The creator economy thrives on individual content producers leveraging digital platforms to monetize creativity and build personal brands, driving economic growth through innovation and community engagement. The circular economy focuses on sustainable business practices by minimizing waste, promoting reuse, and encouraging resource efficiency to foster environmental and economic resilience. Explore the dynamic interplay between these two economies to understand their unique impacts on modern entrepreneurship.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between the Creator Economy and Circular Economy is crucial for entrepreneurs to tailor their business models effectively and target relevant markets. The Creator Economy focuses on individual content creators monetizing digital assets, while the Circular Economy emphasizes sustainable resource management and waste reduction. This knowledge helps entrepreneurs align strategies with economic trends and consumer demands. Clear differentiation enhances innovation and investment decisions in emerging economic sectors.
Comparison Table
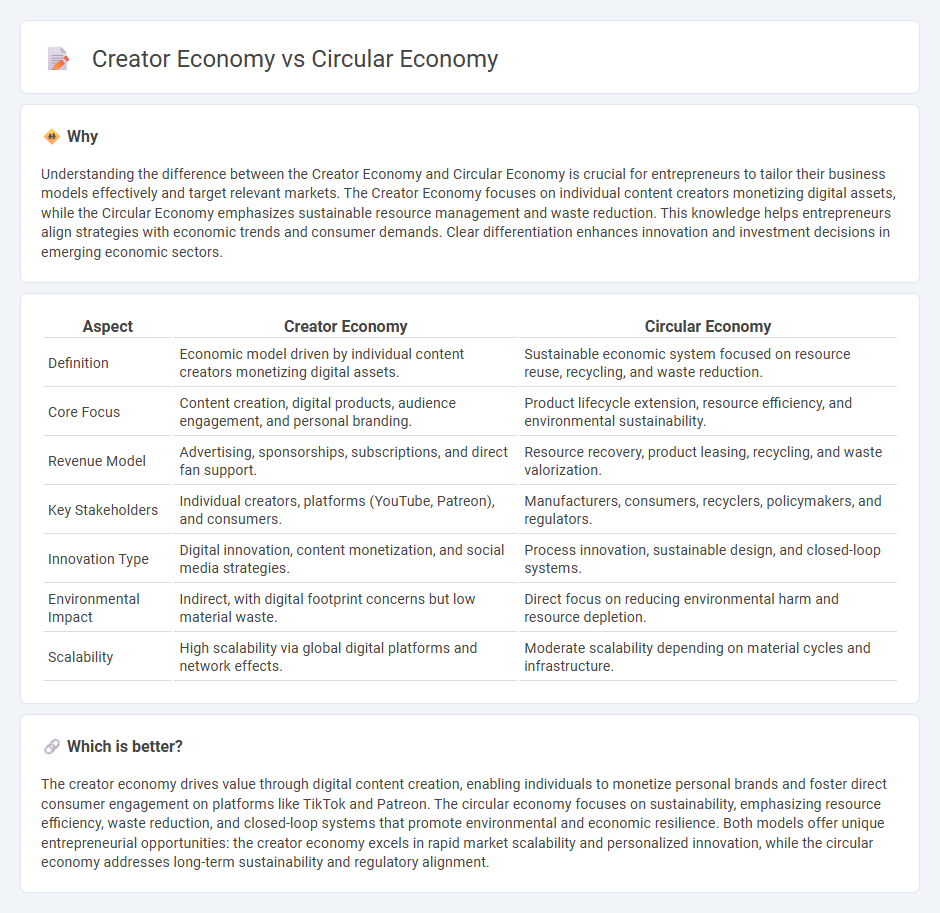
| Aspect | Creator Economy | Circular Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic model driven by individual content creators monetizing digital assets. | Sustainable economic system focused on resource reuse, recycling, and waste reduction. |
| Core Focus | Content creation, digital products, audience engagement, and personal branding. | Product lifecycle extension, resource efficiency, and environmental sustainability. |
| Revenue Model | Advertising, sponsorships, subscriptions, and direct fan support. | Resource recovery, product leasing, recycling, and waste valorization. |
| Key Stakeholders | Individual creators, platforms (YouTube, Patreon), and consumers. | Manufacturers, consumers, recyclers, policymakers, and regulators. |
| Innovation Type | Digital innovation, content monetization, and social media strategies. | Process innovation, sustainable design, and closed-loop systems. |
| Environmental Impact | Indirect, with digital footprint concerns but low material waste. | Direct focus on reducing environmental harm and resource depletion. |
| Scalability | High scalability via global digital platforms and network effects. | Moderate scalability depending on material cycles and infrastructure. |
Which is better?
The creator economy drives value through digital content creation, enabling individuals to monetize personal brands and foster direct consumer engagement on platforms like TikTok and Patreon. The circular economy focuses on sustainability, emphasizing resource efficiency, waste reduction, and closed-loop systems that promote environmental and economic resilience. Both models offer unique entrepreneurial opportunities: the creator economy excels in rapid market scalability and personalized innovation, while the circular economy addresses long-term sustainability and regulatory alignment.
Connection
The creator economy thrives on digital content production and monetization, fueling entrepreneurship through innovative platforms and personalized consumer engagement. Circular economy principles emphasize resource efficiency and waste reduction, inspiring creators to adopt sustainable practices in product design and distribution. Both economies intersect by promoting sustainable value creation and resource optimization, driving new entrepreneurial models focused on continuous innovation and environmental stewardship.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency (Circular economy)
The circular economy emphasizes maximizing resource efficiency by minimizing waste through reuse, recycling, and sustainable product design, ultimately reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. It employs closed-loop systems that keep materials in circulation for extended periods, promoting sustainability across industries. Explore how circular economy principles can revolutionize resource management and drive sustainable growth.
Digital Platforms (Creator economy)
The circular economy emphasizes resource efficiency and waste reduction through reuse, recycling, and sustainable product design, promoting environmental sustainability. In contrast, the creator economy centers on digital platforms that empower independent content creators to monetize their skills, driving innovation and personalized consumer engagement. Explore the evolving dynamics of these economies to understand their impact on digital transformation and sustainable growth.
Value Chain Innovation
Circular economy emphasizes closing resource loops through sustainable design, reuse, and recycling, reducing waste and environmental impact within value chains. Creator economy prioritizes individual empowerment and content monetization, leveraging digital platforms to innovate the value chain by directly connecting creators and consumers. Explore deeper insights on how these economic models reshape value chain innovation.
Source and External Links
Circular economy - Wikipedia - The circular economy is a model of resource production and consumption emphasizing sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to minimize waste and environmental impact while extending product life cycles and combating global challenges like climate change and pollution.
What is a circular economy? | Ellen MacArthur Foundation - A circular economy is a system where materials are kept in use through maintenance, reuse, refurbishment, remanufacture, and recycling, aiming to eliminate waste and pollution, regenerate nature, and decouple economic growth from finite resource consumption based on three design-driven principles.
What is Circular Economy & How Does It Work? : Complete Guide - The circular economy is an industrial system designed to be restorative and regenerative, continuously cycling materials through reuse, repair, and remanufacture to reduce waste and emissions, providing an alternative to the traditional linear "take-make-dispose" economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com