Quick commerce leverages local inventory and ultra-fast delivery to fulfill customer orders within minutes or hours, optimizing speed and convenience in urban areas. Drop shipping eliminates the need for inventory holding by forwarding orders directly from suppliers to consumers, reducing upfront costs but often increasing delivery times. Explore the differences in efficiency, cost, and customer satisfaction between these two logistics models to determine the best fit for your business.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quick commerce and drop shipping is vital because quick commerce focuses on ultra-fast delivery, often under an hour, enhancing customer satisfaction through immediacy. Drop shipping involves selling products without holding inventory, relying on third-party suppliers to ship directly to customers, which affects supply chain control and inventory management. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses optimize logistics strategies, reduce costs, and improve fulfillment efficiency. Accurate knowledge ensures competitive advantage in meeting market demands and customer expectations.
Comparison Table
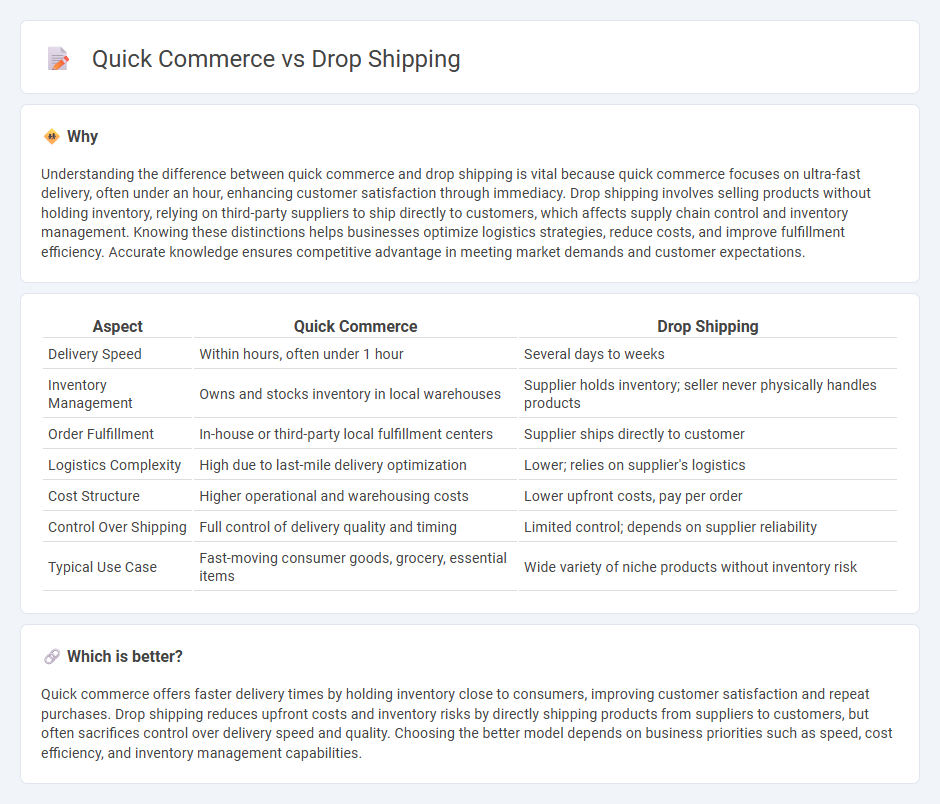
| Aspect | Quick Commerce | Drop Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | Within hours, often under 1 hour | Several days to weeks |
| Inventory Management | Owns and stocks inventory in local warehouses | Supplier holds inventory; seller never physically handles products |
| Order Fulfillment | In-house or third-party local fulfillment centers | Supplier ships directly to customer |
| Logistics Complexity | High due to last-mile delivery optimization | Lower; relies on supplier's logistics |
| Cost Structure | Higher operational and warehousing costs | Lower upfront costs, pay per order |
| Control Over Shipping | Full control of delivery quality and timing | Limited control; depends on supplier reliability |
| Typical Use Case | Fast-moving consumer goods, grocery, essential items | Wide variety of niche products without inventory risk |
Which is better?
Quick commerce offers faster delivery times by holding inventory close to consumers, improving customer satisfaction and repeat purchases. Drop shipping reduces upfront costs and inventory risks by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, but often sacrifices control over delivery speed and quality. Choosing the better model depends on business priorities such as speed, cost efficiency, and inventory management capabilities.
Connection
Quick commerce revolutionizes logistics by emphasizing ultra-fast delivery, which aligns with drop shipping's model of direct shipping from suppliers to customers without inventory holding. Drop shipping enhances quick commerce efficiency by reducing fulfillment time and operational costs, enabling retailers to meet growing consumer demand for rapid order processing. Together, these strategies optimize supply chain management through seamless coordination between suppliers, logistics providers, and e-commerce platforms.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Drop shipping relies on third-party suppliers to manage inventory, eliminating the need for sellers to hold stock and reducing upfront costs. Quick commerce emphasizes fast, local inventory turnover with strategically placed warehouses to ensure rapid delivery, demanding precise inventory tracking and replenishment systems. Explore the nuances of inventory management strategies in both models to optimize your e-commerce operations.
Fulfillment Speed
Drop shipping offers extended fulfillment times as products ship directly from suppliers, often resulting in delays compared to quick commerce models that prioritize ultra-fast delivery within hours by leveraging local warehouses. Quick commerce accelerates order processing and last-mile logistics to meet consumer demand for near-immediate product availability. Explore more insights on optimizing fulfillment strategies to enhance customer satisfaction and business efficiency.
Last-Mile Delivery
Drop shipping relies on third-party suppliers to handle product storage and shipping, often resulting in longer delivery times due to multiple logistical handoffs. Quick commerce prioritizes ultra-fast last-mile delivery, leveraging local warehouses and real-time inventory management to fulfill orders within minutes or hours. Explore how optimizing last-mile delivery strategies can enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency in both models.
Source and External Links
Drop-Shipping: What you Need to Know Before You Buy or Sell Online - Drop-shipping is a retail method where the seller lists goods without stocking them, and when an order is made, they forward it to a supplier who ships directly to the buyer while the seller keeps the profit margin.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail model where the seller markets and sells products but does not stock inventory, instead transferring orders to a supplier who ships directly to the customer, reducing overhead costs but limiting quality and shipping control.
What is Dropshipping: A Comprehensive Guide for Entrepreneurs - FedEx - Dropshipping is an ecommerce fulfillment method where a store sells products without stocking them; instead, the store purchases items from a supplier who ships directly to the customer, with the store earning the profit margin between sale and supplier price.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com