No code startups leverage platforms that enable building software applications without traditional programming, allowing entrepreneurs to rapidly launch products with minimal technical skills and lower costs. Creator economy startups focus on empowering content creators to monetize and scale their audience through innovative tools and platforms that enhance engagement and revenue streams. Explore how these two dynamic models transform entrepreneurship and offer unique opportunities for business growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between no code startups and creator economy startups is crucial for tailoring business strategies, investment approaches, and product development. No code startups leverage platforms that enable app and software development without traditional programming, accelerating time-to-market and reducing technical barriers. Creator economy startups focus on monetizing individual creators' content and community, emphasizing personal branding and audience engagement. Recognizing these distinctions optimizes resource allocation and market positioning for entrepreneurs.
Comparison Table
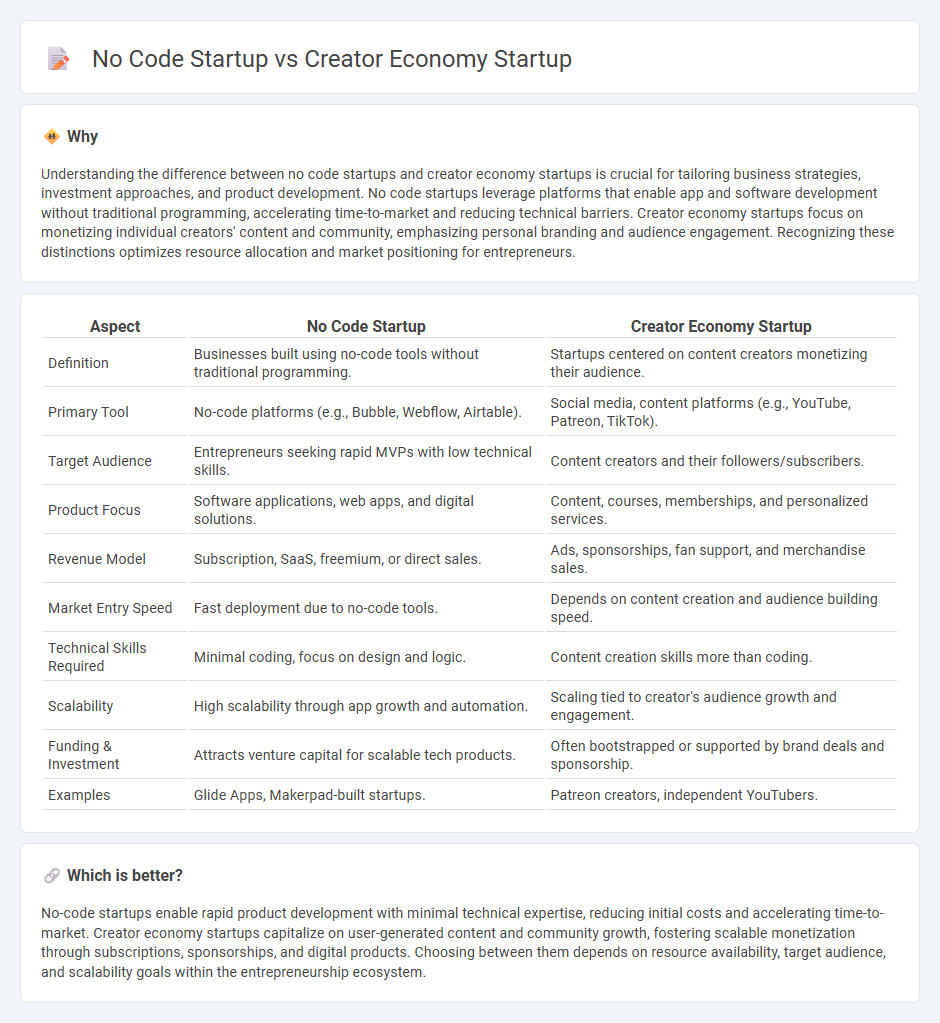
| Aspect | No Code Startup | Creator Economy Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Businesses built using no-code tools without traditional programming. | Startups centered on content creators monetizing their audience. |
| Primary Tool | No-code platforms (e.g., Bubble, Webflow, Airtable). | Social media, content platforms (e.g., YouTube, Patreon, TikTok). |
| Target Audience | Entrepreneurs seeking rapid MVPs with low technical skills. | Content creators and their followers/subscribers. |
| Product Focus | Software applications, web apps, and digital solutions. | Content, courses, memberships, and personalized services. |
| Revenue Model | Subscription, SaaS, freemium, or direct sales. | Ads, sponsorships, fan support, and merchandise sales. |
| Market Entry Speed | Fast deployment due to no-code tools. | Depends on content creation and audience building speed. |
| Technical Skills Required | Minimal coding, focus on design and logic. | Content creation skills more than coding. |
| Scalability | High scalability through app growth and automation. | Scaling tied to creator's audience growth and engagement. |
| Funding & Investment | Attracts venture capital for scalable tech products. | Often bootstrapped or supported by brand deals and sponsorship. |
| Examples | Glide Apps, Makerpad-built startups. | Patreon creators, independent YouTubers. |
Which is better?
No-code startups enable rapid product development with minimal technical expertise, reducing initial costs and accelerating time-to-market. Creator economy startups capitalize on user-generated content and community growth, fostering scalable monetization through subscriptions, sponsorships, and digital products. Choosing between them depends on resource availability, target audience, and scalability goals within the entrepreneurship ecosystem.
Connection
No-code startups empower creators in the creator economy by providing accessible tools that eliminate the need for traditional coding skills, accelerating product development and market entry. This synergy reduces barriers to entrepreneurship, enabling creators to monetize their skills and content effectively. Consequently, the no-code movement fuels innovation and scalability within the creator economy, driving economic growth and democratizing startup opportunities.
Key Terms
Monetization
Creator economy startups monetize primarily through direct creator support mechanisms such as subscriptions, tips, and merchandise sales, leveraging personalized content to build loyal audiences. No-code startups generate revenue by offering user-friendly platforms and tools that reduce development costs and time, often using freemium models, subscription plans, or enterprise licensing. Explore further to understand how each model optimizes monetization strategies for scalable growth.
Platform Dependency
Creator economy startups heavily rely on platform dependency, often building businesses on social media networks and content sharing platforms to reach audiences and monetize creativity. No code startups emphasize platform independence, providing tools that enable users to build applications without coding, reducing reliance on traditional development ecosystems. Explore in-depth insights on how platform dependency shapes growth strategies in both startup types.
Technical Barriers
Creator economy startups face technical barriers such as building scalable platforms that support diverse content formats, integrating payment systems, and ensuring seamless user experiences for creators and followers. No code startups confront challenges in developing intuitive interfaces that enable users with minimal programming skills to create robust applications while maintaining flexibility and security. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how each startup type addresses their unique technical hurdles and innovation strategies.
Source and External Links
Top Creator Economy Startups and the VCs That Fund Them in 2025 - This article highlights leading creator economy startups like Caffeine, Spotter, and Jellysmack that empower creators to monetize content innovatively, and discusses how VCs are investing heavily in this booming sector in 2025.
10 Innovative Creator Economy Startups To Watch In 2025 - Wonnda - Provides an overview of the creator economy ecosystem, explaining how startups like Passionfroot and Stir support content creators with tools for content planning and monetization, emphasizing the mutual value exchange between creators, audiences, platforms, and advertisers.
16 Content Creation Startups and Companies | Built In - Lists key startups such as Patreon, Linktree, Kajabi, and Caffeine that provide software platforms and tools designed to help creators produce content, manage their workflows, grow their audiences, and monetize their personal brands effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com