Yard management focuses on the efficient oversight of vehicle movement and storage within a facility's yard, optimizing loading, unloading, and parking processes to reduce delays and improve throughput. Freight forwarding involves coordinating the shipment of goods across multiple carriers and transportation modes, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with international regulations. Explore more to understand how yard management and freight forwarding complement each other in the logistics chain.
Why it is important
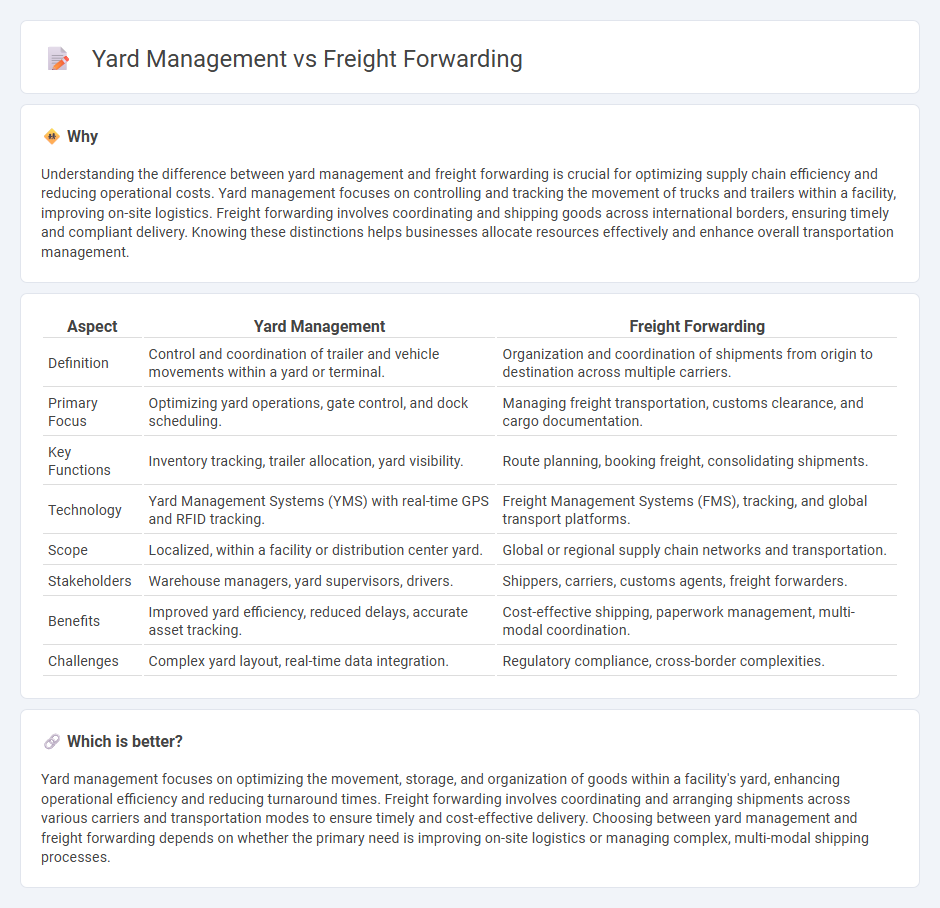
Understanding the difference between yard management and freight forwarding is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Yard management focuses on controlling and tracking the movement of trucks and trailers within a facility, improving on-site logistics. Freight forwarding involves coordinating and shipping goods across international borders, ensuring timely and compliant delivery. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses allocate resources effectively and enhance overall transportation management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Yard Management | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control and coordination of trailer and vehicle movements within a yard or terminal. | Organization and coordination of shipments from origin to destination across multiple carriers. |
| Primary Focus | Optimizing yard operations, gate control, and dock scheduling. | Managing freight transportation, customs clearance, and cargo documentation. |
| Key Functions | Inventory tracking, trailer allocation, yard visibility. | Route planning, booking freight, consolidating shipments. |
| Technology | Yard Management Systems (YMS) with real-time GPS and RFID tracking. | Freight Management Systems (FMS), tracking, and global transport platforms. |
| Scope | Localized, within a facility or distribution center yard. | Global or regional supply chain networks and transportation. |
| Stakeholders | Warehouse managers, yard supervisors, drivers. | Shippers, carriers, customs agents, freight forwarders. |
| Benefits | Improved yard efficiency, reduced delays, accurate asset tracking. | Cost-effective shipping, paperwork management, multi-modal coordination. |
| Challenges | Complex yard layout, real-time data integration. | Regulatory compliance, cross-border complexities. |
Which is better?
Yard management focuses on optimizing the movement, storage, and organization of goods within a facility's yard, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing turnaround times. Freight forwarding involves coordinating and arranging shipments across various carriers and transportation modes to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery. Choosing between yard management and freight forwarding depends on whether the primary need is improving on-site logistics or managing complex, multi-modal shipping processes.
Connection
Yard management optimizes the organization and flow of vehicles and inventory within a logistics facility, directly impacting the efficiency of freight forwarding operations by ensuring timely loading and unloading. Effective yard management reduces turnaround times, minimizes delays, and enhances the accuracy of shipment tracking critical for freight forwarding. Coordinated yard and freight forwarding systems improve supply chain visibility, enabling seamless transportation planning and execution.
Key Terms
**Freight Forwarding:**
Freight forwarding involves coordinating the shipment of goods from origin to destination, including customs clearance, documentation, and carrier selection, ensuring efficient and cost-effective transport. It manages logistics across air, sea, and land, optimizing routes and consolidating shipments to meet delivery deadlines. Discover more about how freight forwarding streamlines supply chain operations and enhances global trade efficiency.
Bill of Lading
Freight forwarding centers on managing the Bill of Lading as a critical legal document that details cargo, shipment terms, and ownership, ensuring seamless international shipment coordination. Yard management focuses on the physical handling and tracking of containers and vehicles in the yard but relies on accurate Bill of Lading information to organize load and dispatch operations. Explore more to understand how optimizing Bill of Lading processes enhances both freight forwarding efficiency and yard management accuracy.
Customs Clearance
Freight forwarding primarily involves coordinating international shipments, including customs clearance, export documentation, and compliance with trade regulations to ensure smooth border crossings. Yard management centers on organizing and controlling trailer movements, storage, and loading/unloading within a facility, focusing less on customs processes. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how these functions optimize supply chain efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? - Freight forwarding involves strategic planning and coordination of international goods movement via air, sea, rail, or highway, where freight forwarders act as intermediaries managing logistics and customs clearance to ensure timely and safe delivery.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key ... - Freight forwarding is the process that includes export haulage, customs clearance, and origin handling, ensuring shipments meet regulations and arrive intact, often involving specialized handling of hazardous or perishable goods.
About Freight Forwarding - Freight forwarding facilitates international trade by ensuring that goods move efficiently from origin to destination, offering services like consolidation, storage, customs handling, insurance, and total supply chain management at optimal cost and condition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com