Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) operate on blockchain technology, enabling transparent and democratic decision-making without centralized control, contrasting with traditional corporations that rely on hierarchical management and legal frameworks. DAOs emphasize community ownership and algorithm-driven governance, which can reduce administrative overhead and enhance participant engagement compared to the structured, compliance-focused nature of corporations. Explore the evolving landscape of entrepreneurship to understand how DAOs and corporations shape future business models.
Why it is important
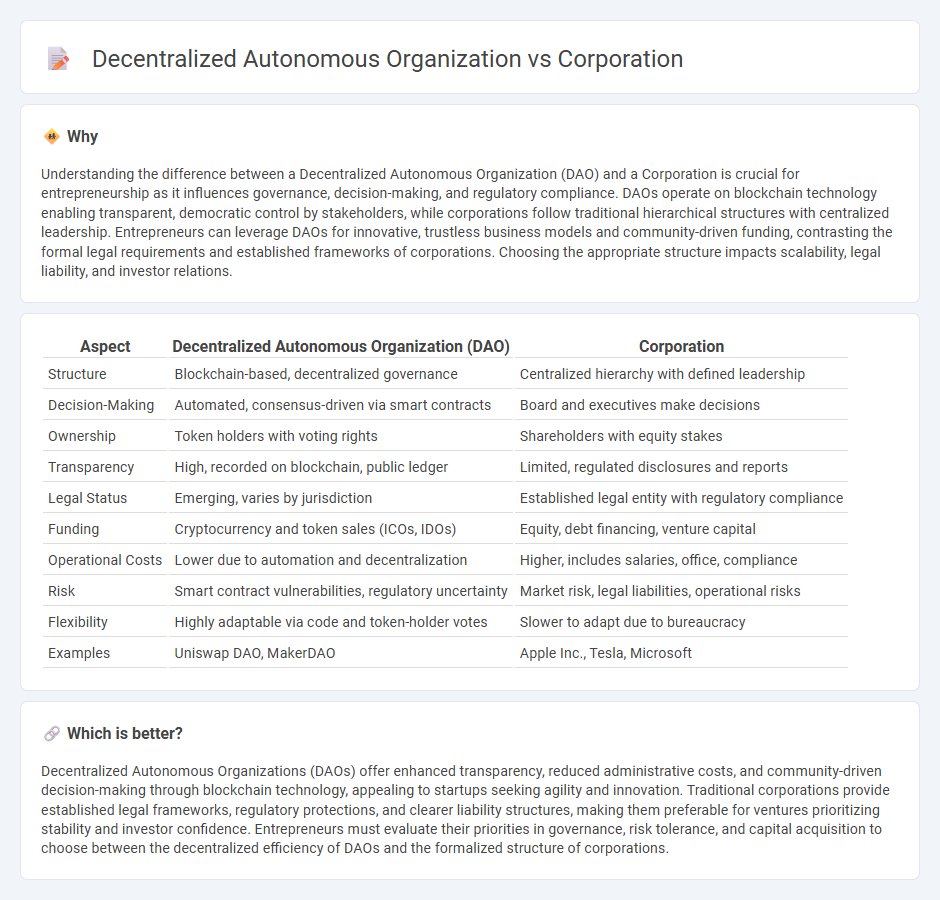
Understanding the difference between a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and a Corporation is crucial for entrepreneurship as it influences governance, decision-making, and regulatory compliance. DAOs operate on blockchain technology enabling transparent, democratic control by stakeholders, while corporations follow traditional hierarchical structures with centralized leadership. Entrepreneurs can leverage DAOs for innovative, trustless business models and community-driven funding, contrasting the formal legal requirements and established frameworks of corporations. Choosing the appropriate structure impacts scalability, legal liability, and investor relations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) | Corporation |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Blockchain-based, decentralized governance | Centralized hierarchy with defined leadership |
| Decision-Making | Automated, consensus-driven via smart contracts | Board and executives make decisions |
| Ownership | Token holders with voting rights | Shareholders with equity stakes |
| Transparency | High, recorded on blockchain, public ledger | Limited, regulated disclosures and reports |
| Legal Status | Emerging, varies by jurisdiction | Established legal entity with regulatory compliance |
| Funding | Cryptocurrency and token sales (ICOs, IDOs) | Equity, debt financing, venture capital |
| Operational Costs | Lower due to automation and decentralization | Higher, includes salaries, office, compliance |
| Risk | Smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty | Market risk, legal liabilities, operational risks |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable via code and token-holder votes | Slower to adapt due to bureaucracy |
| Examples | Uniswap DAO, MakerDAO | Apple Inc., Tesla, Microsoft |
Which is better?
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer enhanced transparency, reduced administrative costs, and community-driven decision-making through blockchain technology, appealing to startups seeking agility and innovation. Traditional corporations provide established legal frameworks, regulatory protections, and clearer liability structures, making them preferable for ventures prioritizing stability and investor confidence. Entrepreneurs must evaluate their priorities in governance, risk tolerance, and capital acquisition to choose between the decentralized efficiency of DAOs and the formalized structure of corporations.
Connection
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and corporations both serve as frameworks for structured group collaboration and resource management in entrepreneurship, with DAOs leveraging blockchain technology to enable transparent, decentralized decision-making without centralized leadership. Corporations typically rely on hierarchical governance structures, while DAOs implement smart contracts to automate processes and enforce rules, enhancing operational efficiency and trust among stakeholders. The convergence of DAOs and corporations signals a transformative shift in entrepreneurial organization models toward more democratic, technology-driven ecosystems.
Key Terms
Centralized Governance
Centralized governance in corporations consolidates decision-making authority within a defined hierarchy, enabling streamlined control and accountability through boards and executives. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) distribute governance across token holders using blockchain-based smart contracts, reducing single points of failure and emphasizing consensus mechanisms. Explore how centralized governance models impact organizational efficiency and stakeholder engagement to understand their distinct operational dynamics.
Token-based Voting
Corporations typically utilize traditional shareholder voting systems where voting power is proportional to the number of shares owned, while decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) leverage token-based voting that grants participants influence based on their token holdings on blockchain platforms. Token-based voting in DAOs enhances transparency, security, and inclusivity, enabling real-time governance without intermediaries, contrasting with the more centralized and regulated corporate voting frameworks. Explore the evolving dynamics between corporate governance and DAO token-based voting to understand the future of organizational decision-making.
Legal Entity
A corporation is a legally recognized entity established under state laws, providing limited liability protection to its shareholders and subject to regulatory oversight, taxation, and formal governance structures. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) operate through blockchain technology, lacking a traditional legal entity status, which creates uncertainties in liability, jurisdiction, and regulatory compliance. Explore the evolving legal frameworks and implications shaping the future of corporations and DAOs.
Source and External Links
Guide to Corporations: Definition and Types - Shopify - A corporation is a legal business entity owned by shareholders and managed by an elected board of directors, providing limited liability protection by separating the business's obligations and assets from those of its owners.
What is a Corporation? - Various Types and Reasons to Incorporate - Corporations are legal entities created to operate for profit or nonprofit purposes, allowing them to enter contracts, sue or be sued, own property, and have shareholders not personally liable for corporate debts.
Corporation - Wikipedia - A corporation is recognized by law as a single legal entity with shareholders who have limited liability, formed through registration or charter, enabling it to act independently from its owners and protect investors from personal liability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com