Solopreneurship offers complete control and streamlined decision-making by allowing individuals to independently manage their business operations. Partnerships combine diverse skills and resources from multiple founders, fostering collaboration and shared responsibilities. Explore the advantages and challenges of each model to determine which suits your entrepreneurial goals best.
Why it is important
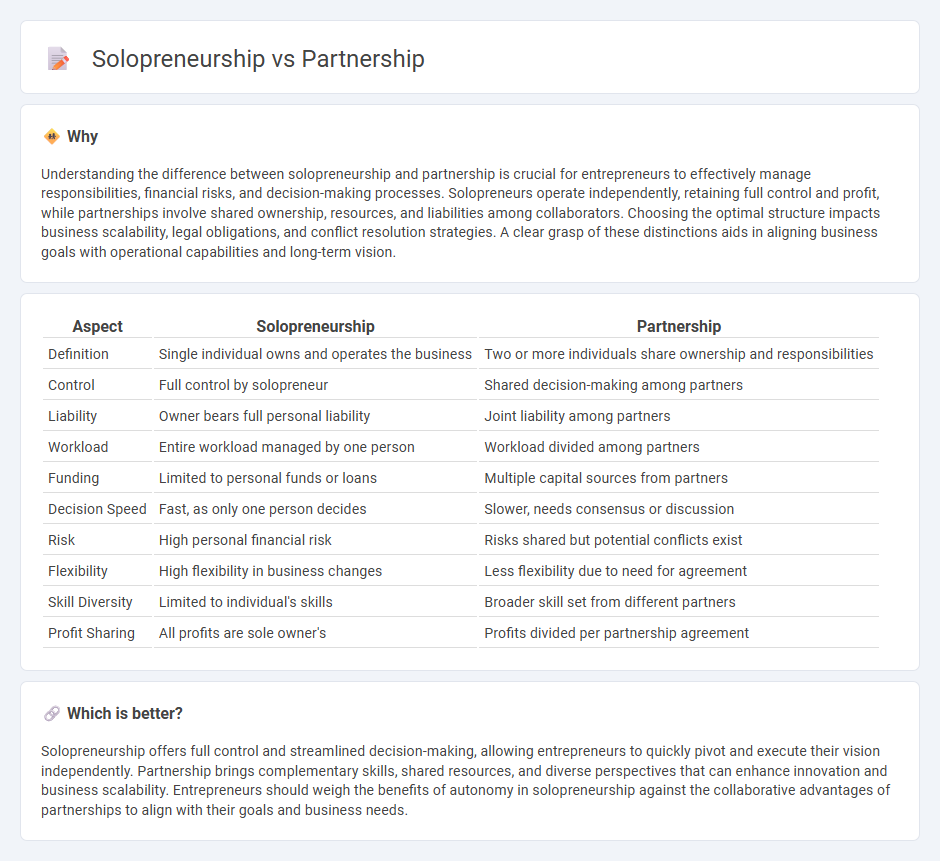
Understanding the difference between solopreneurship and partnership is crucial for entrepreneurs to effectively manage responsibilities, financial risks, and decision-making processes. Solopreneurs operate independently, retaining full control and profit, while partnerships involve shared ownership, resources, and liabilities among collaborators. Choosing the optimal structure impacts business scalability, legal obligations, and conflict resolution strategies. A clear grasp of these distinctions aids in aligning business goals with operational capabilities and long-term vision.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Solopreneurship | Partnership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single individual owns and operates the business | Two or more individuals share ownership and responsibilities |
| Control | Full control by solopreneur | Shared decision-making among partners |
| Liability | Owner bears full personal liability | Joint liability among partners |
| Workload | Entire workload managed by one person | Workload divided among partners |
| Funding | Limited to personal funds or loans | Multiple capital sources from partners |
| Decision Speed | Fast, as only one person decides | Slower, needs consensus or discussion |
| Risk | High personal financial risk | Risks shared but potential conflicts exist |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in business changes | Less flexibility due to need for agreement |
| Skill Diversity | Limited to individual's skills | Broader skill set from different partners |
| Profit Sharing | All profits are sole owner's | Profits divided per partnership agreement |
Which is better?
Solopreneurship offers full control and streamlined decision-making, allowing entrepreneurs to quickly pivot and execute their vision independently. Partnership brings complementary skills, shared resources, and diverse perspectives that can enhance innovation and business scalability. Entrepreneurs should weigh the benefits of autonomy in solopreneurship against the collaborative advantages of partnerships to align with their goals and business needs.
Connection
Solopreneurship and partnership intersect through the foundational principles of entrepreneurship, where individual initiative often evolves into collaborative ventures to leverage diverse skills and resources. Solopreneurs frequently transition to partnerships to scale operations, share risk, and increase innovation capacity, while partnerships may begin from solopreneurial roots seeking expanded market reach. This dynamic connection facilitates adaptive business models that balance autonomy with collective expertise, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Partnerships involve shared ownership, where two or more individuals jointly manage assets, profits, and liabilities, fostering collaboration but requiring clear agreements to avoid conflicts. Solopreneurship offers sole ownership and complete control over business decisions, profits, and responsibilities, enabling agility but placing full risk on the individual. Discover detailed insights into how ownership structure impacts business success and legal obligations.
Decision-Making Authority
Partnerships distribute decision-making authority among co-owners, often requiring consensus or collaborative input, which can diversify perspectives but slow down the process. Solopreneurs retain full control over decisions, enabling rapid actions aligned closely with personal vision but bearing sole responsibility for outcomes. Explore the advantages and challenges of each approach to determine which decision-making structure suits your business goals.
Risk Distribution
Partnerships distribute financial and operational risks among multiple stakeholders, reducing individual exposure and providing shared accountability. In contrast, solopreneurs bear the full burden of risks, including market fluctuations and decision-making pressures, which can impact business stability. Explore deeper insights on risk management strategies by comparing partnership structures with solopreneurship models.
Source and External Links
Partnership - Wikipedia - A partnership is an agreement where parties agree to cooperate to advance their mutual interests, which can include individuals, businesses, or organizations sharing profits and responsibilities in a business together.
Definition of Partnership: How They Work, Taxation and Types - A partnership is a legally binding agreement between two or more people who share ownership, responsibilities, and management of a company, often combining resources and skills for business growth.
Partnership - Overview, Types of Partners, Types of Partnerships - Partnerships are unincorporated business entities formed by two or more parties, with types including general, limited, and limited liability partnerships, where profit or loss is shared among partners who may have varying levels of legal liability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com