Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce productivity, assigning tasks and monitoring performance in real-time, often prioritizing efficiency over employee autonomy. In contrast, servant leadership focuses on empowering employees by fostering trust, collaboration, and personal growth, emphasizing the well-being and development of the workforce. Explore how these distinct management styles impact employee satisfaction and organizational success.
Why it is important
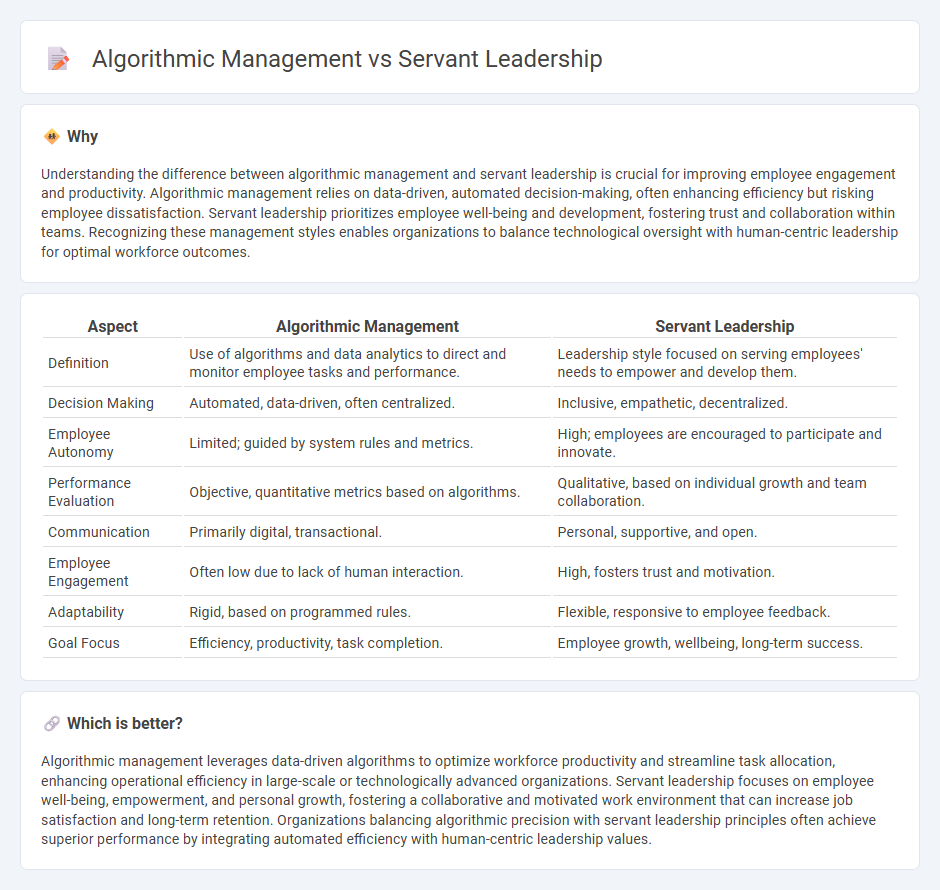
Understanding the difference between algorithmic management and servant leadership is crucial for improving employee engagement and productivity. Algorithmic management relies on data-driven, automated decision-making, often enhancing efficiency but risking employee dissatisfaction. Servant leadership prioritizes employee well-being and development, fostering trust and collaboration within teams. Recognizing these management styles enables organizations to balance technological oversight with human-centric leadership for optimal workforce outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Management | Servant Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of algorithms and data analytics to direct and monitor employee tasks and performance. | Leadership style focused on serving employees' needs to empower and develop them. |
| Decision Making | Automated, data-driven, often centralized. | Inclusive, empathetic, decentralized. |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited; guided by system rules and metrics. | High; employees are encouraged to participate and innovate. |
| Performance Evaluation | Objective, quantitative metrics based on algorithms. | Qualitative, based on individual growth and team collaboration. |
| Communication | Primarily digital, transactional. | Personal, supportive, and open. |
| Employee Engagement | Often low due to lack of human interaction. | High, fosters trust and motivation. |
| Adaptability | Rigid, based on programmed rules. | Flexible, responsive to employee feedback. |
| Goal Focus | Efficiency, productivity, task completion. | Employee growth, wellbeing, long-term success. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce productivity and streamline task allocation, enhancing operational efficiency in large-scale or technologically advanced organizations. Servant leadership focuses on employee well-being, empowerment, and personal growth, fostering a collaborative and motivated work environment that can increase job satisfaction and long-term retention. Organizations balancing algorithmic precision with servant leadership principles often achieve superior performance by integrating automated efficiency with human-centric leadership values.
Connection
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven systems to optimize employee productivity and task allocation, while servant leadership focuses on empowering and supporting employees' growth and well-being. The connection lies in integrating algorithmic insights with servant leadership principles to create a balanced work environment that enhances efficiency without compromising employee engagement and morale. This synergy fosters improved job satisfaction and organizational performance by aligning technology with human-centered leadership.
Key Terms
Empowerment
Servant leadership emphasizes empowering employees through trust, support, and shared purpose, fostering intrinsic motivation and personal growth in the workplace. Algorithmic management, by contrast, relies on data-driven decision-making and automated task allocation, often prioritizing efficiency over individual empowerment. Explore how these contrasting approaches impact employee autonomy and organizational culture in greater depth.
Automation
Servant leadership emphasizes empowering employees and fostering collaboration, while algorithmic management relies heavily on automation and data-driven decision-making to optimize workflows. Automation in algorithmic management enhances efficiency through real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, contrasting with the human-centered approach of servant leadership. Discover how these distinct management styles impact organizational culture and operational success.
Decision-making
Servant leadership emphasizes decision-making that prioritizes employee well-being and ethical considerations, fostering trust and collaboration within teams. Algorithmic management relies on data-driven insights and automated processes to optimize efficiency and consistency in decisions, often prioritizing performance metrics over personal factors. Explore how these contrasting approaches impact organizational culture and productivity.
Source and External Links
Beyond Ego: How Servant Leadership Transforms Teams and ... - Servant leadership is a style that prioritizes the growth, wellbeing, and success of the team, emphasizing empathy, listening, stewardship, and setting ego aside to serve others effectively.
Servant leadership - Wikipedia - Servant leadership is a philosophy where leaders share power, put employees' needs first, and help people develop and perform their best, focusing on the growth and wellbeing of those served rather than organizational hierarchy.
What is Servant Leadership? - Robert K. Greenleaf - Coined by Robert K. Greenleaf in 1970, servant leadership focuses on serving others first, prioritizing their highest needs, and fostering their personal growth to create healthier, wiser, and more autonomous individuals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com