Cold chain logistics focuses on maintaining temperature-sensitive products, ensuring the integrity of perishable goods from origin to destination. Last mile delivery emphasizes the final step in the supply chain, optimizing the transit from distribution centers to end consumers for speed and accuracy. Explore more about how these critical logistics components enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cold chain and last mile delivery is crucial because cold chain logistics ensure temperature-sensitive products remain safe and effective, while last mile delivery focuses on efficient, timely distribution to the end consumer. Cold chain management involves specialized refrigeration and monitoring technologies to preserve product integrity for pharmaceuticals, perishable foods, and chemicals. Effective last mile delivery optimizes route planning and customer communication to reduce costs and enhance customer satisfaction. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses implement proper handling protocols and improve supply chain reliability.
Comparison Table
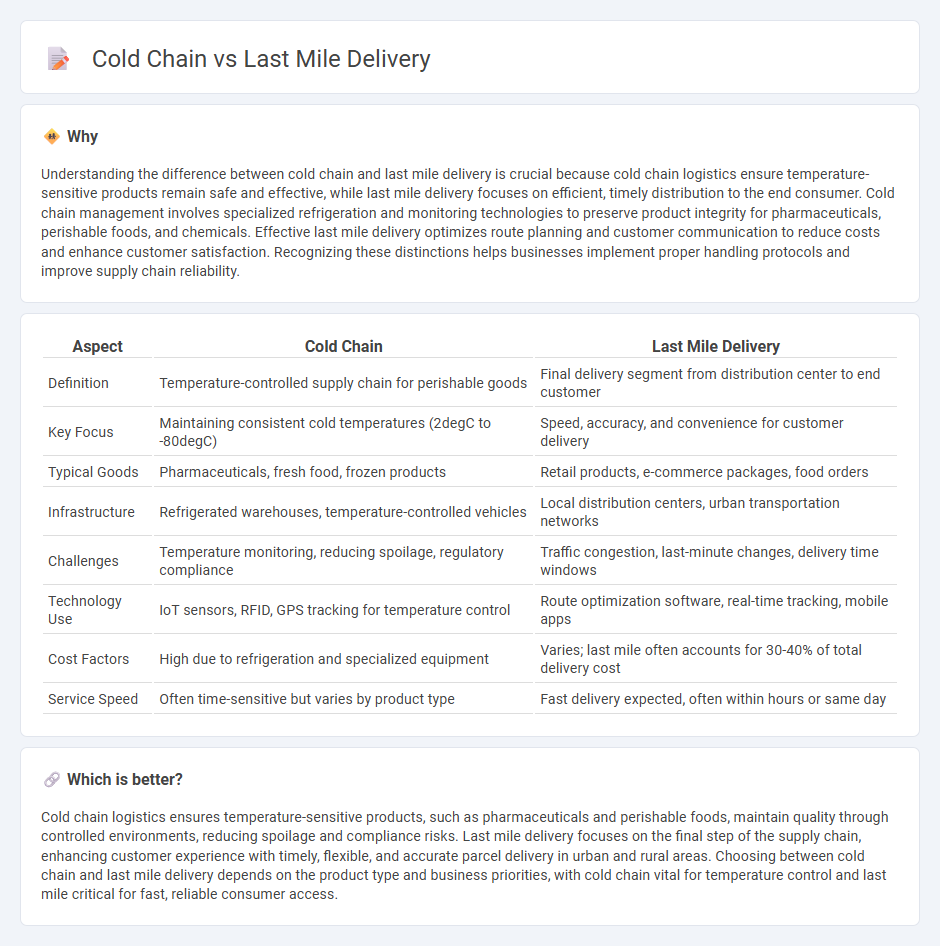
| Aspect | Cold Chain | Last Mile Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods | Final delivery segment from distribution center to end customer |
| Key Focus | Maintaining consistent cold temperatures (2degC to -80degC) | Speed, accuracy, and convenience for customer delivery |
| Typical Goods | Pharmaceuticals, fresh food, frozen products | Retail products, e-commerce packages, food orders |
| Infrastructure | Refrigerated warehouses, temperature-controlled vehicles | Local distribution centers, urban transportation networks |
| Challenges | Temperature monitoring, reducing spoilage, regulatory compliance | Traffic congestion, last-minute changes, delivery time windows |
| Technology Use | IoT sensors, RFID, GPS tracking for temperature control | Route optimization software, real-time tracking, mobile apps |
| Cost Factors | High due to refrigeration and specialized equipment | Varies; last mile often accounts for 30-40% of total delivery cost |
| Service Speed | Often time-sensitive but varies by product type | Fast delivery expected, often within hours or same day |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods, maintain quality through controlled environments, reducing spoilage and compliance risks. Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of the supply chain, enhancing customer experience with timely, flexible, and accurate parcel delivery in urban and rural areas. Choosing between cold chain and last mile delivery depends on the product type and business priorities, with cold chain vital for temperature control and last mile critical for fast, reliable consumer access.
Connection
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals and perishables, maintain their required conditions throughout transportation and storage. Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of getting these goods from distribution centers to end consumers, where maintaining cold chain integrity is critical to prevent spoilage and ensure safety. Integrating advanced tracking technologies and refrigerated vehicles in last mile delivery optimizes cold chain management and enhances customer satisfaction.
Key Terms
**Last Mile Delivery:**
Last mile delivery involves the final step of the logistics process, ensuring packages reach customers swiftly and intact, often within urban settings that demand efficient route planning and real-time tracking. Key challenges include managing delivery speed, reducing costs, and enhancing customer experience while navigating traffic congestion and urban density. Explore comprehensive strategies and technologies to optimize last mile delivery performance and meet evolving consumer expectations.
Route Optimization
Last mile delivery relies heavily on precise route optimization to ensure timely and cost-effective parcel distribution, whereas cold chain logistics demand route planning that maintains strict temperature controls throughout transit to preserve product integrity. Advanced GPS tracking, real-time traffic data, and dynamic rerouting are essential in both systems but are especially critical in cold chain to prevent spoilage of perishable goods. Explore how cutting-edge route optimization technologies are transforming efficiency and reliability in last mile delivery and cold chain operations.
Proof of Delivery
Proof of Delivery (POD) plays a crucial role in last mile delivery by verifying timely and accurate shipment handover, ensuring customer satisfaction. In cold chain logistics, POD also confirms the integrity of temperature-sensitive goods throughout transit, reducing spoilage risks and compliance breaches. Explore more to understand how POD technology enhances efficiency and reliability in both delivery systems.
Source and External Links
Last mile delivery: solutions for your business | DHL Discover - Last mile delivery refers to the final step of moving goods from a distribution center to the customer's doorstep, focusing on affordability, speed, and accuracy, with innovations like drones and autonomous robots being trialed to improve this process.
What is Last-Mile Delivery? Logistics, Costs, and Top Carriers - Last-mile delivery involves transporting a package from a fulfillment center to the final destination, usually a residence, and is one of the most expensive logistics phases, with costs around $10.10 per order and significant emphasis on tracking for customer satisfaction.
Last Mile Delivery Logistics, Trends and Data for Retailers Explained - Last-mile delivery is the final phase of shipping products from warehouse to consumer, crucial for customer satisfaction and business growth, with fast and reliable delivery services enhancing sales, convenience, and operational efficiency despite being costly and complex.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com