Cold chain management ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive products through controlled environments during storage and transportation, crucial for pharmaceuticals, perishables, and chemicals. Freight forwarding coordinates the efficient movement of goods across various transport modes, handling documentation, customs clearance, and route optimization. Explore the key differences between these logistics services to enhance supply chain efficiency.
Why it is important
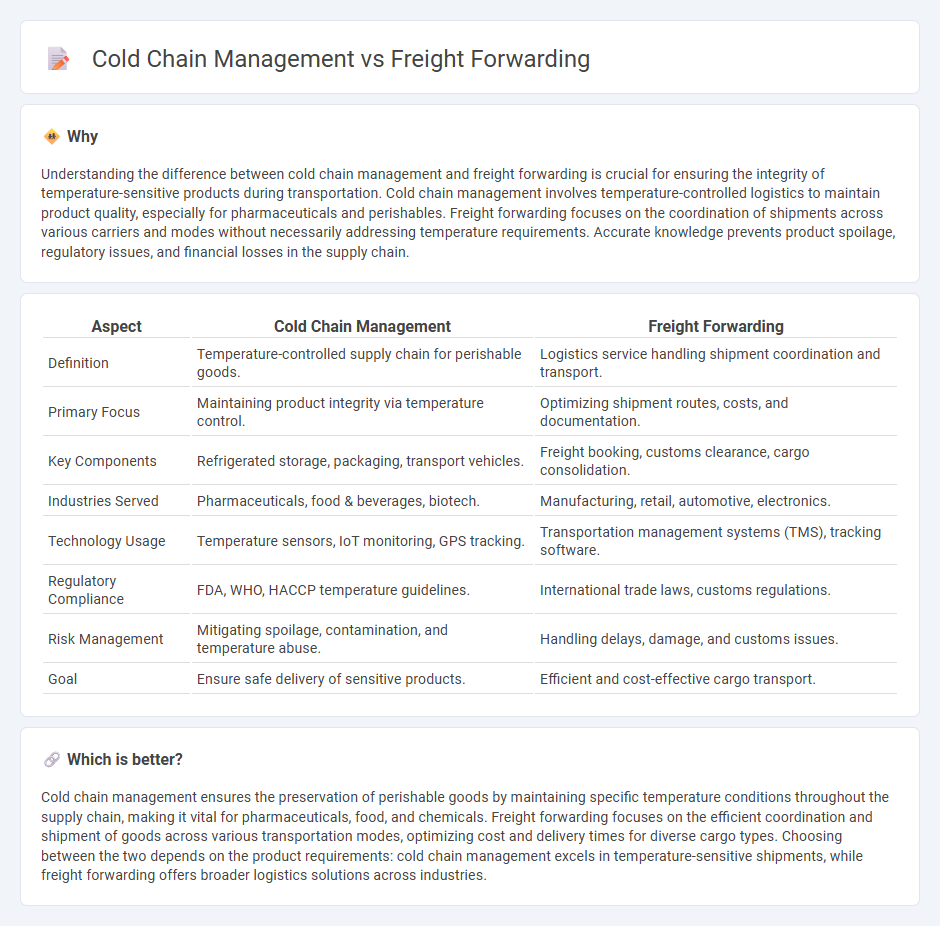
Understanding the difference between cold chain management and freight forwarding is crucial for ensuring the integrity of temperature-sensitive products during transportation. Cold chain management involves temperature-controlled logistics to maintain product quality, especially for pharmaceuticals and perishables. Freight forwarding focuses on the coordination of shipments across various carriers and modes without necessarily addressing temperature requirements. Accurate knowledge prevents product spoilage, regulatory issues, and financial losses in the supply chain.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Management | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. | Logistics service handling shipment coordination and transport. |
| Primary Focus | Maintaining product integrity via temperature control. | Optimizing shipment routes, costs, and documentation. |
| Key Components | Refrigerated storage, packaging, transport vehicles. | Freight booking, customs clearance, cargo consolidation. |
| Industries Served | Pharmaceuticals, food & beverages, biotech. | Manufacturing, retail, automotive, electronics. |
| Technology Usage | Temperature sensors, IoT monitoring, GPS tracking. | Transportation management systems (TMS), tracking software. |
| Regulatory Compliance | FDA, WHO, HACCP temperature guidelines. | International trade laws, customs regulations. |
| Risk Management | Mitigating spoilage, contamination, and temperature abuse. | Handling delays, damage, and customs issues. |
| Goal | Ensure safe delivery of sensitive products. | Efficient and cost-effective cargo transport. |
Which is better?
Cold chain management ensures the preservation of perishable goods by maintaining specific temperature conditions throughout the supply chain, making it vital for pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals. Freight forwarding focuses on the efficient coordination and shipment of goods across various transportation modes, optimizing cost and delivery times for diverse cargo types. Choosing between the two depends on the product requirements: cold chain management excels in temperature-sensitive shipments, while freight forwarding offers broader logistics solutions across industries.
Connection
Cold chain management ensures the continuous temperature-controlled supply of perishable goods, directly impacting the efficiency of freight forwarding by requiring specialized handling and transportation solutions. Freight forwarders coordinate complex logistics involving refrigerated containers, temperature monitoring technology, and timely transit schedules to maintain product integrity throughout the shipment process. Effective integration of cold chain protocols within freight forwarding prevents spoilage, reduces waste, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards in sectors like pharmaceuticals and food distribution.
Key Terms
**Freight Forwarding:**
Freight forwarding involves organizing shipments and managing transportation logistics across various modes such as sea, air, and land to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery. It includes services like customs brokerage, cargo insurance, and documentation, optimizing supply chain efficiency for global trade. Explore detailed insights on freight forwarding strategies and best practices to enhance your logistics operations.
Bill of Lading
Freight forwarding involves coordinating the shipment of goods, with the Bill of Lading serving as a key legal document that details the cargo and terms of transport. Cold chain management ensures temperature-sensitive goods maintain quality through controlled environments, requiring specialized handling information on the Bill of Lading for compliance and traceability. Discover how the Bill of Lading integrates with both processes to optimize shipping accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Incoterms
Freight forwarding involves coordinating shipments across global supply chains, whereas cold chain management specifically ensures temperature-controlled transport for perishable goods. Understanding Incoterms like FOB (Free On Board) or DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) is crucial in defining responsibilities and risk transfer for both freight forwarding and cold chain logistics. Explore detailed Incoterms applications to optimize your shipping strategy and compliance.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? | Clarksons - Freight forwarding involves the strategic planning and coordination of international goods transport via air, sea, rail, or highway, where freight forwarders act as intermediaries managing logistics, customs, and transportation to ensure timely and safe delivery.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key Stages - Freight forwarding is a process where companies act as intermediaries to arrange and coordinate shipments internationally, handling export haulage, customs clearance, and inspection to manage the legal and logistic aspects of cargo transport.
About Freight Forwarding - FIATA - Freight forwarding encompasses services related to transportation, handling, storage, customs, insurance, and supply chain management to facilitate international trade by ensuring goods arrive on time, in good condition, and cost-effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com