Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, member-driven decision-making without centralized leadership, contrasting sharply with traditional nonprofits governed by hierarchical boards. DAOs offer real-time voting and automated fund management through smart contracts, enhancing efficiency and accountability in resource allocation. Explore how these innovative organizational structures are reshaping entrepreneurship and philanthropy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and traditional nonprofits is crucial for entrepreneurs to leverage blockchain technology's transparency and automation. DAOs operate on smart contracts, enabling decentralized decision-making and fundraising without intermediaries, contrasting with the hierarchical structure of traditional nonprofits. This knowledge empowers entrepreneurs to choose governance models that enhance trust, efficiency, and global participation. Selecting the appropriate organizational form impacts fundraising strategies, legal compliance, and community engagement in innovative ventures.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) | Traditional Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
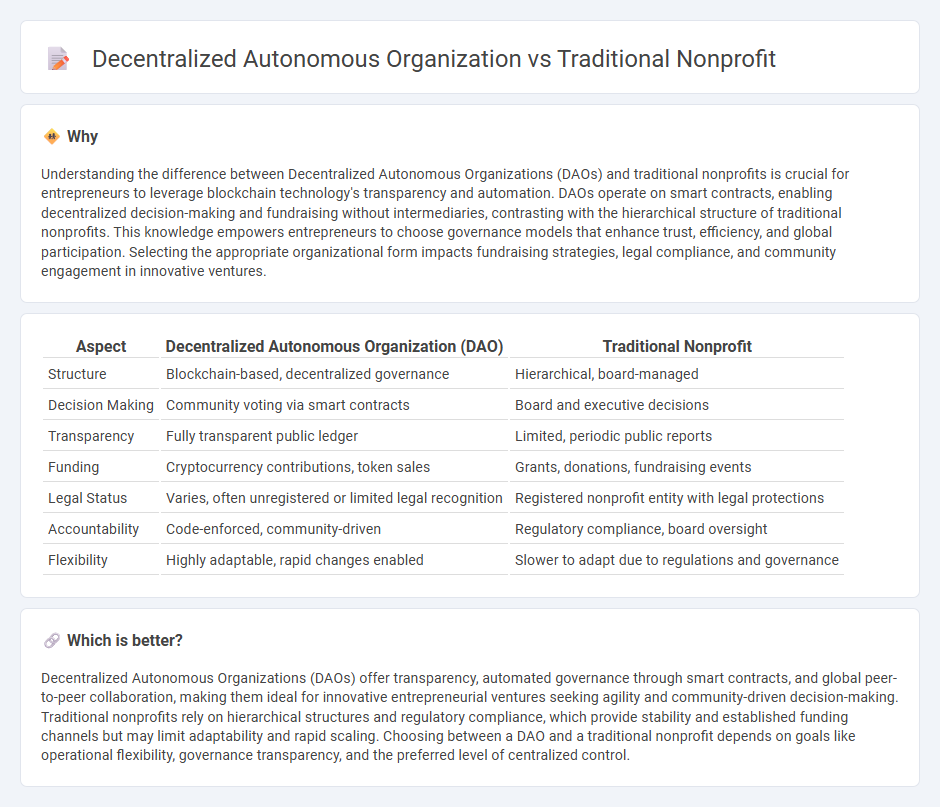
| Structure | Blockchain-based, decentralized governance | Hierarchical, board-managed |
| Decision Making | Community voting via smart contracts | Board and executive decisions |
| Transparency | Fully transparent public ledger | Limited, periodic public reports |
| Funding | Cryptocurrency contributions, token sales | Grants, donations, fundraising events |
| Legal Status | Varies, often unregistered or limited legal recognition | Registered nonprofit entity with legal protections |
| Accountability | Code-enforced, community-driven | Regulatory compliance, board oversight |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable, rapid changes enabled | Slower to adapt due to regulations and governance |
Which is better?
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer transparency, automated governance through smart contracts, and global peer-to-peer collaboration, making them ideal for innovative entrepreneurial ventures seeking agility and community-driven decision-making. Traditional nonprofits rely on hierarchical structures and regulatory compliance, which provide stability and established funding channels but may limit adaptability and rapid scaling. Choosing between a DAO and a traditional nonprofit depends on goals like operational flexibility, governance transparency, and the preferred level of centralized control.
Connection
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and traditional nonprofits share a focus on mission-driven goals, but DAOs leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent governance and smart contracts, enhancing trust and operational efficiency. Traditional nonprofits rely on centralized boards and manual processes, while DAOs facilitate decentralized decision-making and automatic fund allocation, reducing administrative overhead. Both structures aim to maximize social impact through collective participation and resource management.
Key Terms
Governance structure
Traditional nonprofits operate under hierarchical governance, often with a board of directors overseeing decision-making and compliance with regulations. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) utilize blockchain-based smart contracts to enable transparent, collective decision-making, allowing stakeholders to vote on proposals without centralized control. Explore deeper insights into how governance structures impact organizational efficiency and community engagement.
Funding mechanisms
Traditional nonprofits primarily rely on donations, grants, and government funding, often requiring extensive paperwork and oversight. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) utilize blockchain technology to facilitate direct funding through cryptocurrency contributions, enabling transparent and automated allocation of resources via smart contracts. Explore how evolving funding mechanisms empower these organizations by learning more about their financial innovations.
Decision-making process
Traditional nonprofits rely on hierarchical decision-making processes where board members and executives hold authority, often resulting in slower consensus and less transparency. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) use blockchain technology to enable collective decision-making through token-based voting, ensuring transparency and faster implementation of community-driven proposals. Explore how these structures impact organizational efficiency and member engagement in detail.
Source and External Links
Traditional Non-Profits vs. Private Foundations - Traditional nonprofits primarily focus on direct service provision, community engagement, and advocacy, addressing specific societal issues, with governance by a board of directors and funding from diverse streams such as grants, donations, and fundraising events.
Nonprofit organization - A nonprofit organization operates for social or public benefit rather than profit, with excess revenue reinvested into its mission, and can include a wide variety of entities like charities, schools, and foundations under various legal frameworks.
non-profit organizations | Wex - Law.Cornell.Edu - Non-profit organizations are typically formed to pursue purposes other than generating profit and are governed by state laws, often including entities such as charities, public schools, hospitals, and associations, with no distribution of income to members or leaders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com