Container pooling enhances efficiency by sharing standardized containers among multiple users, reducing costs and environmental impact through optimized asset utilization. Reverse logistics focuses on the return and reuse or disposal of products and packaging, emphasizing sustainability and waste reduction. Explore more about how container pooling and reverse logistics transform supply chain management.
Why it is important
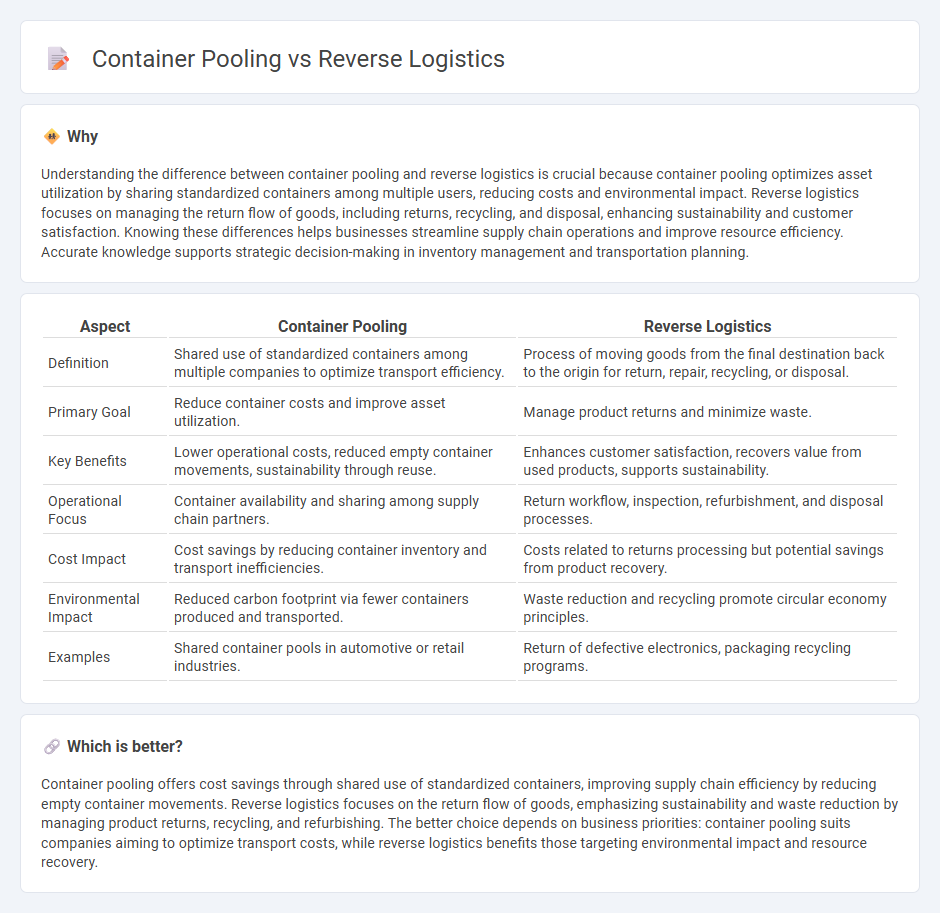
Understanding the difference between container pooling and reverse logistics is crucial because container pooling optimizes asset utilization by sharing standardized containers among multiple users, reducing costs and environmental impact. Reverse logistics focuses on managing the return flow of goods, including returns, recycling, and disposal, enhancing sustainability and customer satisfaction. Knowing these differences helps businesses streamline supply chain operations and improve resource efficiency. Accurate knowledge supports strategic decision-making in inventory management and transportation planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Container Pooling | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared use of standardized containers among multiple companies to optimize transport efficiency. | Process of moving goods from the final destination back to the origin for return, repair, recycling, or disposal. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce container costs and improve asset utilization. | Manage product returns and minimize waste. |
| Key Benefits | Lower operational costs, reduced empty container movements, sustainability through reuse. | Enhances customer satisfaction, recovers value from used products, supports sustainability. |
| Operational Focus | Container availability and sharing among supply chain partners. | Return workflow, inspection, refurbishment, and disposal processes. |
| Cost Impact | Cost savings by reducing container inventory and transport inefficiencies. | Costs related to returns processing but potential savings from product recovery. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint via fewer containers produced and transported. | Waste reduction and recycling promote circular economy principles. |
| Examples | Shared container pools in automotive or retail industries. | Return of defective electronics, packaging recycling programs. |
Which is better?
Container pooling offers cost savings through shared use of standardized containers, improving supply chain efficiency by reducing empty container movements. Reverse logistics focuses on the return flow of goods, emphasizing sustainability and waste reduction by managing product returns, recycling, and refurbishing. The better choice depends on business priorities: container pooling suits companies aiming to optimize transport costs, while reverse logistics benefits those targeting environmental impact and resource recovery.
Connection
Container pooling enhances reverse logistics by streamlining the return and reuse of shipping containers, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact. By sharing standardized containers among multiple users, companies optimize storage and handling efficiency during the reverse flow of goods. This integration supports circular supply chain practices, minimizing waste and improving resource utilization in logistics operations.
Key Terms
Reverse Logistics:
Reverse logistics involves managing the return flow of products from consumers back to manufacturers for reuse, recycling, or disposal, enhancing sustainability and cost efficiency. It optimizes supply chain operations by reducing waste, recovering value, and improving customer satisfaction through efficient handling of returns, repairs, and end-of-life products. Discover in-depth strategies and benefits of reverse logistics to transform your supply chain management.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics streamlines the process of returning products by efficiently managing the transportation, inspection, and refurbishment of goods to minimize waste and recover value. Container pooling optimizes returns management by sharing reusable containers among multiple stakeholders, reducing costs and environmental impact through standardized, circular supply chains. Explore how integrating reverse logistics with container pooling can enhance your returns management strategy and sustainability goals.
Remanufacturing
Reverse logistics involves the process of returning used products for remanufacturing, repair, or recycling, optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Container pooling enhances this by providing reusable containers that streamline the transportation and storage of returned goods, reducing costs and environmental impact. Discover how integrating these approaches can revolutionize remanufacturing workflows.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distributor for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal, aimed at recapturing value and improving supply chain efficiency with sustainability goals.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages the return of goods from customers to sellers or manufacturers, involving processes such as return authorization, scheduling shipment, refunds, and refurbishment, varying widely across industries like beverage, construction, and food.
Reverse logistics - Wikipedia - Reverse logistics encompasses operations related to the upstream movement of products for value recovery or proper disposal, including remanufacturing and refurbishing, and is increasingly relevant due to environmental concerns and green supply chain practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com