Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, automated governance without centralized control, fostering global participation and real-time decision-making. Cooperatives operate on democratic principles where members share ownership and profits, emphasizing local community engagement and mutual support. Explore the distinct advantages and challenges of DAOs versus cooperatives to understand their transformative impact on modern entrepreneurship.
Why it is important
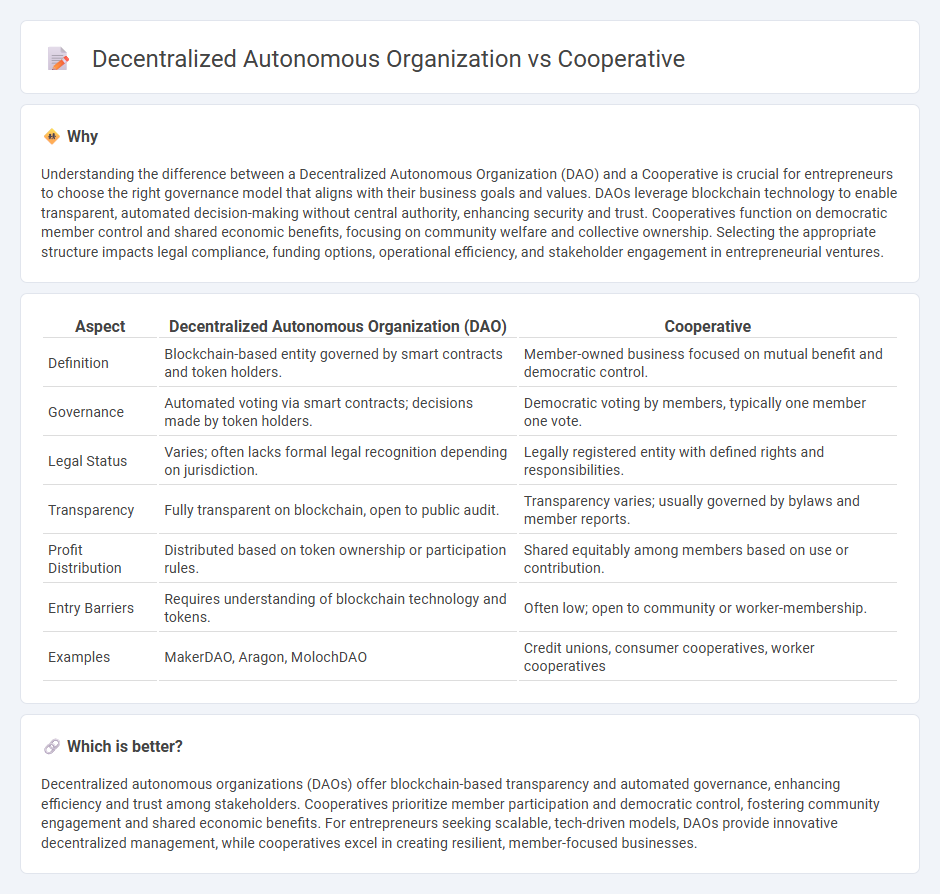
Understanding the difference between a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and a Cooperative is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right governance model that aligns with their business goals and values. DAOs leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, automated decision-making without central authority, enhancing security and trust. Cooperatives function on democratic member control and shared economic benefits, focusing on community welfare and collective ownership. Selecting the appropriate structure impacts legal compliance, funding options, operational efficiency, and stakeholder engagement in entrepreneurial ventures.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) | Cooperative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blockchain-based entity governed by smart contracts and token holders. | Member-owned business focused on mutual benefit and democratic control. |
| Governance | Automated voting via smart contracts; decisions made by token holders. | Democratic voting by members, typically one member one vote. |
| Legal Status | Varies; often lacks formal legal recognition depending on jurisdiction. | Legally registered entity with defined rights and responsibilities. |
| Transparency | Fully transparent on blockchain, open to public audit. | Transparency varies; usually governed by bylaws and member reports. |
| Profit Distribution | Distributed based on token ownership or participation rules. | Shared equitably among members based on use or contribution. |
| Entry Barriers | Requires understanding of blockchain technology and tokens. | Often low; open to community or worker-membership. |
| Examples | MakerDAO, Aragon, MolochDAO | Credit unions, consumer cooperatives, worker cooperatives |
Which is better?
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) offer blockchain-based transparency and automated governance, enhancing efficiency and trust among stakeholders. Cooperatives prioritize member participation and democratic control, fostering community engagement and shared economic benefits. For entrepreneurs seeking scalable, tech-driven models, DAOs provide innovative decentralized management, while cooperatives excel in creating resilient, member-focused businesses.
Connection
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and cooperatives share a foundational principle of democratic governance, empowering members with voting rights and collective decision-making. Both structures prioritize transparency, member participation, and equitable distribution of profits, aligning with core entrepreneurial values of collaboration and shared ownership. DAOs utilize blockchain technology to enhance trust and automation in governance, while cooperatives rely on established legal frameworks to foster community-focused enterprise.
Key Terms
Governance structure
Cooperatives operate through member-driven governance with democratic voting rights ensuring equal control among participants, often formalized in bylaws and annual general meetings. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) utilize blockchain technology to enforce governance via smart contracts, enabling transparent, automated decision-making without centralized intermediaries. Explore the comparative strengths and challenges of these governance models to understand their impact on organizational efficiency and member engagement.
Member ownership
Member ownership in cooperatives is characterized by democratic control, where each member typically has one vote regardless of their capital contribution, ensuring equal influence. In decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), ownership is often token-based, with voting power proportional to the number of tokens held, reflecting a more investment-driven structure. Explore the distinct governance models and member rights that define ownership in both entities.
Decision-making mechanism
Cooperative organizations rely on democratic decision-making processes where members vote to influence policies and operational strategies, ensuring equal participation and shared control. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) operate through blockchain-based smart contracts that automate decisions, minimizing human intervention and enhancing transparency. Explore the distinct decision-making frameworks to understand which structure aligns better with your organizational goals.
Source and External Links
What is a Cooperative? - A cooperative is an organization owned and controlled by its members to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs through a democratically controlled business that often returns profits to members and focuses on shared benefits rather than investments.
Cooperative - Wikipedia - A cooperative is a legal entity owned and democratically controlled by its members, distributing economic benefits proportionally based on participation rather than capital investment, and can take many forms such as worker, consumer, producer, purchasing, or housing cooperatives.
National Cooperative Business Association: NCBA CLUSA - NCBA CLUSA is a long-established organization that advances and advocates for the cooperative business model to empower people with access to economic opportunities and promote shared prosperity globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com