Last mile delivery focuses on efficiently transporting goods from distribution centers to the final customer, ensuring timely and accurate arrivals in urban or rural areas. Reverse logistics involves managing returned products, recycling, or disposal processes, optimizing cost recovery and sustainability. Explore in-depth insights to understand the distinct challenges and strategies shaping both last mile delivery and reverse logistics.
Why it is important
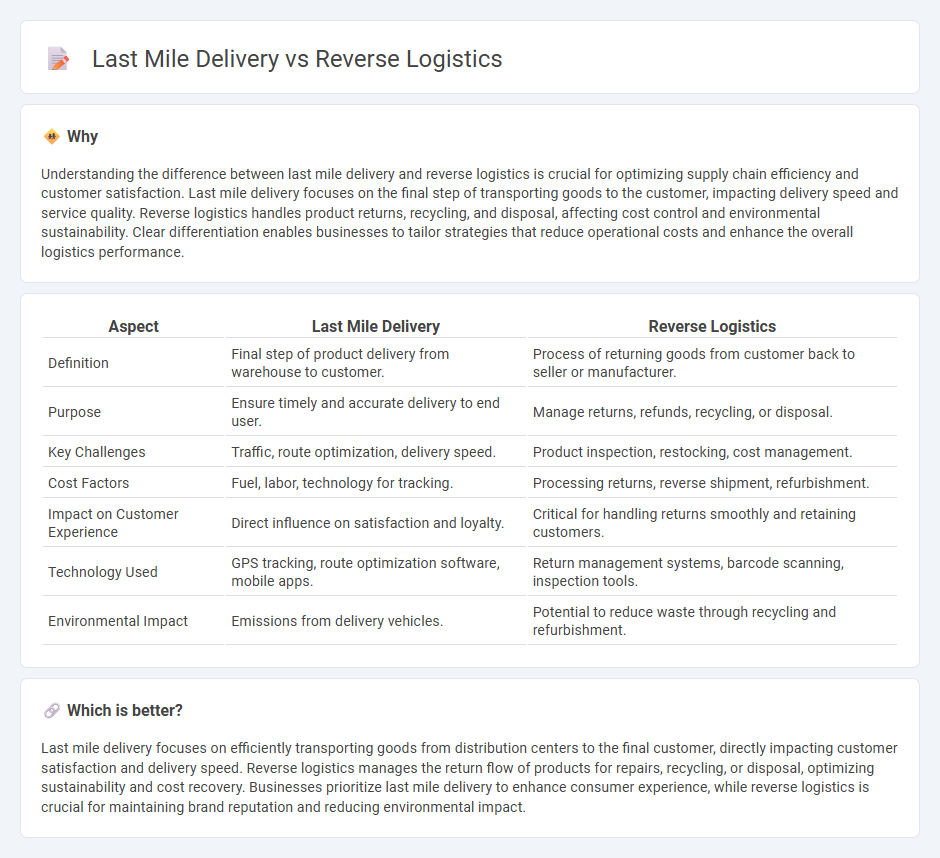
Understanding the difference between last mile delivery and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of transporting goods to the customer, impacting delivery speed and service quality. Reverse logistics handles product returns, recycling, and disposal, affecting cost control and environmental sustainability. Clear differentiation enables businesses to tailor strategies that reduce operational costs and enhance the overall logistics performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Last Mile Delivery | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final step of product delivery from warehouse to customer. | Process of returning goods from customer back to seller or manufacturer. |
| Purpose | Ensure timely and accurate delivery to end user. | Manage returns, refunds, recycling, or disposal. |
| Key Challenges | Traffic, route optimization, delivery speed. | Product inspection, restocking, cost management. |
| Cost Factors | Fuel, labor, technology for tracking. | Processing returns, reverse shipment, refurbishment. |
| Impact on Customer Experience | Direct influence on satisfaction and loyalty. | Critical for handling returns smoothly and retaining customers. |
| Technology Used | GPS tracking, route optimization software, mobile apps. | Return management systems, barcode scanning, inspection tools. |
| Environmental Impact | Emissions from delivery vehicles. | Potential to reduce waste through recycling and refurbishment. |
Which is better?
Last mile delivery focuses on efficiently transporting goods from distribution centers to the final customer, directly impacting customer satisfaction and delivery speed. Reverse logistics manages the return flow of products for repairs, recycling, or disposal, optimizing sustainability and cost recovery. Businesses prioritize last mile delivery to enhance consumer experience, while reverse logistics is crucial for maintaining brand reputation and reducing environmental impact.
Connection
Last mile delivery and reverse logistics are interconnected components of supply chain management that focus on the final stages of product movement. Efficient last mile delivery enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely delivery, while reverse logistics manages returns, exchanges, and recycling, optimizing the flow of goods back through the supply chain. Integrating both processes reduces overall transportation costs and improves inventory management, leading to sustainable logistics operations.
Key Terms
Reverse Logistics:
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from the final destination back to the manufacturer or distribution center for returns, recycling, refurbishment, or disposal, playing a critical role in supply chain sustainability and cost management. It requires efficient handling of returned products, accurate tracking systems, and collaboration between retailers, carriers, and customers to reduce waste and recover value. Explore comprehensive strategies and technologies shaping the future of reverse logistics to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics centers on the efficient handling and processing of returned products, ensuring optimal returns management and minimizing losses for businesses. Last mile delivery focuses on the final leg of product shipment to the customer, impacting delivery speed and customer satisfaction. Explore how integrating reverse logistics with last mile delivery enhances overall returns management strategies.
Refurbishment
Reverse logistics in refurbishment involves the process of returning, repairing, and restoring used products to like-new condition for resale or reuse, emphasizing sustainability and cost-efficiency. Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of transporting refurbished items from distribution centers to the end customer, optimizing speed and customer satisfaction. Discover how integrating reverse logistics and last mile delivery can streamline refurbishment workflows and enhance operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from the customer back to the manufacturer for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal, emphasizing cost-effective flow and sustainability in supply chain management.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages returns, surplus goods, and refurbishments by coordinating transportation and handling of goods moving in the opposite direction of the traditional supply chain from customers to sellers or manufacturers.
Reverse logistics - Wikipedia - Reverse logistics refers to the upstream movement of goods for value recovery or proper disposal, including remanufacturing and refurbishing, and has grown due to environmental and green supply chain concerns with a market estimated at nearly $1 trillion as of 2023.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com