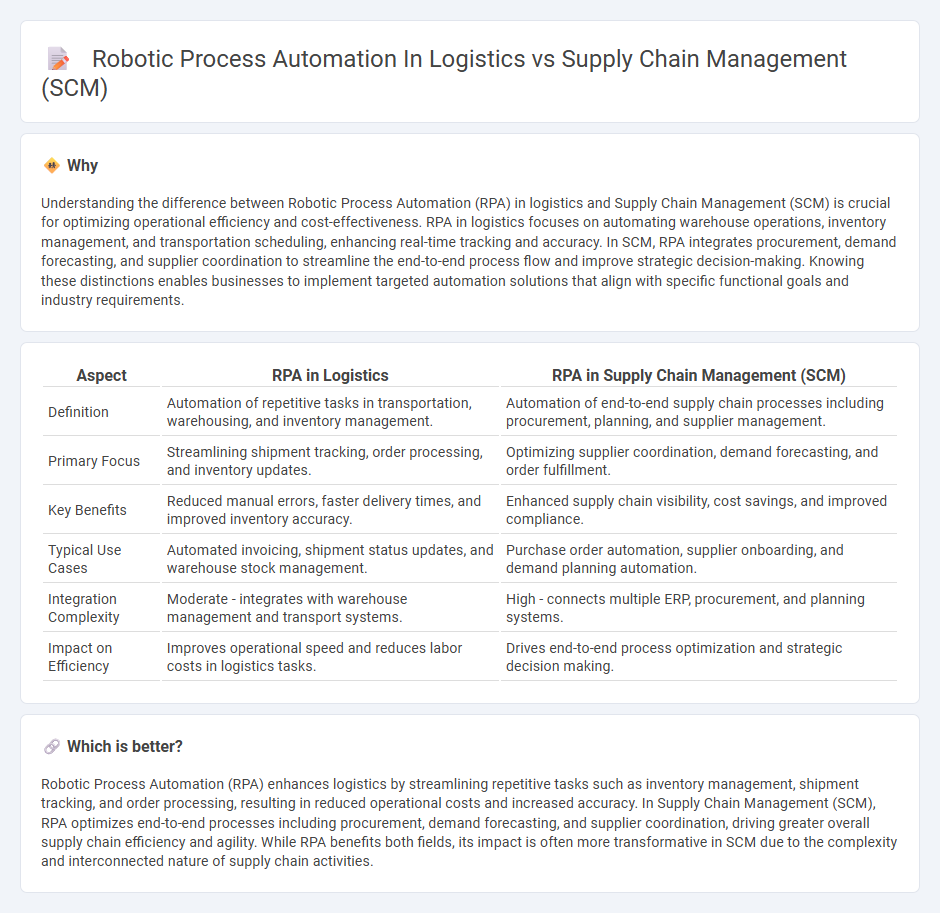
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics and Supply Chain Management (SCM) is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. RPA in logistics focuses on automating warehouse operations, inventory management, and transportation scheduling, enhancing real-time tracking and accuracy. In SCM, RPA integrates procurement, demand forecasting, and supplier coordination to streamline the end-to-end process flow and improve strategic decision-making. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to implement targeted automation solutions that align with specific functional goals and industry requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | RPA in Logistics | RPA in Supply Chain Management (SCM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation of repetitive tasks in transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. | Automation of end-to-end supply chain processes including procurement, planning, and supplier management. |
| Primary Focus | Streamlining shipment tracking, order processing, and inventory updates. | Optimizing supplier coordination, demand forecasting, and order fulfillment. |
| Key Benefits | Reduced manual errors, faster delivery times, and improved inventory accuracy. | Enhanced supply chain visibility, cost savings, and improved compliance. |
| Typical Use Cases | Automated invoicing, shipment status updates, and warehouse stock management. | Purchase order automation, supplier onboarding, and demand planning automation. |
| Integration Complexity | Moderate - integrates with warehouse management and transport systems. | High - connects multiple ERP, procurement, and planning systems. |
| Impact on Efficiency | Improves operational speed and reduces labor costs in logistics tasks. | Drives end-to-end process optimization and strategic decision making. |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances logistics by streamlining repetitive tasks such as inventory management, shipment tracking, and order processing, resulting in reduced operational costs and increased accuracy. In Supply Chain Management (SCM), RPA optimizes end-to-end processes including procurement, demand forecasting, and supplier coordination, driving greater overall supply chain efficiency and agility. While RPA benefits both fields, its impact is often more transformative in SCM due to the complexity and interconnected nature of supply chain activities.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances logistics and supply chain management (SCM) by automating repetitive tasks such as inventory tracking, order processing, and shipment scheduling, leading to increased operational efficiency. Integration of RPA with SCM systems allows real-time data synchronization across procurement, warehousing, and distribution, reducing human errors and accelerating decision-making processes. These automated workflows improve supply chain visibility, optimize resource allocation, and boost overall productivity in logistics operations.
Key Terms
**Supply Chain Management (SCM):**
Supply Chain Management (SCM) integrates planning, sourcing, production, and logistics to optimize the flow of goods, information, and finances across the supply network. SCM utilizes demand forecasting, inventory management, and supplier collaboration to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Explore the impact of SCM strategies on logistics performance and business outcomes.
Inventory Management
Supply chain management (SCM) optimizes inventory management by coordinating procurement, storage, and distribution to reduce costs and improve order fulfillment accuracy. Robotic process automation (RPA) enhances inventory management by automating data entry, stock level monitoring, and real-time reporting, reducing human errors and speeding up processes. Explore how integrating SCM and RPA can transform inventory management for greater efficiency and accuracy.
Demand Forecasting
Supply chain management (SCM) integrates demand forecasting by analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to optimize inventory levels and reduce stockouts. Robotic process automation (RPA) enhances demand forecasting accuracy by automating data collection, cleansing, and predictive analytics, enabling faster and more precise insights. Discover more about how SCM and RPA jointly transform demand forecasting in logistics for improved operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Supply Chain Management? - Supply chain management (SCM) coordinates a business's entire production flow from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished goods, optimizing the global network of suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers to minimize costs, waste, and time, thereby enhancing profitability and competitive advantage.
What is Supply Chain Management (SCM)? - SCM is the process of transforming raw materials into finished goods and delivering them to end consumers, encompassing planning, forecasting, sourcing, manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, and logistics, with modern digital tools enhancing visibility, efficiency, and risk mitigation.
What is SCM (Supply Chain Management) - SCM manages the flow of goods, data, and finances for a product, including procurement, production, logistics, order management, and global trade, evolving from a linear function to sophisticated, integrated digital systems involving all supply chain stakeholders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com