Exit as a service offers entrepreneurs a streamlined and technology-driven approach to selling their businesses, focusing on maximizing value through structured transactions and strategic buyers. Recapitalization involves restructuring a company's debt and equity mixture to improve financial stability and provide liquidity without a full exit, often appealing to founders seeking continued control. Explore the differences between these options to determine the best strategy for your entrepreneurial journey.
Why it is important
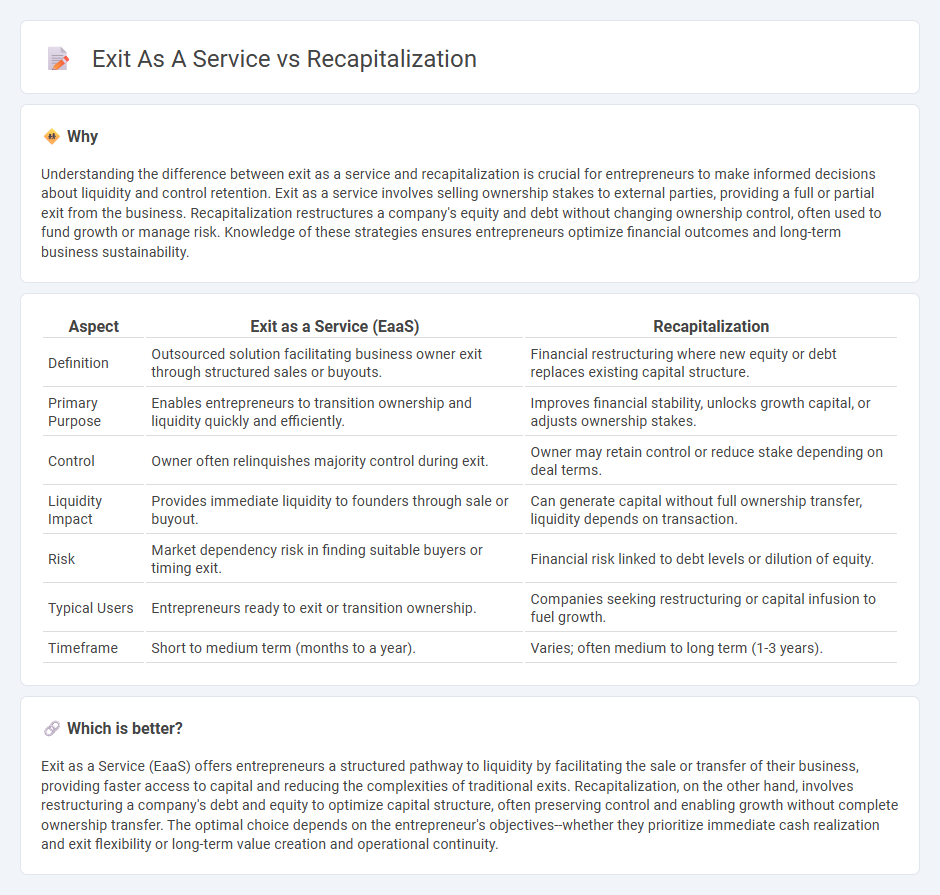
Understanding the difference between exit as a service and recapitalization is crucial for entrepreneurs to make informed decisions about liquidity and control retention. Exit as a service involves selling ownership stakes to external parties, providing a full or partial exit from the business. Recapitalization restructures a company's equity and debt without changing ownership control, often used to fund growth or manage risk. Knowledge of these strategies ensures entrepreneurs optimize financial outcomes and long-term business sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Exit as a Service (EaaS) | Recapitalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourced solution facilitating business owner exit through structured sales or buyouts. | Financial restructuring where new equity or debt replaces existing capital structure. |
| Primary Purpose | Enables entrepreneurs to transition ownership and liquidity quickly and efficiently. | Improves financial stability, unlocks growth capital, or adjusts ownership stakes. |
| Control | Owner often relinquishes majority control during exit. | Owner may retain control or reduce stake depending on deal terms. |
| Liquidity Impact | Provides immediate liquidity to founders through sale or buyout. | Can generate capital without full ownership transfer, liquidity depends on transaction. |
| Risk | Market dependency risk in finding suitable buyers or timing exit. | Financial risk linked to debt levels or dilution of equity. |
| Typical Users | Entrepreneurs ready to exit or transition ownership. | Companies seeking restructuring or capital infusion to fuel growth. |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term (months to a year). | Varies; often medium to long term (1-3 years). |
Which is better?
Exit as a Service (EaaS) offers entrepreneurs a structured pathway to liquidity by facilitating the sale or transfer of their business, providing faster access to capital and reducing the complexities of traditional exits. Recapitalization, on the other hand, involves restructuring a company's debt and equity to optimize capital structure, often preserving control and enabling growth without complete ownership transfer. The optimal choice depends on the entrepreneur's objectives--whether they prioritize immediate cash realization and exit flexibility or long-term value creation and operational continuity.
Connection
Exit as a service (EaaS) facilitates entrepreneurs in strategically planning their business exit through tailored solutions, which often involve recapitalization to restructure ownership and optimize financial outcomes. Recapitalization enables the infusion of new capital or the rearrangement of debt and equity, enhancing company valuation and making the exit process smoother and more profitable. Both concepts are interconnected by their focus on maximizing liquidity events and aligning stakeholder interests during transitions in ownership.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Recapitalization restructures a company's ownership by replacing existing equity or debt, often allowing current shareholders to retain partial control, whereas Exit as a Service facilitates a full ownership transfer, typically enabling founders or investors to liquidate their positions entirely. Recapitalization strategies can include issuing new equity or debt instruments to optimize capital structure, while Exit as a Service platforms streamline transaction processes for selling ownership stakes to third parties or strategic buyers. Explore the differences in ownership implications and strategic outcomes to determine the best fit for your business goals.
Liquidity Event
Recapitalization restructures a company's debt or equity to improve financial stability, often extending the business lifecycle without full ownership transfer. Exit as a Service provides founders and investors with a streamlined liquidity event by facilitating partial or full sale transactions, maximizing immediate capital access. Explore how these strategies impact shareholder value and timing by learning more about their financial implications.
Control Transition
Recapitalization involves restructuring a company's capital to stabilize finances while maintaining significant control for existing owners, whereas an exit as a service (EaaS) facilitates a complete ownership transfer, often prioritizing operational handover and strategic transition. Control transition in recapitalization tends to be gradual, allowing original stakeholders to retain influence, whereas EaaS typically accelerates control transfer to new investors or buyers. Explore detailed strategies on how these approaches impact ownership dynamics and decision-making authority.
Source and External Links
Recapitalization - Wikipedia - Recapitalization is a corporate reorganization involving a substantial change in a company's capital structure, often exchanging equity for debt or vice versa, with types including leveraged recapitalization, leveraged buyouts, and nationalization.
What is Recapitalization: Small Business Specifics - TAB Bank - Recapitalization is a financial process where a company restructures its debt-to-equity ratio to stabilize or improve its capital structure, using strategies like leveraged or equity recapitalization depending on company needs.
A Guide to Recapitalization - Wilcox Investment Bankers - Recapitalization optimizes the balance between debt and equity to fund growth or reduce risk, employing strategies such as issuing new shares or taking on debt to repurchase shares, aiming to enhance financial stability and shareholder value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com