Quiet hiring focuses on strategically reallocating employee skills and roles within an organization without formal job postings, enhancing productivity and retention. Quiet firing, conversely, involves subtly encouraging underperforming employees to leave by reducing responsibilities or opportunities, often without direct communication. Discover more about these nuanced workforce strategies and their impacts on employment dynamics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quiet hiring and quiet firing is crucial for employees to recognize changes in workload and job security. Quiet hiring often means organizations are delegating additional responsibilities without formal recruitment, impacting work-life balance. Quiet firing refers to subtle tactics aimed at encouraging employees to leave without explicit termination, affecting career stability. Awareness of these practices helps employees make informed decisions about their career paths and negotiation strategies.
Comparison Table
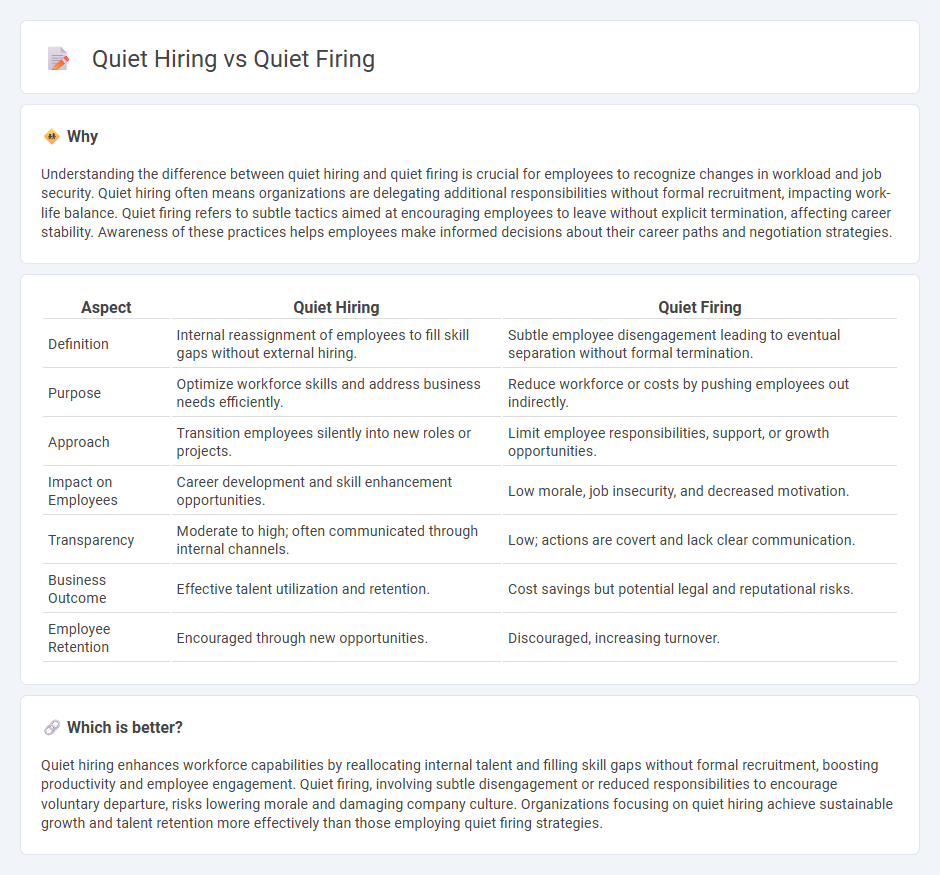
| Aspect | Quiet Hiring | Quiet Firing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal reassignment of employees to fill skill gaps without external hiring. | Subtle employee disengagement leading to eventual separation without formal termination. |
| Purpose | Optimize workforce skills and address business needs efficiently. | Reduce workforce or costs by pushing employees out indirectly. |
| Approach | Transition employees silently into new roles or projects. | Limit employee responsibilities, support, or growth opportunities. |
| Impact on Employees | Career development and skill enhancement opportunities. | Low morale, job insecurity, and decreased motivation. |
| Transparency | Moderate to high; often communicated through internal channels. | Low; actions are covert and lack clear communication. |
| Business Outcome | Effective talent utilization and retention. | Cost savings but potential legal and reputational risks. |
| Employee Retention | Encouraged through new opportunities. | Discouraged, increasing turnover. |
Which is better?
Quiet hiring enhances workforce capabilities by reallocating internal talent and filling skill gaps without formal recruitment, boosting productivity and employee engagement. Quiet firing, involving subtle disengagement or reduced responsibilities to encourage voluntary departure, risks lowering morale and damaging company culture. Organizations focusing on quiet hiring achieve sustainable growth and talent retention more effectively than those employing quiet firing strategies.
Connection
Quiet hiring and quiet firing are connected strategies companies use to manage workforce changes discreetly. Quiet hiring involves reallocating or upskilling existing employees without public job postings, while quiet firing focuses on subtly encouraging underperforming staff to leave through reduced responsibilities or engagement. Both practices aim to optimize talent management while minimizing disruption and maintaining organizational stability.
Key Terms
Performance Management
Quiet firing occurs when managers subtly reduce an employee's responsibilities or opportunities, signaling poor performance without formal termination. Quiet hiring involves reallocating tasks to high performers without expanding headcount, often boosting team productivity while masking actual resource constraints. Explore how Performance Management strategies can effectively address these subtle workforce dynamics.
Workforce Optimization
Quiet firing involves subtly reducing an employee's responsibilities or opportunities to encourage voluntary departure, while quiet hiring focuses on reallocating tasks and increasing workload through existing staff to fill gaps without overt recruitment. Both strategies aim to optimize workforce efficiency by balancing talent management and operational demands. Explore the nuances of these practices to enhance your organization's workforce optimization approach.
Employee Retention
Quiet firing involves subtly pushing employees out by reducing responsibilities or opportunities, leading to disengagement and turnover, which directly threatens employee retention. Quiet hiring strategically enhances teams by integrating new skills or redistributing roles without public announcements, promoting internal growth and increased retention rates. Explore these nuanced strategies to optimize your workforce retention and development practices.
Source and External Links
What Is Quiet Firing & What Are the Signs? - Paychex - Quiet firing refers to management creating a poor work environment to push employees to resign voluntarily, often by reducing responsibilities, excluding from important meetings, or assigning less desirable duties, making it a passive, non-confrontational approach to employee separation potentially bordering on illegal constructive discharge.
Quiet Firing: What It Is and How to Spot It - Team Building - Quiet firing involves creating non-ideal work conditions that encourage underperforming employees to quit, and prevention can include fostering honest communication, assessing management practices, and building strong employee rapport to avoid unfair treatment and alienation.
Quiet Firing - BambooHR - Quiet firing is an old workplace practice of neglecting or pressuring employees to quit, often to avoid the costs and difficulties of outright firing, characterized by setting unrealistic goals, withholding opportunities, or diminishing roles, also known as "silent sacking" or "silent firing."
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com