Digital collectibles represent unique digital assets that can be owned and traded, often tied to entertainment and gaming industries, while non-fungible tokens (NFTs) extend this concept on blockchain technology, providing verifiable ownership and provenance across various sectors including art and real estate. NFTs have transformed entrepreneurship by enabling creators to monetize digital works and establish direct relationships with their audience, fostering new business models and revenue streams. Explore the evolving landscape of digital assets to understand how NFTs revolutionize ownership and innovation in entrepreneurship.
Why it is important
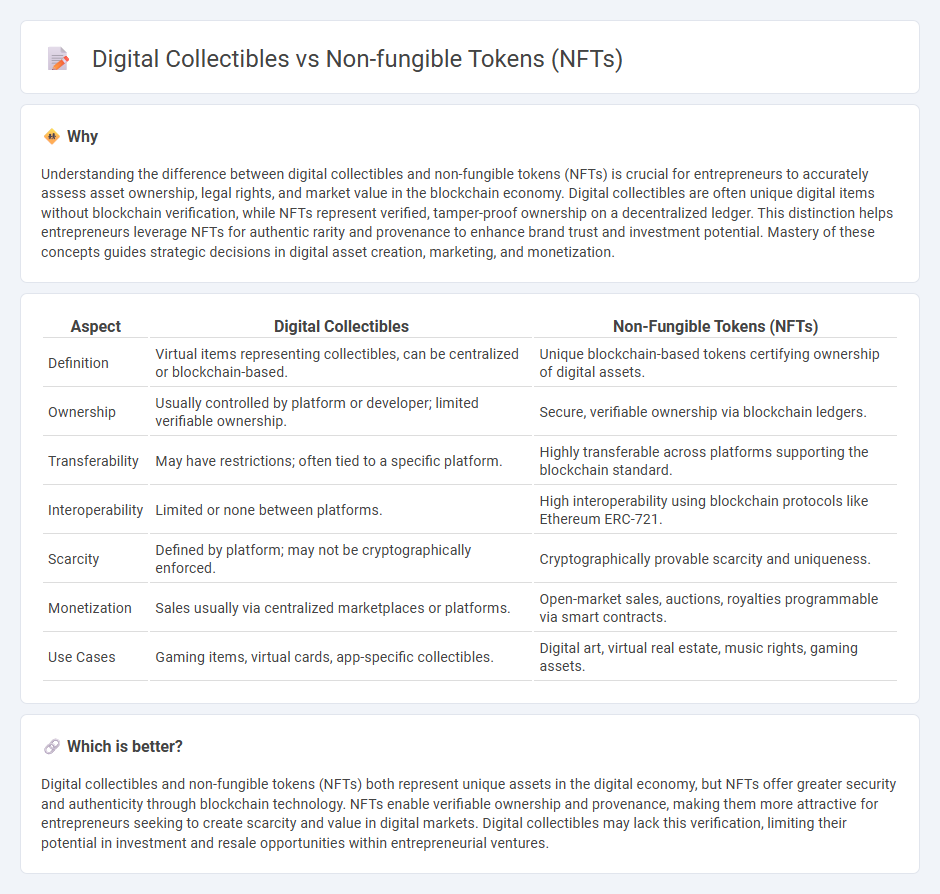
Understanding the difference between digital collectibles and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) is crucial for entrepreneurs to accurately assess asset ownership, legal rights, and market value in the blockchain economy. Digital collectibles are often unique digital items without blockchain verification, while NFTs represent verified, tamper-proof ownership on a decentralized ledger. This distinction helps entrepreneurs leverage NFTs for authentic rarity and provenance to enhance brand trust and investment potential. Mastery of these concepts guides strategic decisions in digital asset creation, marketing, and monetization.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Collectibles | Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual items representing collectibles, can be centralized or blockchain-based. | Unique blockchain-based tokens certifying ownership of digital assets. |
| Ownership | Usually controlled by platform or developer; limited verifiable ownership. | Secure, verifiable ownership via blockchain ledgers. |
| Transferability | May have restrictions; often tied to a specific platform. | Highly transferable across platforms supporting the blockchain standard. |
| Interoperability | Limited or none between platforms. | High interoperability using blockchain protocols like Ethereum ERC-721. |
| Scarcity | Defined by platform; may not be cryptographically enforced. | Cryptographically provable scarcity and uniqueness. |
| Monetization | Sales usually via centralized marketplaces or platforms. | Open-market sales, auctions, royalties programmable via smart contracts. |
| Use Cases | Gaming items, virtual cards, app-specific collectibles. | Digital art, virtual real estate, music rights, gaming assets. |
Which is better?
Digital collectibles and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) both represent unique assets in the digital economy, but NFTs offer greater security and authenticity through blockchain technology. NFTs enable verifiable ownership and provenance, making them more attractive for entrepreneurs seeking to create scarcity and value in digital markets. Digital collectibles may lack this verification, limiting their potential in investment and resale opportunities within entrepreneurial ventures.
Connection
Digital collectibles and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are intrinsically linked as NFTs provide a blockchain-based certification of ownership and authenticity for digital assets. Entrepreneurs leverage NFTs to create unique digital products, enabling new revenue streams and innovative business models in the digital economy. The decentralized nature of NFTs ensures scarcity and provenance, transforming traditional concepts of ownership within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Blockchain
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets verified on a blockchain, ensuring provenance and ownership authenticity, while digital collectibles may not necessarily use blockchain technology, limiting their traceability and security. NFTs utilize decentralized ledger systems such as Ethereum to provide immutable records, contrasting with traditional digital collectibles that often rely on centralized databases. Explore how blockchain transforms ownership and trading of digital assets by diving deeper into NFT technology and its implications.
Ownership Rights
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) provide verifiable ownership rights through blockchain technology, ensuring unique digital assets cannot be duplicated or altered, unlike traditional digital collectibles which often lack proof of exclusive ownership. NFTs enable true asset scarcity and transferability, granting owners full control over their digital property, whereas standard digital collectibles may only represent limited access or usage rights without legal ownership. Explore how NFTs revolutionize digital ownership and redefine value in online marketplaces.
Scarcity
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) utilize blockchain technology to certify the uniqueness and ownership of digital assets, creating verifiable scarcity that enhances their value. Digital collectibles may not always employ blockchain, leading to potential duplicability and less assured rarity compared to NFTs. Explore how scarcity influences market demand and investment potential in NFTs versus traditional digital collectibles to understand their value dynamics better.
Source and External Links
Non-fungible token - NFTs are unique digital identifiers recorded on a blockchain that certify ownership and authenticity of digital assets, differing from fungible cryptocurrencies; despite initial hype, by 2023 most NFT collections had no monetary value and the market collapsed after a peak in 2021.
What is a non-fungible token (NFT)? - NFTs are unique cryptoassets used to authenticate ownership of digital items like artwork, with some pieces (e.g., by artist Beeple) selling for millions despite no physical form, representing a new type of digital collector asset.
What is a non-fungible token (NFT)? - NFTs are cryptographic tokens representing unique digital or physical items, allowing owners to prove authenticity and ownership, and enabling trustless trade of assets ranging from art to tickets and real estate.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com