Solopreneurship involves a single individual managing all aspects of a business, allowing for full control and flexibility but often requiring multitasking across various roles. Small business ownership typically includes a team or employees working under the owner, enabling scalability and division of responsibilities but with more complex management. Explore the differences in structure, risks, and growth opportunities to determine the best path for your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
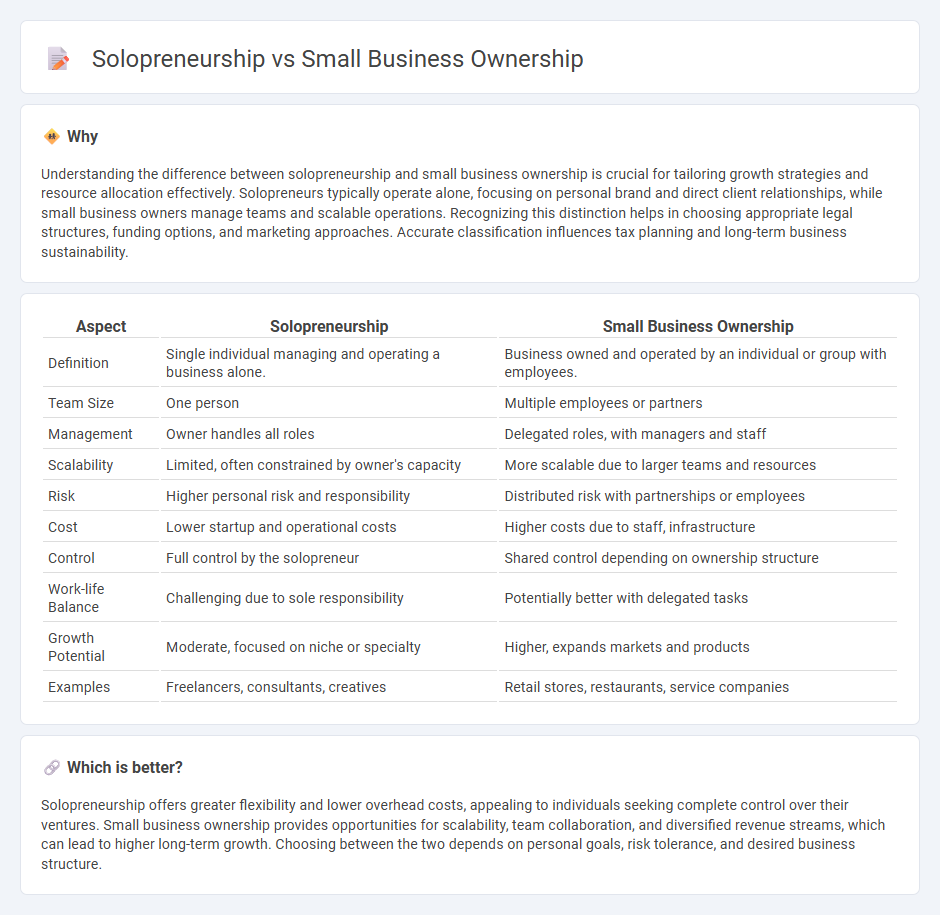
Understanding the difference between solopreneurship and small business ownership is crucial for tailoring growth strategies and resource allocation effectively. Solopreneurs typically operate alone, focusing on personal brand and direct client relationships, while small business owners manage teams and scalable operations. Recognizing this distinction helps in choosing appropriate legal structures, funding options, and marketing approaches. Accurate classification influences tax planning and long-term business sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Solopreneurship | Small Business Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single individual managing and operating a business alone. | Business owned and operated by an individual or group with employees. |
| Team Size | One person | Multiple employees or partners |
| Management | Owner handles all roles | Delegated roles, with managers and staff |
| Scalability | Limited, often constrained by owner's capacity | More scalable due to larger teams and resources |
| Risk | Higher personal risk and responsibility | Distributed risk with partnerships or employees |
| Cost | Lower startup and operational costs | Higher costs due to staff, infrastructure |
| Control | Full control by the solopreneur | Shared control depending on ownership structure |
| Work-life Balance | Challenging due to sole responsibility | Potentially better with delegated tasks |
| Growth Potential | Moderate, focused on niche or specialty | Higher, expands markets and products |
| Examples | Freelancers, consultants, creatives | Retail stores, restaurants, service companies |
Which is better?
Solopreneurship offers greater flexibility and lower overhead costs, appealing to individuals seeking complete control over their ventures. Small business ownership provides opportunities for scalability, team collaboration, and diversified revenue streams, which can lead to higher long-term growth. Choosing between the two depends on personal goals, risk tolerance, and desired business structure.
Connection
Solopreneurship and small business ownership both emphasize individual initiative and direct control over business operations, often requiring a broad skill set in marketing, finance, and product development. Solopreneurs typically manage all aspects of their ventures independently, while small business owners may employ teams but maintain hands-on involvement. This close connection highlights the entrepreneurial spirit's role in driving growth, innovation, and economic contribution at both individual and community levels.
Key Terms
Liability Structure
Small business ownership often involves forming entities like LLCs or corporations, providing personal liability protection by separating personal assets from business debts and legal claims. Solopreneurs typically operate as sole proprietors, bearing unlimited personal liability since business liabilities are not legally distinct from personal assets. Understanding the liability implications of each structure is crucial for informed decision-making and protecting personal financial security; explore more about liability options and benefits for your business model.
Scalability
Small business ownership typically involves building a team and systems to scale operations beyond the capacity of a single person, allowing for increased revenue and market reach. Solopreneurship centers on individual expertise and productivity, often limiting scalability due to reliance on one person for all business functions. Explore strategies to transition from solopreneurship to scalable business models for sustainable growth.
Delegation
Small business ownership often involves managing a team to delegate tasks effectively, which boosts overall productivity and scalability. Solopreneurs tend to handle most responsibilities independently, limiting delegation opportunities but maintaining full control over operations. Explore strategies to optimize delegation for both business models and enhance your venture's growth potential.
Source and External Links
The 8 Small Business Owner Structures - PeopleKeep - Small business ownership can take various legal forms, including sole proprietorship, partnership, C corporation, S corporation, B corporation, close corporation, limited liability company (LLC), and nonprofit corporation, with sole proprietorship being the simplest and most common for small, individually-owned businesses.
Small business - Wikipedia - Small businesses are generally defined by having few employees and limited revenue, and their funding may come from personal savings, loans, grants, angel investors, partnerships, or banks, with some using equity crowdfunding or credit cards as sources of capital.
How to start and fund your own business | USAGov - Starting a small business involves planning, funding through personal savings, loans, or investors, and accessing support such as counseling and training from the Small Business Administration, which also offers resources specifically for minority and rural business owners.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com