Quiet hiring enables organizations to fill skill gaps by reallocating existing employees without formal recruitment, reducing costs and retaining talent. Burnout occurs when employees face prolonged stress and workload imbalance, leading to decreased productivity and wellbeing. Explore how balancing quiet hiring strategies can prevent burnout and enhance workforce effectiveness.
Why it is important
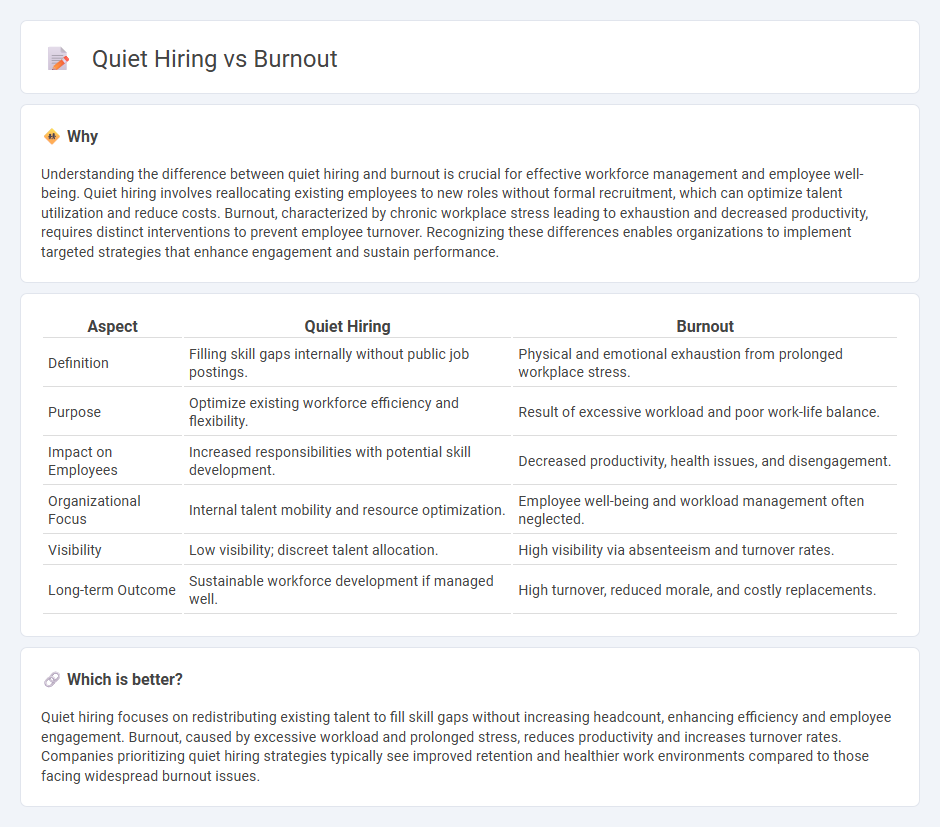
Understanding the difference between quiet hiring and burnout is crucial for effective workforce management and employee well-being. Quiet hiring involves reallocating existing employees to new roles without formal recruitment, which can optimize talent utilization and reduce costs. Burnout, characterized by chronic workplace stress leading to exhaustion and decreased productivity, requires distinct interventions to prevent employee turnover. Recognizing these differences enables organizations to implement targeted strategies that enhance engagement and sustain performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Hiring | Burnout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Filling skill gaps internally without public job postings. | Physical and emotional exhaustion from prolonged workplace stress. |
| Purpose | Optimize existing workforce efficiency and flexibility. | Result of excessive workload and poor work-life balance. |
| Impact on Employees | Increased responsibilities with potential skill development. | Decreased productivity, health issues, and disengagement. |
| Organizational Focus | Internal talent mobility and resource optimization. | Employee well-being and workload management often neglected. |
| Visibility | Low visibility; discreet talent allocation. | High visibility via absenteeism and turnover rates. |
| Long-term Outcome | Sustainable workforce development if managed well. | High turnover, reduced morale, and costly replacements. |
Which is better?
Quiet hiring focuses on redistributing existing talent to fill skill gaps without increasing headcount, enhancing efficiency and employee engagement. Burnout, caused by excessive workload and prolonged stress, reduces productivity and increases turnover rates. Companies prioritizing quiet hiring strategies typically see improved retention and healthier work environments compared to those facing widespread burnout issues.
Connection
Quiet hiring addresses workforce gaps by reallocating existing talent without public job vacancies, often increasing employee workloads and responsibilities. This intensified demand without additional support or recognition significantly contributes to burnout, as employees face prolonged stress and diminished work-life balance. Organizations that fail to manage quiet hiring effectively risk higher turnover rates and decreased overall productivity due to employee exhaustion.
Key Terms
Workload
Burnout results from prolonged excessive workload and insufficient recovery, leading to decreased productivity and employee well-being. Quiet hiring addresses workload challenges by reallocating tasks internally without formal job postings, optimizing resource use and reducing strain on existing staff. Explore in-depth strategies to balance workload and prevent burnout through effective quiet hiring practices.
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement deteriorates significantly under burnout, characterized by chronic stress and emotional exhaustion, which reduces productivity and increases turnover rates. Quiet hiring, involving strategic internal talent reallocation without external recruitment, can mitigate burnout by optimizing workload distribution and enhancing employee satisfaction. Explore effective strategies to balance quiet hiring and prevent burnout to sustain high employee engagement levels.
Talent Acquisition
Burnout in Talent Acquisition results from prolonged stress and overwhelming workloads, leading to decreased productivity and employee disengagement. Quiet hiring, a strategic approach allowing organizations to fill skill gaps by reallocating internal talent or using flexible workforce solutions, helps mitigate burnout by reducing external recruitment pressures. Explore effective techniques to balance talent demands and maintain a healthy, dynamic workforce.
Source and External Links
Burnout: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Prevention, Treatment - WebMD - Burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged overwhelming stress, often related to work or caregiving, resulting in feelings of depletion, cynicism, and reduced motivation that can impact health and productivity.
Burnout: Symptoms, Treatment, and Coping Strategy Tips - HelpGuide - Burnout develops progressively through stages starting with initial enthusiasm, moving into chronic stress, and eventually full burnout characterized by exhaustion, cynicism, health issues, and social withdrawal.
Occupational burnout - Wikipedia - Occupational burnout is classified by the WHO as a work-related phenomenon resulting from chronic unmanaged stress, marked by exhaustion, mental distancing from the job, negativity, and diminished professional efficacy, but is not considered a medical condition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com