Ghost work involves performing tasks without public recognition or direct attribution, often facilitated through digital platforms that distribute microtasks to a distributed workforce. Freelancing entails offering specialized skills or services independently, with workers managing client relationships and branding themselves. Discover the key distinctions and implications between ghost work and freelancing to better understand the evolving employment landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost work and freelancing is crucial for accurately assessing employment rights, compensation structures, and job security. Ghost work involves tasks completed anonymously and typically lacks transparency or recognition, while freelancing is characterized by independent contract work with direct client relationships. Knowing these distinctions helps workers make informed decisions about their career paths and legal protections. Employers also benefit by correctly classifying workers to comply with labor laws and taxation.
Comparison Table
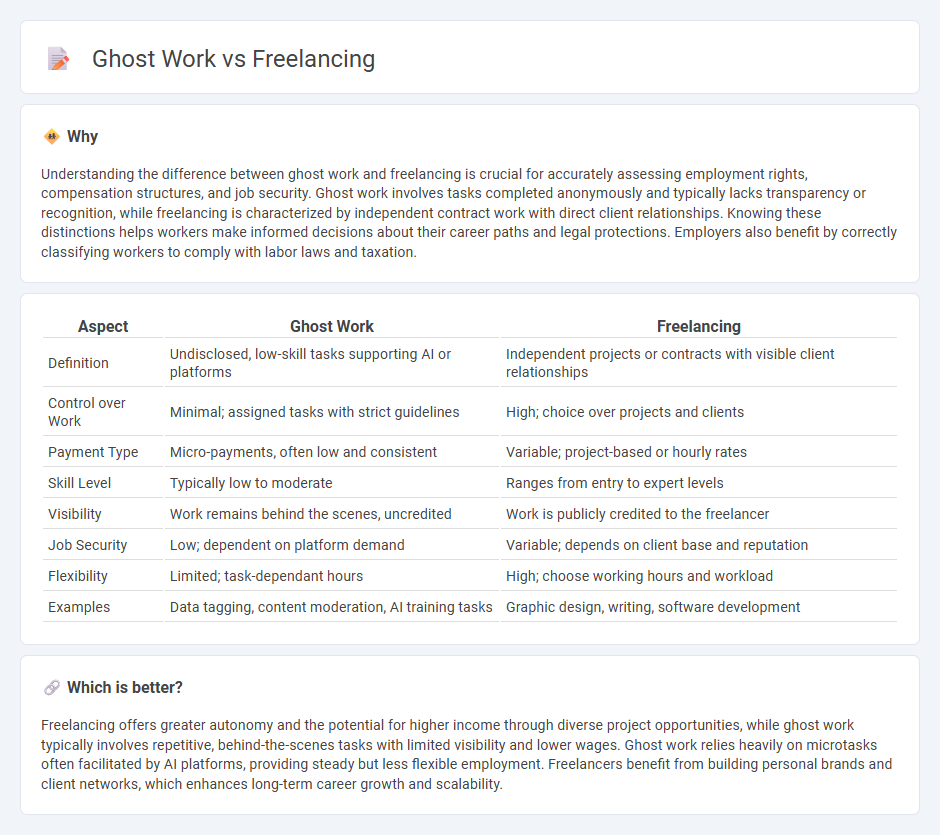
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Freelancing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Undisclosed, low-skill tasks supporting AI or platforms | Independent projects or contracts with visible client relationships |
| Control over Work | Minimal; assigned tasks with strict guidelines | High; choice over projects and clients |
| Payment Type | Micro-payments, often low and consistent | Variable; project-based or hourly rates |
| Skill Level | Typically low to moderate | Ranges from entry to expert levels |
| Visibility | Work remains behind the scenes, uncredited | Work is publicly credited to the freelancer |
| Job Security | Low; dependent on platform demand | Variable; depends on client base and reputation |
| Flexibility | Limited; task-dependant hours | High; choose working hours and workload |
| Examples | Data tagging, content moderation, AI training tasks | Graphic design, writing, software development |
Which is better?
Freelancing offers greater autonomy and the potential for higher income through diverse project opportunities, while ghost work typically involves repetitive, behind-the-scenes tasks with limited visibility and lower wages. Ghost work relies heavily on microtasks often facilitated by AI platforms, providing steady but less flexible employment. Freelancers benefit from building personal brands and client networks, which enhances long-term career growth and scalability.
Connection
Ghost work and freelancing intersect as both involve flexible, task-based employment often facilitated through digital platforms, allowing workers to take on diverse projects without traditional employer-employee relationships. This non-traditional work structure emphasizes autonomy and remote engagement, aligning with the gig economy's shift toward on-demand labor. The prevalence of ghost work in content moderation, data annotation, and other behind-the-scenes tasks complements freelancing roles by leveraging specialized skills without long-term contracts.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Freelancing offers significant autonomy, allowing individuals to select projects, set schedules, and control work methods, contrasting with ghost work where tasks are often predefined with minimal room for personal discretion. Ghost workers frequently perform repetitive, low-visibility tasks under strict guidelines, limiting their decision-making power and creative input. Explore more about how autonomy varies between freelancing and ghost work.
Compensation
Freelancing often offers higher compensation per project due to direct client relationships and the ability to set rates based on skill and demand. Ghost work typically involves lower pay as tasks are distributed across large platforms or companies, with limited visibility and bargaining power for workers. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which option best aligns with your financial goals.
Attribution
Freelancing involves direct attribution of work, where professionals publicly claim and showcase their projects, enhancing personal brand visibility. Ghost work, in contrast, lacks attribution as tasks are performed anonymously, often behind the scenes without public recognition. Explore further to understand the implications of attribution on career growth and accountability.
Source and External Links
Freelancing 101: What is Freelancing? - GCF Global - Freelancing is a form of self-employment where individuals work independently for various clients, offering flexibility in work location, schedule, and choice of projects.
What Is Freelancing? Basics and Popular Jobs in 2025 - Upwork - Freelancers provide services to clients without being full-time employees, managing their own business, taxes, and professional development while choosing projects that match their skills.
Freelancer - Wikipedia - A freelancer is a self-employed person not committed to a single employer long-term, commonly found in creative, tech, and professional service industries, with benefits including schedule flexibility and client selection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com