Entrepreneurship in e-resale involves leveraging existing products to reach new markets through online platforms, minimizing initial investment and inventory risks. Manufacturing entrepreneurship requires developing unique products from raw materials, offering greater control over quality and branding but demanding higher capital and operational complexity. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which business model aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
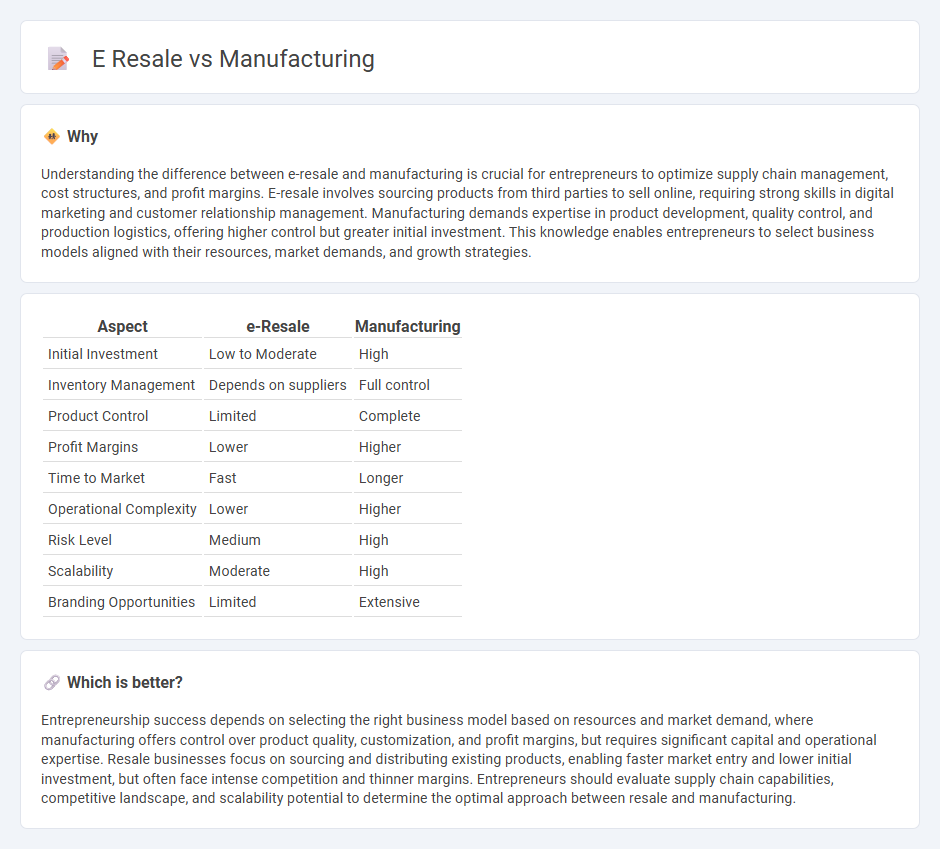
Understanding the difference between e-resale and manufacturing is crucial for entrepreneurs to optimize supply chain management, cost structures, and profit margins. E-resale involves sourcing products from third parties to sell online, requiring strong skills in digital marketing and customer relationship management. Manufacturing demands expertise in product development, quality control, and production logistics, offering higher control but greater initial investment. This knowledge enables entrepreneurs to select business models aligned with their resources, market demands, and growth strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | e-Resale | Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to Moderate | High |
| Inventory Management | Depends on suppliers | Full control |
| Product Control | Limited | Complete |
| Profit Margins | Lower | Higher |
| Time to Market | Fast | Longer |
| Operational Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Risk Level | Medium | High |
| Scalability | Moderate | High |
| Branding Opportunities | Limited | Extensive |
Which is better?
Entrepreneurship success depends on selecting the right business model based on resources and market demand, where manufacturing offers control over product quality, customization, and profit margins, but requires significant capital and operational expertise. Resale businesses focus on sourcing and distributing existing products, enabling faster market entry and lower initial investment, but often face intense competition and thinner margins. Entrepreneurs should evaluate supply chain capabilities, competitive landscape, and scalability potential to determine the optimal approach between resale and manufacturing.
Connection
Resale and manufacturing are interconnected through the supply chain where manufacturers produce goods that resellers distribute to end consumers, creating a seamless flow from production to market. Efficient manufacturing processes drive product availability, enabling resellers to stock diverse inventory, meet demand, and optimize profitability. Data analytics in both sectors enhance forecasting accuracy, inventory management, and customer targeting, strengthening the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Manufacturing supply chains emphasize raw material sourcing, production scheduling, and inventory management to ensure efficient product creation and timely delivery. E-resale supply chains prioritize rapid order fulfillment, real-time inventory updates, and last-mile logistics to meet dynamic consumer demand. Explore the intricacies of both models to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Inventory Management
Manufacturing inventory management involves overseeing raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods to ensure efficient production flow and minimize costs. In contrast, e-resale inventory management emphasizes real-time stock updates, demand forecasting, and rapid replenishment to meet customer expectations and reduce stockouts. Explore effective strategies to optimize inventory management tailored to your business model.
Profit Margin
Manufacturing typically offers higher profit margins due to lower production costs and control over pricing, while e-resale often involves slimmer margins because of market competition and sourcing expenses. Direct manufacturing reduces reliance on third-party suppliers, enhancing profitability through economies of scale and process optimization. Explore detailed strategies to maximize profit margins in both manufacturing and e-resale sectors.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing: Definition, Examples, Types and Guide - Manufacturing is the process transforming raw materials into finished goods, with primary production methods being Make-to-stock, Make-to-order, and Make-to-assemble, each with specific operational risks and strategies for risk management.
Manufacturing - Manufacturing is the industrial-scale creation of goods using equipment, labor, and processes to transform raw materials into finished products, encompassing a broad range of activities from handicrafts to high-tech production.
What is Manufacturing: The Ultimate Guide (2024) -- Katana - Manufacturing involves converting raw materials into finished products using labor and machinery, with various process types including repetitive, discrete, and job shop manufacturing depending on product demand and production scale.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com