The passion economy focuses on individuals monetizing unique skills and personal brands, fostering deep connections with niche audiences. In contrast, the sharing economy emphasizes asset utilization by enabling peer-to-peer access to goods and services. Explore the nuances between these models to understand their impact on modern entrepreneurship.
Why it is important
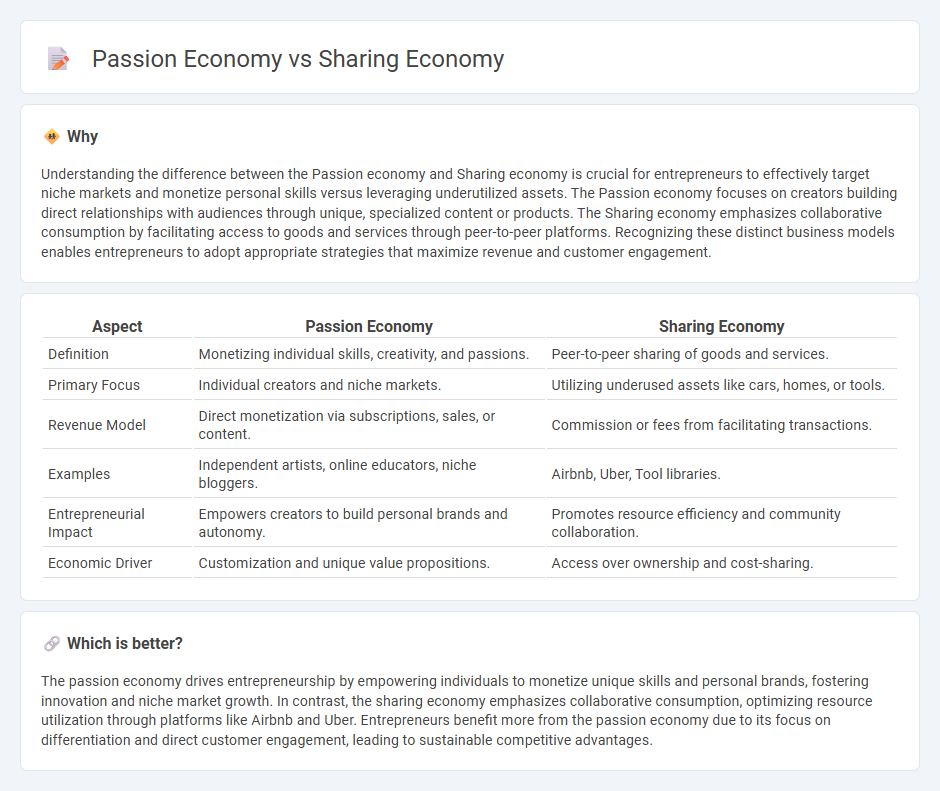
Understanding the difference between the Passion economy and Sharing economy is crucial for entrepreneurs to effectively target niche markets and monetize personal skills versus leveraging underutilized assets. The Passion economy focuses on creators building direct relationships with audiences through unique, specialized content or products. The Sharing economy emphasizes collaborative consumption by facilitating access to goods and services through peer-to-peer platforms. Recognizing these distinct business models enables entrepreneurs to adopt appropriate strategies that maximize revenue and customer engagement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Passion Economy | Sharing Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetizing individual skills, creativity, and passions. | Peer-to-peer sharing of goods and services. |
| Primary Focus | Individual creators and niche markets. | Utilizing underused assets like cars, homes, or tools. |
| Revenue Model | Direct monetization via subscriptions, sales, or content. | Commission or fees from facilitating transactions. |
| Examples | Independent artists, online educators, niche bloggers. | Airbnb, Uber, Tool libraries. |
| Entrepreneurial Impact | Empowers creators to build personal brands and autonomy. | Promotes resource efficiency and community collaboration. |
| Economic Driver | Customization and unique value propositions. | Access over ownership and cost-sharing. |
Which is better?
The passion economy drives entrepreneurship by empowering individuals to monetize unique skills and personal brands, fostering innovation and niche market growth. In contrast, the sharing economy emphasizes collaborative consumption, optimizing resource utilization through platforms like Airbnb and Uber. Entrepreneurs benefit more from the passion economy due to its focus on differentiation and direct customer engagement, leading to sustainable competitive advantages.
Connection
The passion economy and sharing economy are interconnected through their foundation on community-driven value exchange and personalized experiences. The passion economy empowers individuals to monetize unique skills and creative passions, while the sharing economy facilitates resource access and collaborative consumption. Both economies leverage digital platforms to enable direct peer-to-peer interactions, fostering trust and economic opportunity within niche markets.
Key Terms
Sharing economy:
The sharing economy leverages digital platforms to enable peer-to-peer exchange of goods and services, optimizing underutilized assets like cars, homes, and skills for economic value. Key players include companies like Airbnb, Uber, and TaskRabbit, which facilitate resource efficiency and cost savings by connecting providers with consumers directly. Discover how the sharing economy reshapes traditional business models and empowers collaborative consumption.
Peer-to-peer (P2P)
The sharing economy centers on peer-to-peer (P2P) resource exchange, enabling individuals to rent or share assets like cars, homes, or tools, optimizing underutilized goods and promoting cost efficiency. In contrast, the passion economy leverages P2P networks to monetize unique skills, creativity, and niche content, empowering individuals to build personalized brands and generate income driven by personal expertise and audience engagement. Explore deeper insights into how P2P dynamics are reshaping economic models and empowering individuals in both economies.
Asset utilization
The sharing economy centers on maximizing asset utilization by enabling peer-to-peer access to underused physical resources like cars, homes, and tools, driving efficiency through collaborative consumption. The passion economy shifts focus towards individual talents and creativity, allowing content creators and freelancers to monetize unique skills without relying heavily on shared physical assets. Explore how these economic models redefine resource use and income generation strategies.
Source and External Links
What Is the Sharing Economy - Example Companies, Definition ... - The sharing economy is a flexible economic network where people exchange tangible and intangible resources at scale via technology, improving efficiency by letting participants use items like cars or homes without owning them outright.
Sharing Economy - Definition, Model, Pros and Cons - A sharing economy is an economic model in which goods and resources become shared services through collaborative use, mainly enabled by big data and online platforms, allowing owners to monetize underused assets like spare bedrooms or vehicles.
Sharing economy - Wikipedia - The sharing economy is a socio-economic system where consumers share in the creation, distribution, and consumption of goods and services, providing access without ownership and fostering community strength, flexibility, and innovation while lowering costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com