Digital nomad visas offer remote workers legal permission to stay and work in a foreign country for extended periods, typically ranging from six months to two years, enhancing flexibility and cultural immersion. Telecommuting arrangements enable employees to work remotely while maintaining their employment with a home-based company, often without relocation or visa changes. Explore the key differences and benefits of digital nomad visas versus telecommuting setups to optimize your global work lifestyle.
Why it is important
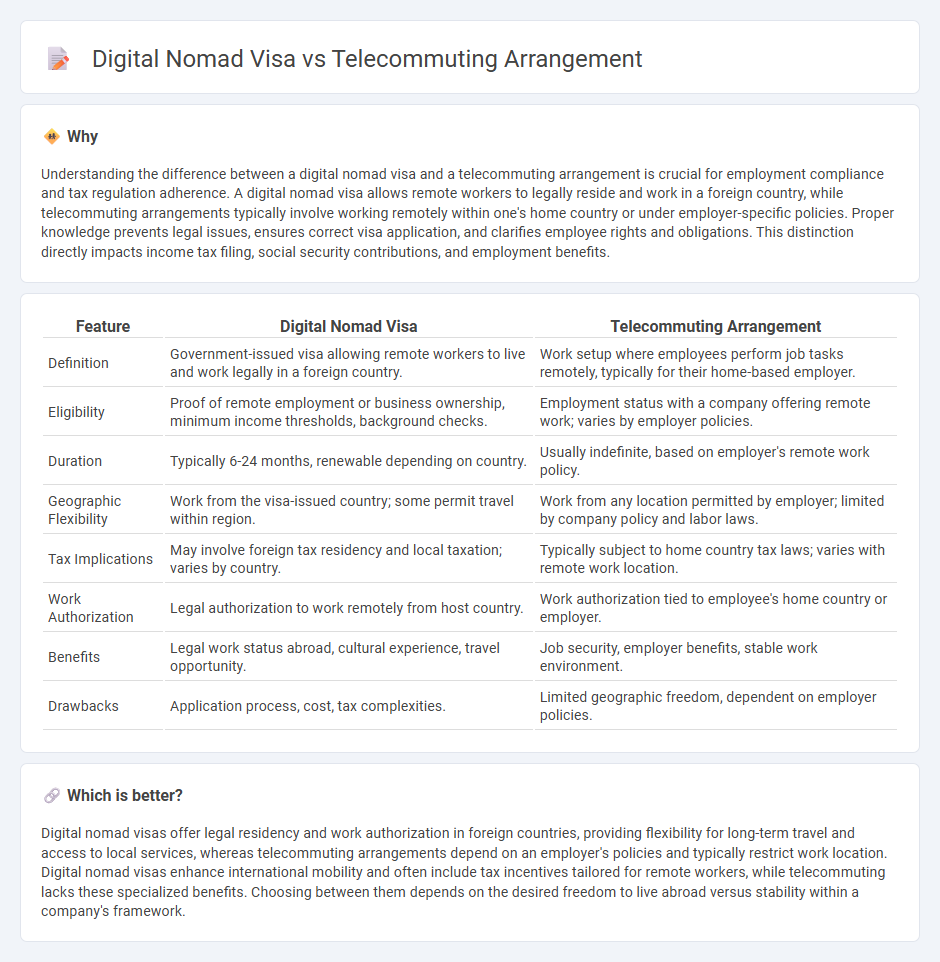
Understanding the difference between a digital nomad visa and a telecommuting arrangement is crucial for employment compliance and tax regulation adherence. A digital nomad visa allows remote workers to legally reside and work in a foreign country, while telecommuting arrangements typically involve working remotely within one's home country or under employer-specific policies. Proper knowledge prevents legal issues, ensures correct visa application, and clarifies employee rights and obligations. This distinction directly impacts income tax filing, social security contributions, and employment benefits.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Nomad Visa | Telecommuting Arrangement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-issued visa allowing remote workers to live and work legally in a foreign country. | Work setup where employees perform job tasks remotely, typically for their home-based employer. |
| Eligibility | Proof of remote employment or business ownership, minimum income thresholds, background checks. | Employment status with a company offering remote work; varies by employer policies. |
| Duration | Typically 6-24 months, renewable depending on country. | Usually indefinite, based on employer's remote work policy. |
| Geographic Flexibility | Work from the visa-issued country; some permit travel within region. | Work from any location permitted by employer; limited by company policy and labor laws. |
| Tax Implications | May involve foreign tax residency and local taxation; varies by country. | Typically subject to home country tax laws; varies with remote work location. |
| Work Authorization | Legal authorization to work remotely from host country. | Work authorization tied to employee's home country or employer. |
| Benefits | Legal work status abroad, cultural experience, travel opportunity. | Job security, employer benefits, stable work environment. |
| Drawbacks | Application process, cost, tax complexities. | Limited geographic freedom, dependent on employer policies. |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer legal residency and work authorization in foreign countries, providing flexibility for long-term travel and access to local services, whereas telecommuting arrangements depend on an employer's policies and typically restrict work location. Digital nomad visas enhance international mobility and often include tax incentives tailored for remote workers, while telecommuting lacks these specialized benefits. Choosing between them depends on the desired freedom to live abroad versus stability within a company's framework.
Connection
Digital nomad visas enable remote workers to live and work legally in foreign countries, promoting global telecommuting arrangements. These visas support flexible employment models by allowing professionals to maintain their jobs while exploring international locations. Telecommuting arrangements benefit from digital nomad visas by providing legal frameworks that facilitate remote work across borders.
Key Terms
Remote Work Policy
Telecommuting arrangements typically involve employees working remotely while remaining legally tied to their employer's country, adhering to company-specific remote work policies focused on productivity, security, and compliance. Digital nomad visas grant legal stay for remote workers from different countries, requiring adherence to host country regulations and often formalizing remote work with clarity on taxation and employment rights. Explore further to understand how businesses and remote professionals can optimize work policies under each model.
Location Independence
Telecommuting arrangements allow employees to work remotely while maintaining employment with their home country employer, offering flexibility without changing legal residency. Digital nomad visas grant temporary residency in a foreign country specifically designed for remote workers seeking location independence and cultural immersion. Explore the key differences and benefits of both options to determine your ideal work-from-anywhere lifestyle.
Legal Residency Permits
Telecommuting arrangements often do not grant legal residency permits, as they typically rely on the employee's home country work visa while allowing remote work internationally. Digital nomad visas specifically provide legal residency permits, enabling remote workers to live legally in a foreign country for extended periods without traditional work permits. Explore the differences between telecommuting policies and digital nomad visa requirements to understand which option best suits your legal residency needs.
Source and External Links
Sample Telecommuting Policy - Beazley - Telecommuting is an arrangement where employees work from home or another remote location instead of their usual workplace, initiated either by employee request or organizational decision, with approval based on factors like job duties, performance, and cybersecurity, and requiring employees to establish an appropriate remote workspace.
Telecommuting Policy Statement | People & Culture - UC Berkeley - Telecommuting involves performing work off-campus like at home, initiated by either employee or department, formalized through a written agreement after proposal and approval, ensuring clear guidelines and documented arrangements.
Telecommuting - Tripartite Alliance Limited - Telecommuting is a flexi-place work arrangement where tasks are done outside the usual workplace using ICT tools, requiring suitability assessments like cost-benefit analysis and clear telecommuting agreements to ensure successful implementation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com