Tiny acquisitions involve purchasing small, established businesses to quickly gain revenue and market presence, offering less risk compared to starting from scratch. Angel investing focuses on providing early-stage capital to startups with high growth potential but higher uncertainty. Explore the differences and benefits to decide which path aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between tiny acquisitions and angel investing is crucial for entrepreneurs to make informed decisions about capital allocation and growth strategies. Tiny acquisitions involve purchasing small companies to quickly gain market share or new capabilities, while angel investing focuses on providing early-stage capital to startups in exchange for equity. Entrepreneurs who grasp these distinctions can better tailor their approach to funding, exit strategies, and long-term business objectives. This knowledge helps optimize resource use, minimize risks, and maximize returns in the startup ecosystem.
Comparison Table
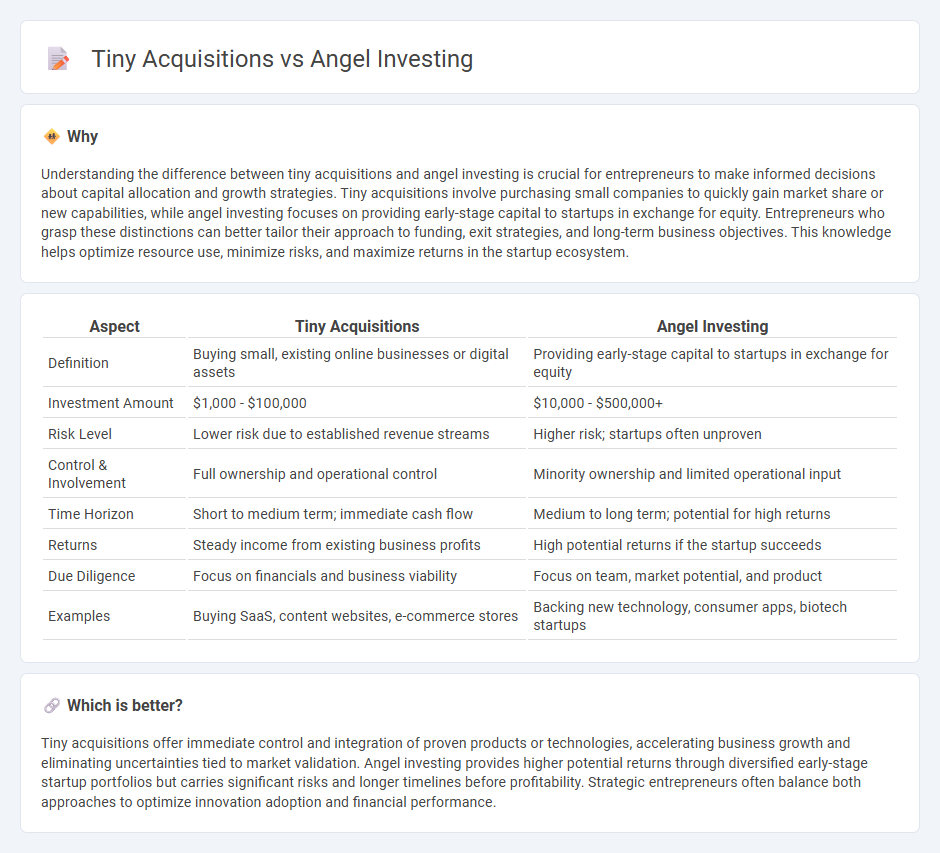
| Aspect | Tiny Acquisitions | Angel Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying small, existing online businesses or digital assets | Providing early-stage capital to startups in exchange for equity |
| Investment Amount | $1,000 - $100,000 | $10,000 - $500,000+ |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to established revenue streams | Higher risk; startups often unproven |
| Control & Involvement | Full ownership and operational control | Minority ownership and limited operational input |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term; immediate cash flow | Medium to long term; potential for high returns |
| Returns | Steady income from existing business profits | High potential returns if the startup succeeds |
| Due Diligence | Focus on financials and business viability | Focus on team, market potential, and product |
| Examples | Buying SaaS, content websites, e-commerce stores | Backing new technology, consumer apps, biotech startups |
Which is better?
Tiny acquisitions offer immediate control and integration of proven products or technologies, accelerating business growth and eliminating uncertainties tied to market validation. Angel investing provides higher potential returns through diversified early-stage startup portfolios but carries significant risks and longer timelines before profitability. Strategic entrepreneurs often balance both approaches to optimize innovation adoption and financial performance.
Connection
Tiny acquisitions often serve as strategic exits for startups, providing early returns to founders and investors. Angel investing fuels these startups by offering crucial seed capital in exchange for equity, enabling rapid growth and innovation. Both processes contribute to a dynamic entrepreneurial ecosystem where small-scale investments and acquisitions drive scalable business expansion.
Key Terms
Equity
Angel investing typically involves providing early-stage capital to startups in exchange for equity, offering potential high returns but with higher risk and longer holding periods. Tiny acquisitions, often characterized by acquiring small businesses or startups, result in immediate equity ownership and control, allowing for faster integration and potential operational synergies. Explore the nuances of equity focus in both strategies to optimize your investment approach.
Early-stage funding
Angel investing provides early-stage startups with crucial capital, mentorship, and industry connections, often filling the gap between seed funding and larger venture capital rounds. Tiny acquisitions, where established companies acquire small startups, offer immediate liquidity to founders but may limit the startup's growth potential as an independent entity. Explore the nuances of early-stage funding strategies to determine the best approach for your startup's growth trajectory.
Micro-acquisitions
Micro-acquisitions involve the strategic purchase of small companies or assets, typically valued under $1 million, to quickly scale business capabilities without extensive integration risks. Unlike angel investing, which provides equity stakes and focuses on long-term growth, micro-acquisitions offer immediate control and direct operational benefits. Explore the advantages of micro-acquisitions to understand how they can accelerate your business expansion.
Source and External Links
Understanding angel financing and investing - Angel investing involves wealthy individuals providing early-stage capital to startups in exchange for equity or convertible debt, often helping founders develop prototypes, conduct market research, and make initial hires, while also offering mentorship and strategic support.
Angel Investors - Angel investors are private, wealthy individuals who invest their own money in small businesses for equity, typically seeking a substantial return on investment and often providing smaller, patient funding compared to venture capitalists.
Angel investor - Angel investors, known also as seed or private investors, are individuals who provide capital early in a venture, with studies showing they expect notable returns and play a key role in startup growth, especially in regions like the UK where their activity and impact investments have grown.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com