Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines back-office tasks such as inventory management and order processing through software algorithms, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) optimize physical material handling by autonomously transporting goods within warehouses, improving workflow and minimizing downtime. Explore how integrating RPA with AGVs can revolutionize logistics operations for superior productivity.
Why it is important
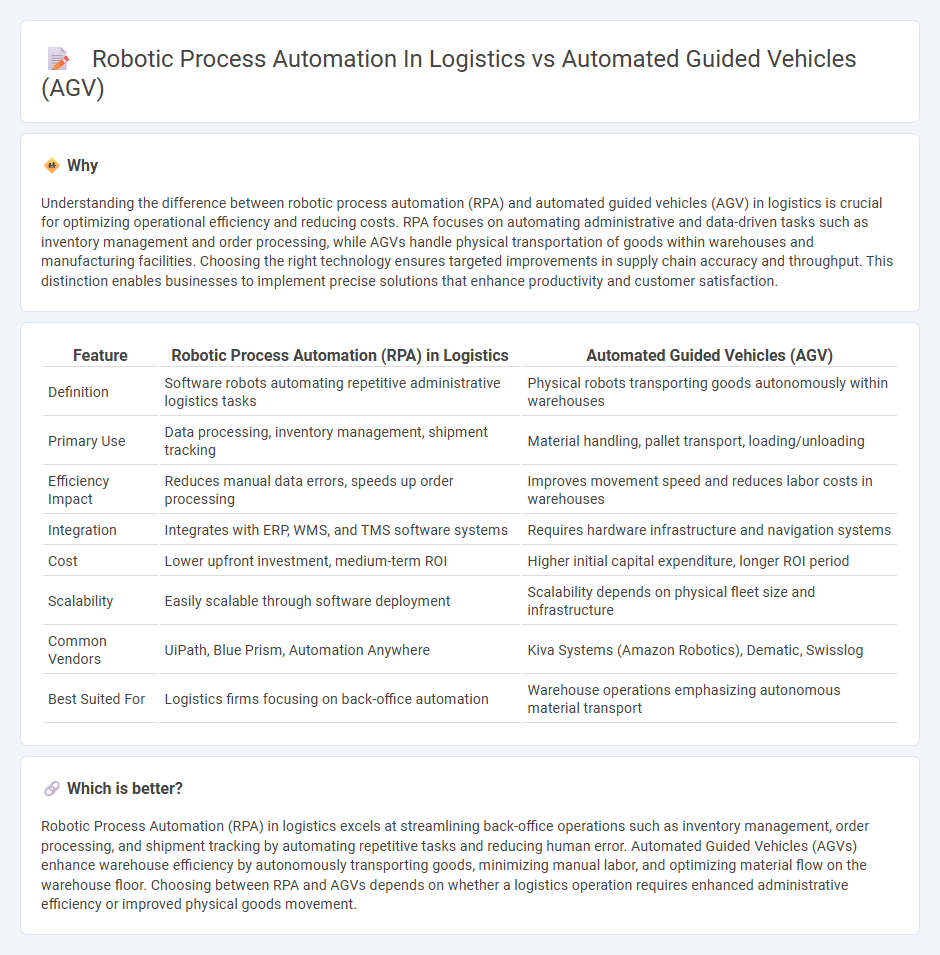
Understanding the difference between robotic process automation (RPA) and automated guided vehicles (AGV) in logistics is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. RPA focuses on automating administrative and data-driven tasks such as inventory management and order processing, while AGVs handle physical transportation of goods within warehouses and manufacturing facilities. Choosing the right technology ensures targeted improvements in supply chain accuracy and throughput. This distinction enables businesses to implement precise solutions that enhance productivity and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Logistics | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating repetitive administrative logistics tasks | Physical robots transporting goods autonomously within warehouses |
| Primary Use | Data processing, inventory management, shipment tracking | Material handling, pallet transport, loading/unloading |
| Efficiency Impact | Reduces manual data errors, speeds up order processing | Improves movement speed and reduces labor costs in warehouses |
| Integration | Integrates with ERP, WMS, and TMS software systems | Requires hardware infrastructure and navigation systems |
| Cost | Lower upfront investment, medium-term ROI | Higher initial capital expenditure, longer ROI period |
| Scalability | Easily scalable through software deployment | Scalability depends on physical fleet size and infrastructure |
| Common Vendors | UiPath, Blue Prism, Automation Anywhere | Kiva Systems (Amazon Robotics), Dematic, Swisslog |
| Best Suited For | Logistics firms focusing on back-office automation | Warehouse operations emphasizing autonomous material transport |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics excels at streamlining back-office operations such as inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking by automating repetitive tasks and reducing human error. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) enhance warehouse efficiency by autonomously transporting goods, minimizing manual labor, and optimizing material flow on the warehouse floor. Choosing between RPA and AGVs depends on whether a logistics operation requires enhanced administrative efficiency or improved physical goods movement.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines repetitive tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking, enhancing operational efficiency. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) complement RPA by physically transporting goods within warehouses and distribution centers, reducing manual labor and minimizing errors. Integration of RPA with AGVs enables synchronized data-driven workflows and real-time inventory updates, unlocking higher productivity and cost savings in logistics operations.
Key Terms
Material Handling
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) enhance material handling in logistics by autonomously transporting goods across warehouses, reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency in physical movements. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines backend logistics operations by automating repetitive data entry, inventory tracking, and order processing tasks, optimizing workflow without physical interaction with materials. Explore how integrating AGVs and RPA can revolutionize material handling and operational efficiency in logistics.
Workflow Automation
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) streamline physical workflow automation in logistics by transporting materials efficiently within warehouses and distribution centers, reducing manual labor and errors. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) optimizes digital workflow by automating repetitive administrative tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking, enhancing operational accuracy and speed. Explore how integrating AGV and RPA technologies can revolutionize logistics workflow automation for maximum efficiency.
Fleet Management
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) enhance logistics fleet management by providing real-time navigation and precise inventory handling, reducing human error and increasing operational efficiency within warehouses. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines administrative fleet tasks such as scheduling, maintenance tracking, and route optimization through software algorithms, minimizing manual workload and boosting accuracy in logistics operations. Explore deeper insights into how AGV and RPA integration can revolutionize fleet management in logistics.
Source and External Links
What Are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)? - Spectra by MHI - AGVs are autonomous, driverless material-handling machines used in warehouses, factories, and hospitals that navigate via internal systems like reflector tape or laser navigation and are coordinated by central control software to improve efficiency amid labor shortages.
Fundamentals of Automated Guided Vehicles - AGVs are self-guided vehicles that transport materials autonomously in industrial settings, following fixed routes with guidance systems such as magnetic strips, differentiating them from more flexible autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) which use advanced sensors and operate dynamically.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) | Meaning, Types & Use ... - AGVs operate on pre-defined paths using technologies like magnetic tape, wires, or laser navigation and include safety sensors; they communicate with a central control system for instructions and are usually battery-powered, often incorporating charging strategies like automatic charging stations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com