Shared warehousing optimizes storage costs by allowing multiple businesses to use the same facility, enhancing flexibility and reducing capital investment. Bonded warehousing offers secure storage for imported goods under customs control, delaying duty payments until the items enter the domestic market. Explore the advantages and applications of each warehousing type to improve your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
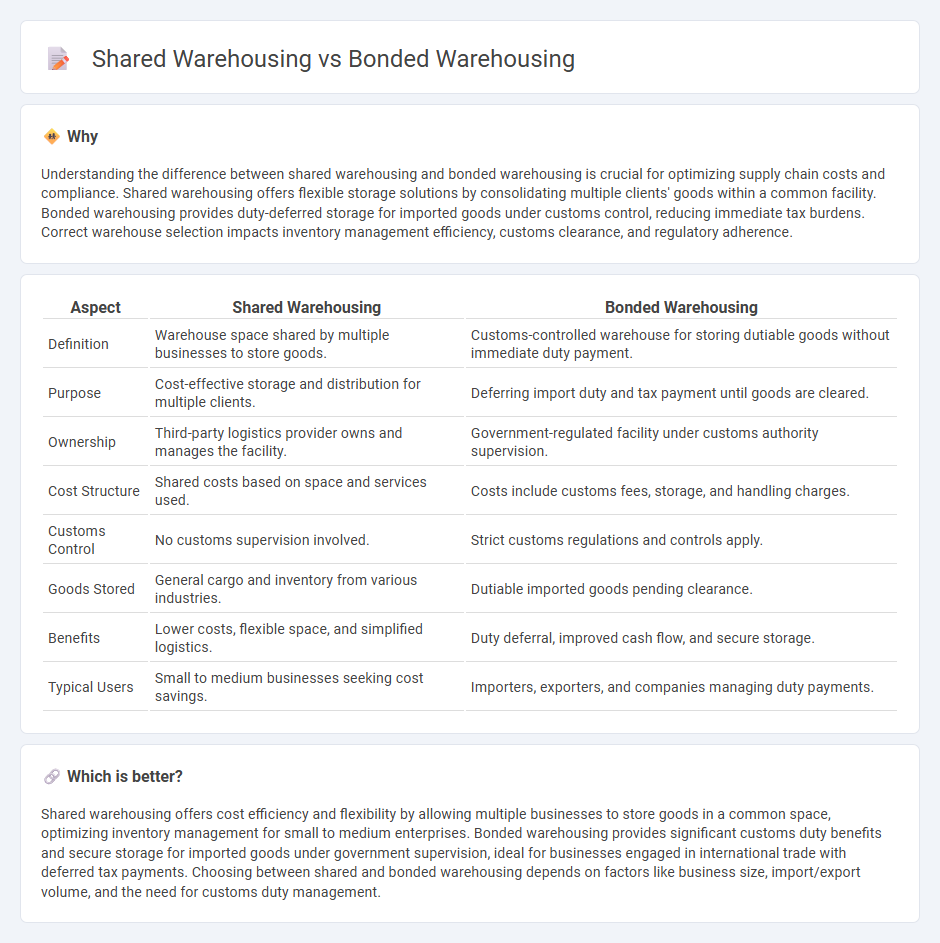
Understanding the difference between shared warehousing and bonded warehousing is crucial for optimizing supply chain costs and compliance. Shared warehousing offers flexible storage solutions by consolidating multiple clients' goods within a common facility. Bonded warehousing provides duty-deferred storage for imported goods under customs control, reducing immediate tax burdens. Correct warehouse selection impacts inventory management efficiency, customs clearance, and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shared Warehousing | Bonded Warehousing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Warehouse space shared by multiple businesses to store goods. | Customs-controlled warehouse for storing dutiable goods without immediate duty payment. |
| Purpose | Cost-effective storage and distribution for multiple clients. | Deferring import duty and tax payment until goods are cleared. |
| Ownership | Third-party logistics provider owns and manages the facility. | Government-regulated facility under customs authority supervision. |
| Cost Structure | Shared costs based on space and services used. | Costs include customs fees, storage, and handling charges. |
| Customs Control | No customs supervision involved. | Strict customs regulations and controls apply. |
| Goods Stored | General cargo and inventory from various industries. | Dutiable imported goods pending clearance. |
| Benefits | Lower costs, flexible space, and simplified logistics. | Duty deferral, improved cash flow, and secure storage. |
| Typical Users | Small to medium businesses seeking cost savings. | Importers, exporters, and companies managing duty payments. |
Which is better?
Shared warehousing offers cost efficiency and flexibility by allowing multiple businesses to store goods in a common space, optimizing inventory management for small to medium enterprises. Bonded warehousing provides significant customs duty benefits and secure storage for imported goods under government supervision, ideal for businesses engaged in international trade with deferred tax payments. Choosing between shared and bonded warehousing depends on factors like business size, import/export volume, and the need for customs duty management.
Connection
Shared warehousing and bonded warehousing are connected through their roles in optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing storage costs. Shared warehousing allows multiple businesses to use a common facility for inventory storage, enhancing flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while bonded warehousing provides a secure environment for storing imported goods without immediate customs duties. Integrating shared warehousing with bonded warehousing enables companies to streamline international logistics by combining cost savings with regulatory compliance for goods in transit.
Key Terms
Bonded Warehousing:
Bonded warehousing offers businesses secure storage for imported goods under customs control, allowing deferred payment of import duties and taxes until goods are released for domestic use. This system enhances cash flow management and reduces upfront costs by postponing customs clearance and providing inventory control within a closed environment. Explore the benefits of bonded warehousing to optimize your supply chain and regulatory compliance.
Customs Control
Bonded warehousing allows goods to be stored under Customs supervision without immediate payment of duties, offering advantages for importers managing cash flow and compliance with regulatory requirements. Shared warehousing involves multiple businesses using the same facilities but typically lacks the specific Customs control that bonded warehouses provide, limiting potential deferment of duties and Customs oversight. Explore detailed differences to optimize your supply chain and Customs strategy.
Duty Suspension
Bonded warehousing allows importers to store goods without immediate payment of customs duties until the items leave the warehouse, enabling duty suspension during storage and reducing upfront costs. Shared warehousing consolidates storage among multiple businesses but typically requires duty payment upon entry, limiting opportunities for duty suspension. Explore detailed differences and benefits to optimize your logistics strategy and duty management.
Source and External Links
Bonded warehouse - Wikipedia - A bonded warehouse is a secured facility where imported, dutiable goods can be stored, manipulated, or undergo limited manufacturing without payment of duty until the goods are exported, destroyed, or released into the domestic market after duty is paid.
Bonded Warehouse: Definition, Classes, and Benefits - Customs bonded warehouses are authorized by authorities like US Customs and Border Protection to store imported goods duty-free until they are either exported or entered into the domestic market, with strict security and documentation requirements throughout the process.
Bonded Warehouses: Manage U.S. Tariffs & Import Costs - Operating a bonded warehouse requires CBP approval, customs bonds to protect government revenue, and compliance with rigorous security, facility, and operational standards, including regular inspections and detailed recordkeeping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com