Solopreneurship involves individuals who create and run their own business independently, managing all aspects from strategy to execution. Intrapreneurship refers to employees within a company who apply entrepreneurial skills to innovate and develop new projects, driving growth from within the organization. Explore the unique challenges and benefits of solopreneurship and intrapreneurship to understand which path suits your goals best.
Why it is important
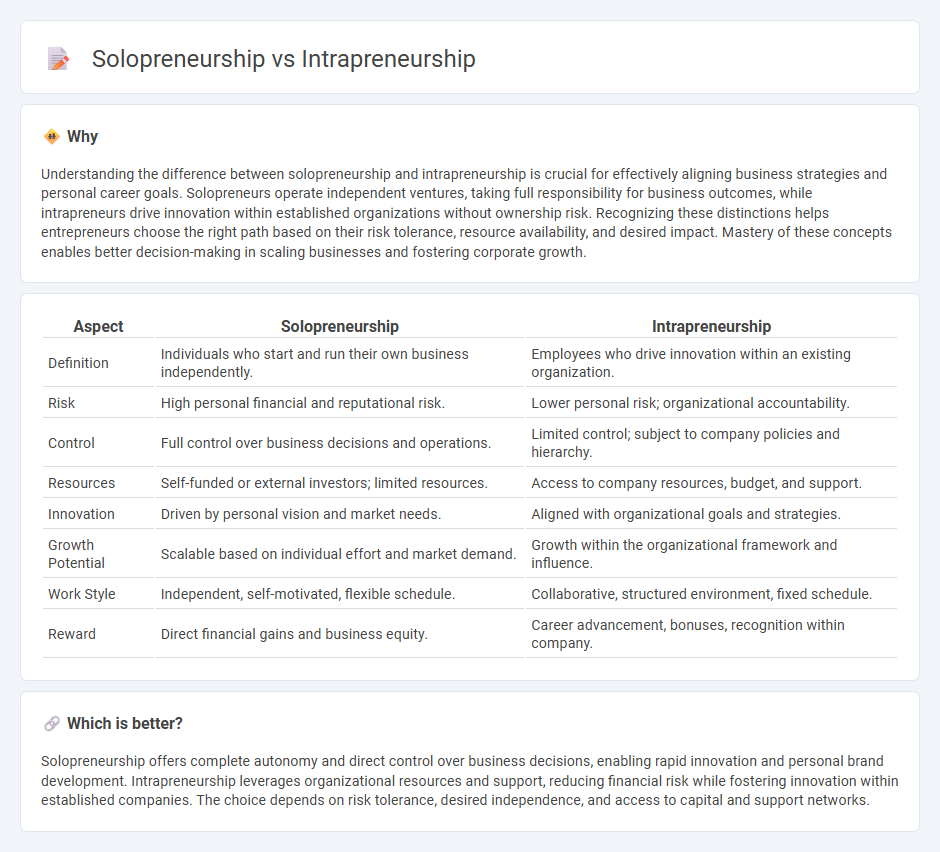
Understanding the difference between solopreneurship and intrapreneurship is crucial for effectively aligning business strategies and personal career goals. Solopreneurs operate independent ventures, taking full responsibility for business outcomes, while intrapreneurs drive innovation within established organizations without ownership risk. Recognizing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs choose the right path based on their risk tolerance, resource availability, and desired impact. Mastery of these concepts enables better decision-making in scaling businesses and fostering corporate growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Solopreneurship | Intrapreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individuals who start and run their own business independently. | Employees who drive innovation within an existing organization. |
| Risk | High personal financial and reputational risk. | Lower personal risk; organizational accountability. |
| Control | Full control over business decisions and operations. | Limited control; subject to company policies and hierarchy. |
| Resources | Self-funded or external investors; limited resources. | Access to company resources, budget, and support. |
| Innovation | Driven by personal vision and market needs. | Aligned with organizational goals and strategies. |
| Growth Potential | Scalable based on individual effort and market demand. | Growth within the organizational framework and influence. |
| Work Style | Independent, self-motivated, flexible schedule. | Collaborative, structured environment, fixed schedule. |
| Reward | Direct financial gains and business equity. | Career advancement, bonuses, recognition within company. |
Which is better?
Solopreneurship offers complete autonomy and direct control over business decisions, enabling rapid innovation and personal brand development. Intrapreneurship leverages organizational resources and support, reducing financial risk while fostering innovation within established companies. The choice depends on risk tolerance, desired independence, and access to capital and support networks.
Connection
Solopreneurship and intrapreneurship both emphasize innovation, self-motivation, and risk-taking within different organizational frameworks. Solopreneurs drive independent business ventures, directly controlling strategy and operations, while intrapreneurs foster entrepreneurial initiatives within established companies to spur growth and competitive advantage. The shared focus on proactive problem-solving and value creation links these two forms of entrepreneurship, facilitating knowledge transfer and dynamic business cultures.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Intrapreneurship offers autonomy within the structure of an established company, allowing employees to innovate while leveraging existing resources and organizational support. Solopreneurship provides full independence, where individuals make all decisions and bear the risks and rewards of their ventures alone. Discover how autonomy shapes success in both intrapreneurship and solopreneurship models.
Resources
Intrapreneurship leverages organizational resources such as funding, infrastructure, and expertise to drive innovation within a company, while solopreneurship relies primarily on individual resources, including personal capital, skills, and networks. Intrapreneurs benefit from collaborative support and existing market access, whereas solopreneurs face greater challenges in resource acquisition but enjoy full control over decision-making and equity. Discover how resource management strategies differ fundamentally between intrapreneurs and solopreneurs.
Risk Ownership
Intrapreneurship involves employees driving innovation within an established company, where the organization shoulders most financial and operational risks, allowing intrapreneurs to focus on creativity and project development without personal monetary exposure. Conversely, solopreneurs fully own the risks of their ventures, managing all aspects from funding to market strategy, which demands high levels of personal investment and risk tolerance. Discover the crucial differences in risk management and how they impact entrepreneurial success.
Source and External Links
Intrapreneurship - Wikipedia - Intrapreneurship is the act of behaving like an entrepreneur within a large organization, combining risk-taking and innovation to create new products or processes, benefiting both the individual and the company.
What is intrapreneurship, and how can you cultivate it at your company? - Stanford Online - Intrapreneurs are employees within established companies who innovate and improve their work and organization by applying entrepreneurial skills, driving business growth without bearing financial risks themselves.
What is Intrapreneurship: Definition, Strategies, and Examples - Intrapreneurship involves empowering employees in large organizations to act like entrepreneurs by taking initiative and leveraging company resources to create innovation and maintain competitiveness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com