Quiet hiring focuses on leveraging internal talent by reallocating existing employees to new roles or projects without external recruitment, enhancing workforce agility and reducing hiring costs. Talent poaching involves actively recruiting skilled individuals from competitors to quickly fill critical roles and gain a competitive advantage in key industries. Explore these strategies to understand their impact on business growth and workforce management.
Why it is important
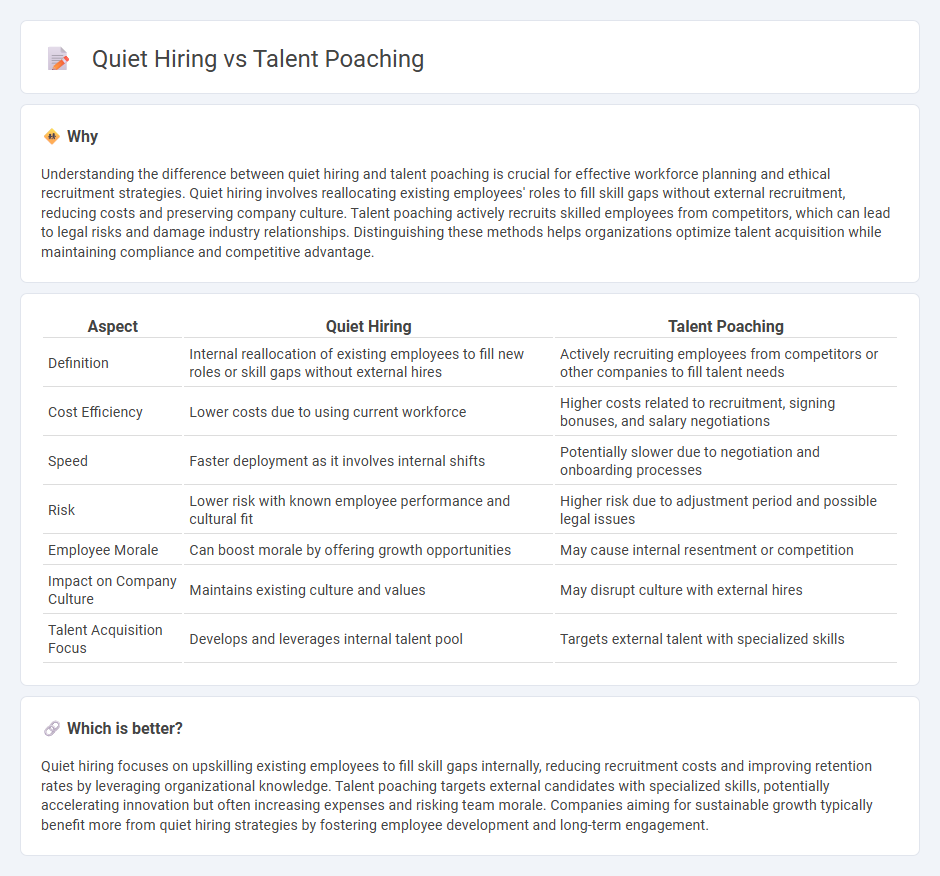
Understanding the difference between quiet hiring and talent poaching is crucial for effective workforce planning and ethical recruitment strategies. Quiet hiring involves reallocating existing employees' roles to fill skill gaps without external recruitment, reducing costs and preserving company culture. Talent poaching actively recruits skilled employees from competitors, which can lead to legal risks and damage industry relationships. Distinguishing these methods helps organizations optimize talent acquisition while maintaining compliance and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Hiring | Talent Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal reallocation of existing employees to fill new roles or skill gaps without external hires | Actively recruiting employees from competitors or other companies to fill talent needs |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs due to using current workforce | Higher costs related to recruitment, signing bonuses, and salary negotiations |
| Speed | Faster deployment as it involves internal shifts | Potentially slower due to negotiation and onboarding processes |
| Risk | Lower risk with known employee performance and cultural fit | Higher risk due to adjustment period and possible legal issues |
| Employee Morale | Can boost morale by offering growth opportunities | May cause internal resentment or competition |
| Impact on Company Culture | Maintains existing culture and values | May disrupt culture with external hires |
| Talent Acquisition Focus | Develops and leverages internal talent pool | Targets external talent with specialized skills |
Which is better?
Quiet hiring focuses on upskilling existing employees to fill skill gaps internally, reducing recruitment costs and improving retention rates by leveraging organizational knowledge. Talent poaching targets external candidates with specialized skills, potentially accelerating innovation but often increasing expenses and risking team morale. Companies aiming for sustainable growth typically benefit more from quiet hiring strategies by fostering employee development and long-term engagement.
Connection
Quiet hiring leverages internal talent redeployment to fill skill gaps without external recruitment, while talent poaching targets acquiring specialized employees from competitors. Both strategies focus on maximizing workforce capabilities to meet evolving organizational demands efficiently. Companies balance these approaches to optimize talent acquisition costs and maintain competitive advantage in dynamic job markets.
Key Terms
Recruitment
Talent poaching involves actively recruiting skilled employees from competitors to quickly fill critical roles, whereas quiet hiring focuses on leveraging internal talent and upskilling existing employees without external recruitment. Recruitment strategies emphasizing talent poaching often incur higher costs and can impact employer branding, while quiet hiring optimizes workforce agility and retention. Discover effective recruitment methods to balance talent acquisition and internal growth.
Employee Retention
Talent poaching undermines employee retention by actively recruiting skilled workers from competitors, leading to increased turnover and operational disruption, while quiet hiring enhances retention by internally developing talent or reallocating existing employees without formal recruitment processes, fostering engagement and loyalty. Companies prioritizing quiet hiring strategies improve workforce stability and reduce costs associated with onboarding and training new hires. Explore effective talent management techniques to strengthen your employee retention efforts.
Workforce Allocation
Talent poaching involves aggressively recruiting skilled employees from competitors to quickly fill critical roles, often disrupting existing team dynamics and increasing turnover risk. Quiet hiring emphasizes reallocating and upskilling current employees without external recruitment, optimizing workforce allocation by enhancing productivity and reducing hiring costs. Explore how strategic workforce allocation through these methods impacts organizational growth and employee engagement.
Source and External Links
What Is Employee Poaching? (Definition and Strategies To Prevent It) - Employee poaching is the legal practice where an employer tries to recruit an employee from a competing company by offering higher pay, better benefits, or career opportunities, typically targeting highly skilled and experienced workers in high-demand industries.
Headhunting vs Talent Poaching | A-Z of HR Terms - Talent poaching involves actively enticing skilled employees from other organizations with incentives, differing from headhunting which is more about recruiting for specific roles, and while headhunting is largely ethical, poaching can raise legal and ethical issues if aggressive or deceptive tactics are used.
Employee poaching - Employee poaching is offering employment to workers currently employed elsewhere in similar fields; it is legally protected but can involve conflicts related to trade secrets or non-compete agreements, which some employers try to use to prevent poaching.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com