Labor hoarding refers to a company retaining excess employees during economic downturns to avoid future hiring costs and maintain institutional knowledge, whereas attrition involves gradually reducing workforce through natural departures without replacements. Understanding the balance between these strategies helps optimize workforce management to maintain productivity and control labor costs. Explore more about how businesses implement labor hoarding and attrition to adapt to market changes effectively.
Why it is important
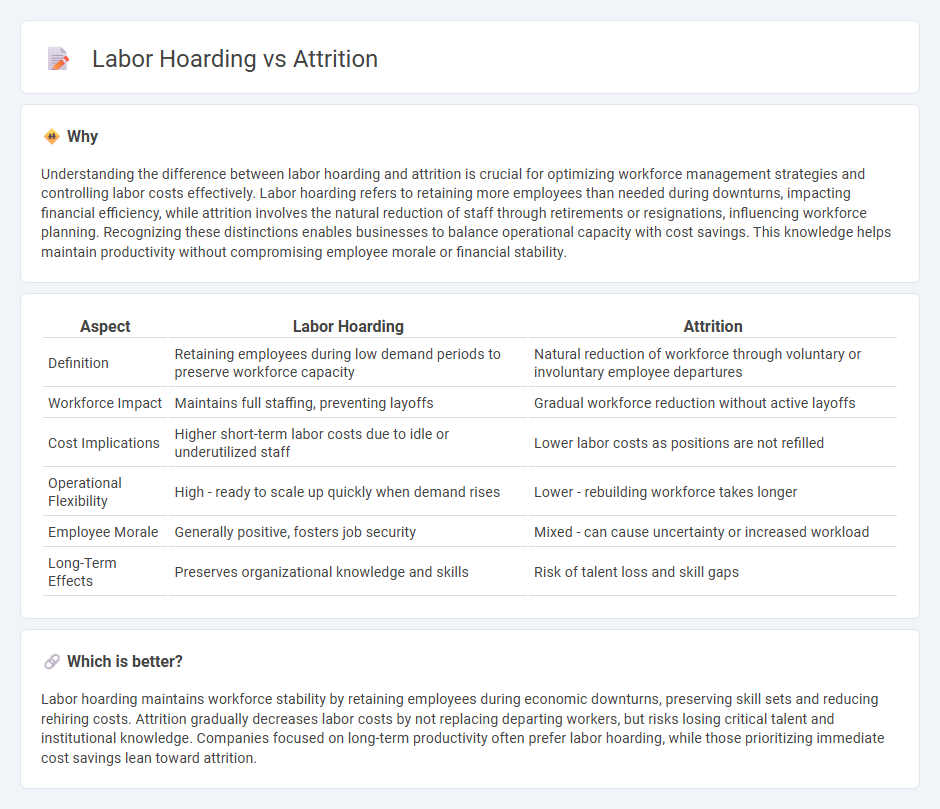
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and attrition is crucial for optimizing workforce management strategies and controlling labor costs effectively. Labor hoarding refers to retaining more employees than needed during downturns, impacting financial efficiency, while attrition involves the natural reduction of staff through retirements or resignations, influencing workforce planning. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to balance operational capacity with cost savings. This knowledge helps maintain productivity without compromising employee morale or financial stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Attrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during low demand periods to preserve workforce capacity | Natural reduction of workforce through voluntary or involuntary employee departures |
| Workforce Impact | Maintains full staffing, preventing layoffs | Gradual workforce reduction without active layoffs |
| Cost Implications | Higher short-term labor costs due to idle or underutilized staff | Lower labor costs as positions are not refilled |
| Operational Flexibility | High - ready to scale up quickly when demand rises | Lower - rebuilding workforce takes longer |
| Employee Morale | Generally positive, fosters job security | Mixed - can cause uncertainty or increased workload |
| Long-Term Effects | Preserves organizational knowledge and skills | Risk of talent loss and skill gaps |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding maintains workforce stability by retaining employees during economic downturns, preserving skill sets and reducing rehiring costs. Attrition gradually decreases labor costs by not replacing departing workers, but risks losing critical talent and institutional knowledge. Companies focused on long-term productivity often prefer labor hoarding, while those prioritizing immediate cost savings lean toward attrition.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than necessary during economic downturns to preserve skilled labor and avoid rehiring costs, influencing attrition by reducing voluntary departures due to increased job security. Attrition, or the natural reduction of workforce through retirements or resignations, can complement labor hoarding by allowing gradual workforce adjustment without layoffs. The interplay between labor hoarding and attrition helps organizations balance labor costs with operational flexibility in fluctuating market conditions.
Key Terms
Turnover
Attrition reduces labor costs by allowing employee departures without replacement, directly impacting turnover rates through natural workforce shrinkage. Labor hoarding involves retaining employees despite reduced demand, minimizing turnover but increasing short-term labor expenses. Explore more to understand how businesses balance these strategies for workforce efficiency.
Retention
Attrition involves the natural reduction of workforce through retirements, resignations, or layoffs, whereas labor hoarding occurs when companies deliberately retain more employees than needed during downturns to preserve skills and minimize future hiring costs. Retention during attrition focuses on minimizing voluntary departures, while labor hoarding emphasizes stabilizing employment to avoid productivity loss and maintain institutional knowledge. Explore deeper insights into how balancing attrition and labor hoarding strategies can optimize workforce retention.
Workforce Utilization
Attrition reduces workforce size naturally without layoffs, optimizing labor costs but potentially straining productivity due to skill gaps. Labor hoarding retains excess employees during downturns, preserving skills and capacity but increasing labor expenses and underutilization. Explore deeper insights into effective workforce utilization strategies balancing attrition and labor hoarding.
Source and External Links
Attrition Definition, Types, Causes & Mitigation Tips - SHRM - Attrition refers to the gradual reduction in workforce through retirements, resignations, deaths, or elimination of positions without replacement, typically involving voluntary departures rather than layoffs or firings, and classified into voluntary, involuntary, and internal attrition types.
ATTRITION Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com - Attrition is the decrease in numbers, size, or strength, often used to describe workforce reduction by not replacing employees who leave voluntarily, or the wearing down of resistance due to continuous pressure.
Understanding Attrition: Definitions, Types, and Strategic Management - Attrition occurs when employees leave a company for any reason and are not replaced, resulting in a permanent decrease in workforce size, and differs from employee turnover which includes positions that are refilled.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com