Print on demand and dropshipping are two popular e-commerce models that minimize upfront inventory costs while offering unique advantages; print on demand allows for customized products produced only after an order is placed, whereas dropshipping involves selling products from suppliers who handle storage and shipping directly. Entrepreneurs leverage print on demand for creative control over designs and branding, while dropshipping provides a broader product range without manufacturing involvement. Explore the distinct benefits and challenges of both models to determine the best fit for your business goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Print on Demand and Dropshipping is crucial for entrepreneurs to select the optimal business model aligned with their goals, budget, and operational preferences. Print on Demand offers customized product creation with lower inventory risk, while Dropshipping allows selling a wide range of products without managing stock upfront. Choosing the right approach impacts profitability, marketing strategies, and customer satisfaction. Effective decision-making in this area drives sustainable growth and competitive advantage in e-commerce.
Comparison Table
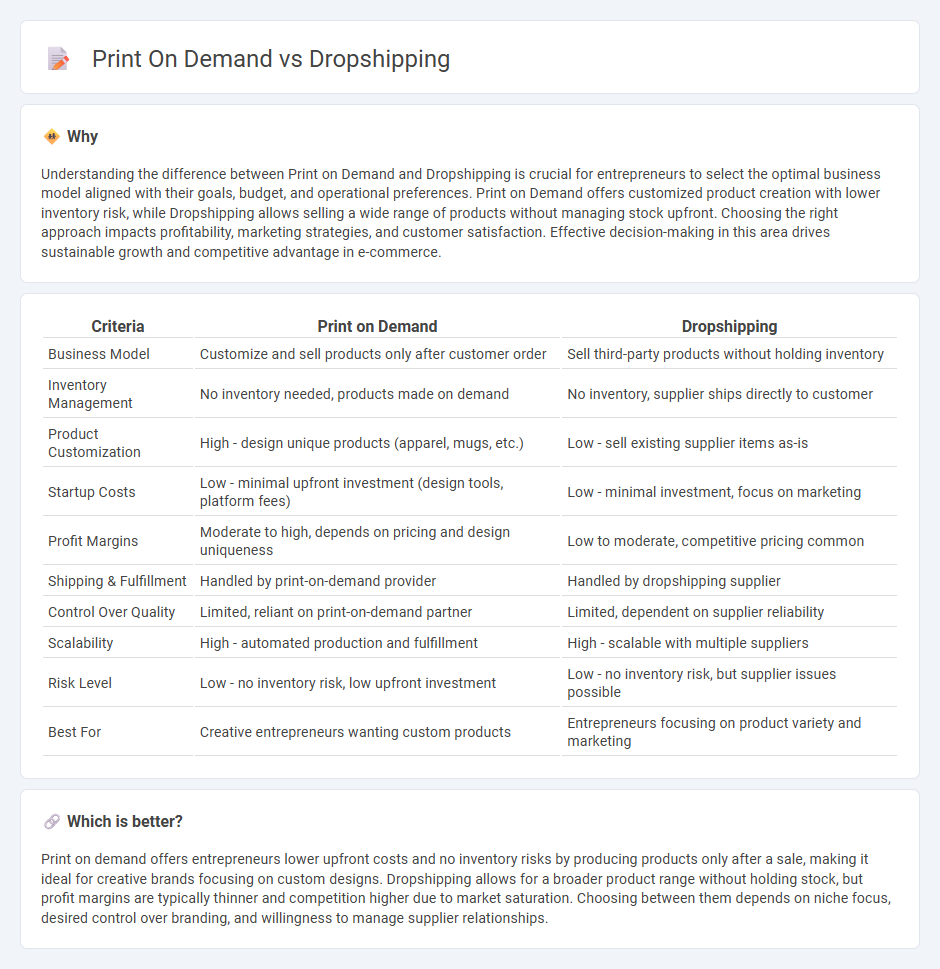
| Criteria | Print on Demand | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Customize and sell products only after customer order | Sell third-party products without holding inventory |
| Inventory Management | No inventory needed, products made on demand | No inventory, supplier ships directly to customer |
| Product Customization | High - design unique products (apparel, mugs, etc.) | Low - sell existing supplier items as-is |
| Startup Costs | Low - minimal upfront investment (design tools, platform fees) | Low - minimal investment, focus on marketing |
| Profit Margins | Moderate to high, depends on pricing and design uniqueness | Low to moderate, competitive pricing common |
| Shipping & Fulfillment | Handled by print-on-demand provider | Handled by dropshipping supplier |
| Control Over Quality | Limited, reliant on print-on-demand partner | Limited, dependent on supplier reliability |
| Scalability | High - automated production and fulfillment | High - scalable with multiple suppliers |
| Risk Level | Low - no inventory risk, low upfront investment | Low - no inventory risk, but supplier issues possible |
| Best For | Creative entrepreneurs wanting custom products | Entrepreneurs focusing on product variety and marketing |
Which is better?
Print on demand offers entrepreneurs lower upfront costs and no inventory risks by producing products only after a sale, making it ideal for creative brands focusing on custom designs. Dropshipping allows for a broader product range without holding stock, but profit margins are typically thinner and competition higher due to market saturation. Choosing between them depends on niche focus, desired control over branding, and willingness to manage supplier relationships.
Connection
Print on demand and dropshipping are interconnected business models that enable entrepreneurs to sell customized products without maintaining inventory or handling shipping logistics. Both rely on third-party suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers, reducing upfront costs and minimizing risks. This synergy allows startups to quickly scale their online stores by leveraging automated fulfillment and wide product variety.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates inventory holding by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing storage costs and stock risks. Print on demand requires no inventory since items are produced only after an order is placed, ensuring zero stock surplus and minimizing waste. Explore the differences further to determine which inventory management strategy best suits your business goals.
Product Customization
Print on demand offers extensive product customization, enabling businesses to create unique, personalized items by printing custom designs directly onto various products. Dropshipping typically involves selling pre-made products from suppliers with little to no customization options, limiting brand differentiation. Explore the advantages of each model to discover which best fits your business goals for product customization.
Order Fulfillment
Dropshipping involves selling products without holding inventory, where suppliers handle order fulfillment by directly shipping items to customers, enabling quicker turnaround but with less control over packaging and delivery. Print on demand customizes products such as apparel or accessories after an order is placed, and the print provider manages the fulfillment process including printing, packaging, and shipping, ensuring unique branding opportunities. Explore more about how each model impacts logistics, customer experience, and scalability.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment model where the seller does not hold inventory but purchases products from a third-party supplier who ships directly to customers; the seller is responsible for marketing and pricing while the supplier handles production and shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers who manage inventory and shipping, while the retailer runs an online store, sets prices, and forwards customer orders to suppliers who then ship products directly to buyers.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a supply chain model where the seller accepts orders without stock, forwarding shipment details to a wholesaler or manufacturer that ships directly to customers, minimizing overhead but with less control over quality and shipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com