Green corridor logistics focus on sustainable, eco-friendly transportation routes that minimize carbon emissions and optimize energy efficiency in supply chain operations. Hub-and-spoke models centralize distribution through key hubs, streamlining inventory management but often increasing total transit distances and emissions. Explore how integrating green corridor principles can transform traditional hub-and-spoke systems for greener logistics solutions.
Why it is important
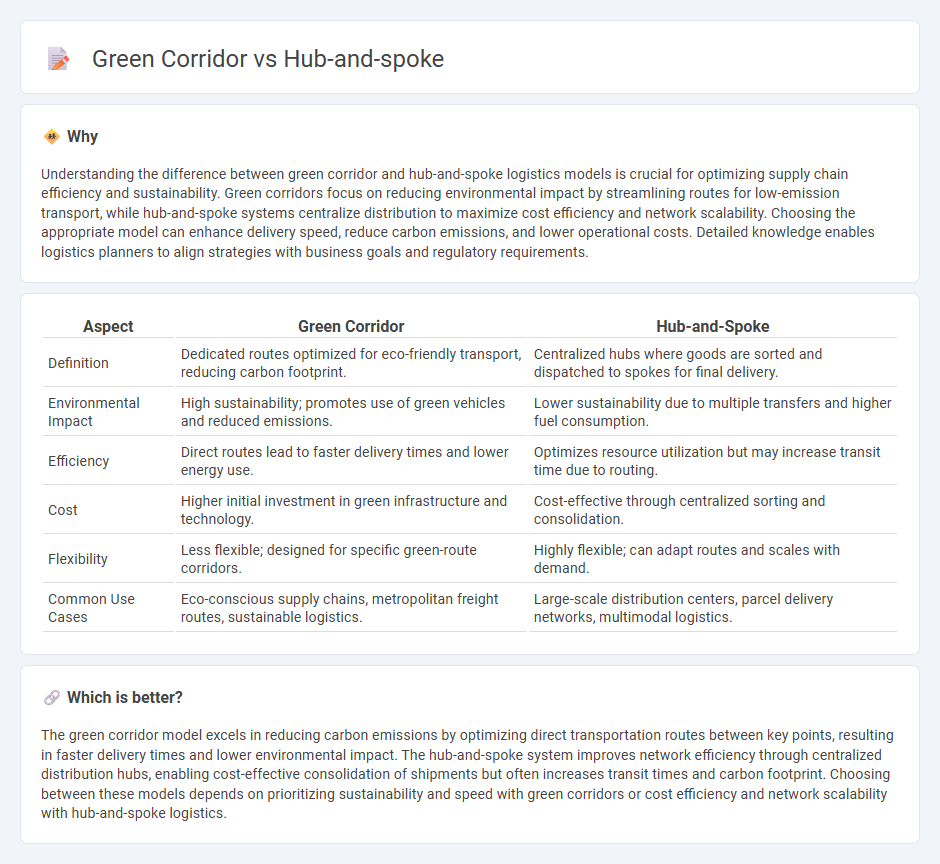
Understanding the difference between green corridor and hub-and-spoke logistics models is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Green corridors focus on reducing environmental impact by streamlining routes for low-emission transport, while hub-and-spoke systems centralize distribution to maximize cost efficiency and network scalability. Choosing the appropriate model can enhance delivery speed, reduce carbon emissions, and lower operational costs. Detailed knowledge enables logistics planners to align strategies with business goals and regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Corridor | Hub-and-Spoke |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dedicated routes optimized for eco-friendly transport, reducing carbon footprint. | Centralized hubs where goods are sorted and dispatched to spokes for final delivery. |
| Environmental Impact | High sustainability; promotes use of green vehicles and reduced emissions. | Lower sustainability due to multiple transfers and higher fuel consumption. |
| Efficiency | Direct routes lead to faster delivery times and lower energy use. | Optimizes resource utilization but may increase transit time due to routing. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment in green infrastructure and technology. | Cost-effective through centralized sorting and consolidation. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; designed for specific green-route corridors. | Highly flexible; can adapt routes and scales with demand. |
| Common Use Cases | Eco-conscious supply chains, metropolitan freight routes, sustainable logistics. | Large-scale distribution centers, parcel delivery networks, multimodal logistics. |
Which is better?
The green corridor model excels in reducing carbon emissions by optimizing direct transportation routes between key points, resulting in faster delivery times and lower environmental impact. The hub-and-spoke system improves network efficiency through centralized distribution hubs, enabling cost-effective consolidation of shipments but often increases transit times and carbon footprint. Choosing between these models depends on prioritizing sustainability and speed with green corridors or cost efficiency and network scalability with hub-and-spoke logistics.
Connection
Green corridors in logistics prioritize sustainable transport routes that reduce carbon emissions, while hub-and-spoke models optimize distribution by consolidating shipments through central hubs. Integrating green corridors within a hub-and-spoke network enhances efficiency by channeling eco-friendly transportation modes along key spokes, minimizing environmental impact. This synergy supports sustainable supply chains by combining strategic route planning with centralized logistics management.
Key Terms
Centralized Distribution (hub-and-spoke)
Centralized Distribution via the hub-and-spoke model optimizes logistics by consolidating inventory at a central hub, reducing delivery costs and improving route efficiency through spokes to regional outlets. This system enhances scalability and inventory control compared to green corridors, which prioritize sustainable, low-emission routes rather than operational centralization. Explore how centralized distribution streamlines supply chains and supports business growth.
Decarbonization (green corridor)
Green corridors prioritize decarbonization by establishing dedicated low-emission transportation routes utilizing electric or hydrogen-fueled vehicles, significantly reducing carbon footprints across supply chains. In contrast, hub-and-spoke models optimize logistics efficiency through centralized distribution but often rely on conventional fuel-dependent transport modes that contribute to higher emissions. Explore how green corridors transform sustainable logistics by integrating clean energy and reducing environmental impact.
Route Optimization
The hub-and-spoke model centralizes logistics by funneling shipments through a primary hub to optimize routes and consolidate cargo, reducing overall transportation costs and enhancing delivery efficiency. In contrast, a green corridor emphasizes direct, environmentally friendly routes that minimize emissions and transit times between specific origin-destination pairs. Explore deeper insights and case studies on how these strategies impact route optimization and sustainability.
Source and External Links
What is a Hub-and-Spoke Network: 9 Tips, Benefits & Limitations - The hub-and-spoke model features a central hub organization coordinating multiple spoke organizations that communicate directly with the hub but not with each other, enabling centralized decision-making and streamlined resource allocation.
Spoke-hub distribution paradigm - Wikipedia - The hub-and-spoke system is a transport topology optimization connecting outlying points (spokes) to a central hub, widely used in aviation and logistics to optimize routes and resource distribution.
Hub-spoke network topology in Azure - Azure Architecture Center - In Azure networking, the hub-spoke topology connects spoke virtual networks to a central hub virtual network that hosts shared services and manages cross-premises connectivity, routing, and security.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com