Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time using algorithms that respond to current traffic, delivery demands, and environmental conditions, optimizing efficiency and reducing travel time. Cluster-based routing groups delivery points into clusters, creating fixed routes within each cluster to streamline operations and improve predictability. Explore the advantages and applications of both methods to enhance your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and cluster-based routing in logistics is crucial for optimizing delivery efficiency and reducing operational costs. Dynamic routing adjusts routes in real-time based on traffic, demand, and vehicle status, improving responsiveness and flexibility. Cluster-based routing groups deliveries into fixed geographical zones, simplifying planning and ensuring consistent service areas. Knowing which method suits specific logistics needs enhances resource allocation and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
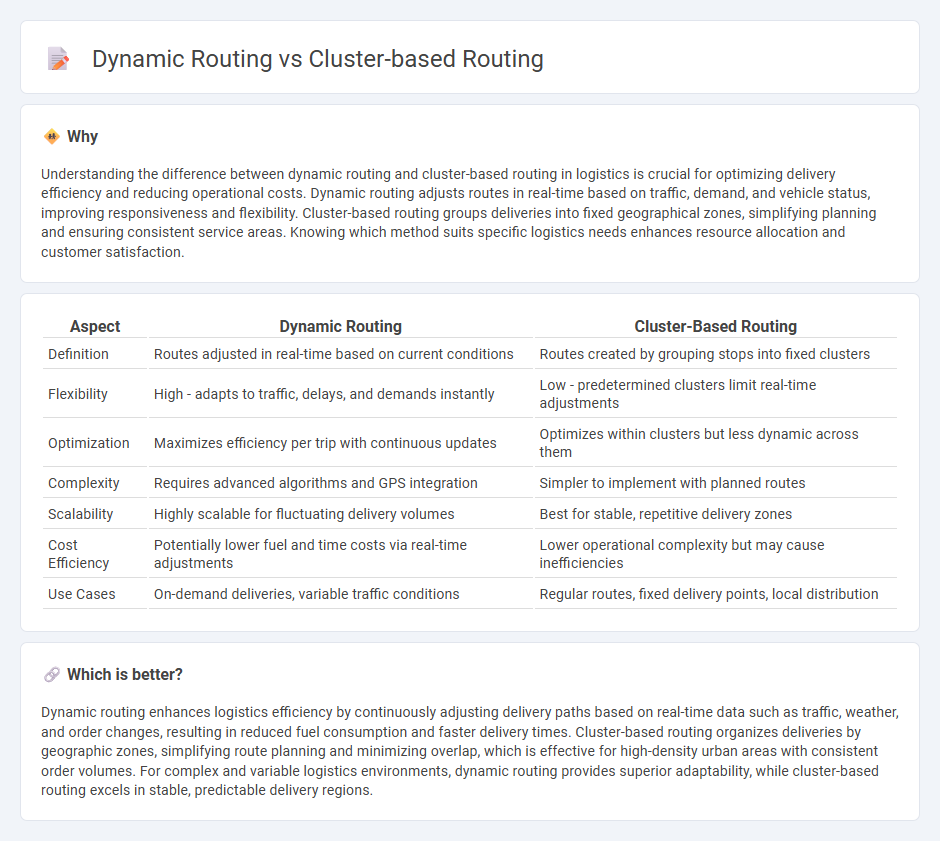
| Aspect | Dynamic Routing | Cluster-Based Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Routes adjusted in real-time based on current conditions | Routes created by grouping stops into fixed clusters |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to traffic, delays, and demands instantly | Low - predetermined clusters limit real-time adjustments |
| Optimization | Maximizes efficiency per trip with continuous updates | Optimizes within clusters but less dynamic across them |
| Complexity | Requires advanced algorithms and GPS integration | Simpler to implement with planned routes |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for fluctuating delivery volumes | Best for stable, repetitive delivery zones |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower fuel and time costs via real-time adjustments | Lower operational complexity but may cause inefficiencies |
| Use Cases | On-demand deliveries, variable traffic conditions | Regular routes, fixed delivery points, local distribution |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing enhances logistics efficiency by continuously adjusting delivery paths based on real-time data such as traffic, weather, and order changes, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and faster delivery times. Cluster-based routing organizes deliveries by geographic zones, simplifying route planning and minimizing overlap, which is effective for high-density urban areas with consistent order volumes. For complex and variable logistics environments, dynamic routing provides superior adaptability, while cluster-based routing excels in stable, predictable delivery regions.
Connection
Dynamic routing and cluster-based routing are interconnected as dynamic routing adapts paths in real-time to optimize delivery times, while cluster-based routing organizes destinations into geographically or functionally related groups. This synergy enhances route efficiency by allowing the system to adjust clusters dynamically based on traffic conditions, delivery constraints, and demand variability. Combining these methods reduces operational costs and improves fleet utilization in logistics networks.
Key Terms
Node Grouping
Cluster-based routing organizes nodes into fixed clusters, improving scalability and energy efficiency by limiting communication within groups. Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time based on network topology changes, enhancing flexibility and fault tolerance. Explore the benefits and use cases of each routing approach to optimize your network performance.
Real-time Adjustment
Cluster-based routing groups network nodes into clusters to reduce routing overhead and improve energy efficiency, making it suitable for static or low-mobility environments. Dynamic routing continually updates routes in real-time based on current network conditions like traffic load or link quality, offering superior adaptability in highly dynamic or mobile scenarios. Explore the benefits and applications of cluster-based versus dynamic routing to enhance network performance in your specific use case.
Route Optimization
Cluster-based routing groups nodes into clusters to reduce routing overhead and improve scalability, enabling efficient route optimization within localized areas. Dynamic routing continuously updates routes based on real-time network conditions, allowing adaptive and optimal path selection across the network. Explore more to understand which routing strategy best suits your network's performance and scalability needs.
Source and External Links
Cluster-based routing protocols for wireless sensor networks - Cluster-based routing divides a wireless sensor network into clusters, each managed by a cluster head responsible for data collection, fusion, and forwarding, which helps reduce energy consumption, simplify node functions, and improve scalability in large networks.
Self-healing and energy-efficient cluster-based routing for ... - Advanced cluster-based routing frameworks integrate self-healing, energy efficiency, and security by dynamically regrouping sensor nodes using optimization algorithms and trust metrics for robust, efficient wireless sensor network communication.
Cluster-Based Routing Protocol with Static Hub (CRPSH) - CRPSH is a cluster-based routing protocol designed to reduce energy consumption and extend the lifetime of IoT infrastructure networks by using a static hub to optimize communication.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com