No-collar work refers to jobs that emphasize creativity, innovation, and technology over traditional manual tasks, often found in digital and knowledge-based industries. Manual labor involves physically demanding tasks typically associated with trades, construction, and manufacturing sectors. Explore the evolving landscape of employment to understand how no-collar and manual labor roles shape the modern workforce.
Why it is important
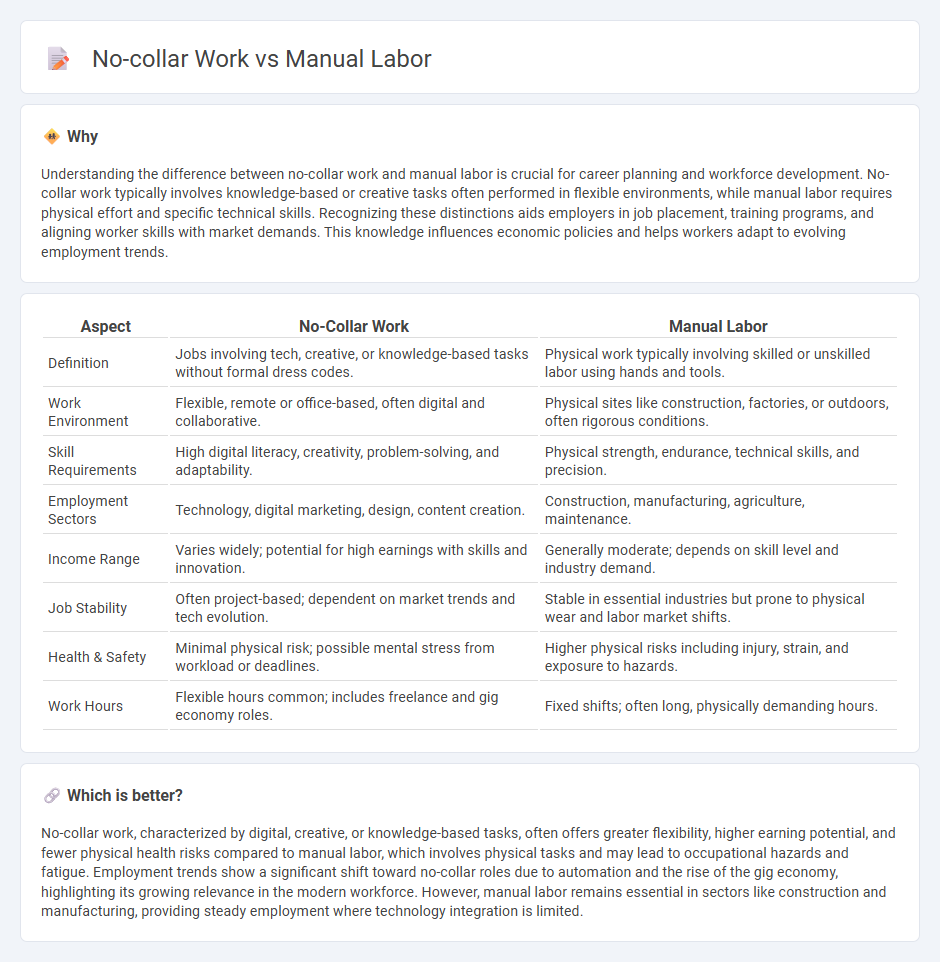
Understanding the difference between no-collar work and manual labor is crucial for career planning and workforce development. No-collar work typically involves knowledge-based or creative tasks often performed in flexible environments, while manual labor requires physical effort and specific technical skills. Recognizing these distinctions aids employers in job placement, training programs, and aligning worker skills with market demands. This knowledge influences economic policies and helps workers adapt to evolving employment trends.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No-Collar Work | Manual Labor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Jobs involving tech, creative, or knowledge-based tasks without formal dress codes. | Physical work typically involving skilled or unskilled labor using hands and tools. |
| Work Environment | Flexible, remote or office-based, often digital and collaborative. | Physical sites like construction, factories, or outdoors, often rigorous conditions. |
| Skill Requirements | High digital literacy, creativity, problem-solving, and adaptability. | Physical strength, endurance, technical skills, and precision. |
| Employment Sectors | Technology, digital marketing, design, content creation. | Construction, manufacturing, agriculture, maintenance. |
| Income Range | Varies widely; potential for high earnings with skills and innovation. | Generally moderate; depends on skill level and industry demand. |
| Job Stability | Often project-based; dependent on market trends and tech evolution. | Stable in essential industries but prone to physical wear and labor market shifts. |
| Health & Safety | Minimal physical risk; possible mental stress from workload or deadlines. | Higher physical risks including injury, strain, and exposure to hazards. |
| Work Hours | Flexible hours common; includes freelance and gig economy roles. | Fixed shifts; often long, physically demanding hours. |
Which is better?
No-collar work, characterized by digital, creative, or knowledge-based tasks, often offers greater flexibility, higher earning potential, and fewer physical health risks compared to manual labor, which involves physical tasks and may lead to occupational hazards and fatigue. Employment trends show a significant shift toward no-collar roles due to automation and the rise of the gig economy, highlighting its growing relevance in the modern workforce. However, manual labor remains essential in sectors like construction and manufacturing, providing steady employment where technology integration is limited.
Connection
No-collar work, often characterized by informal, knowledge-based tasks, intersects with manual labor in sectors where physical skills and technological proficiency coalesce, such as advanced manufacturing and skilled trades. This hybrid employment model emphasizes adaptability and continuous learning, bridging traditional hands-on tasks with digital tools to enhance productivity and job sustainability. Understanding this connection highlights evolving workforce trends and the increasing value of multidisciplinary skill sets in the labor market.
Key Terms
Physical Tasks
Manual labor involves physical tasks that demand strength, endurance, and dexterity, often in industries like construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. In contrast, no-collar work emphasizes cognitive skills, creativity, and problem-solving with minimal physical exertion. Explore how these distinct work types impact productivity and worker health in various sectors.
Automation
Automation is transforming manual labor by replacing repetitive, physical tasks with advanced robotics and AI technology, leading to increased efficiency and reduced human error. No-collar work, characterized by creative, strategic, and technology-driven roles, benefits from automation through enhanced data processing and decision-making capabilities. Explore how automation reshapes job landscapes and skill demands across industries.
Knowledge-Based
Knowledge-based work emphasizes cognitive skills, problem-solving, and strategic thinking, distinguishing it from manual labor that relies on physical effort and repetitive tasks. In industries driven by innovation, knowledge workers contribute to creativity, decision-making, and the development of new technologies or services. Explore how knowledge-based roles transform modern economies and workplace dynamics.
Source and External Links
Benefits of Manual Labor: Preparing You For Your Career - OSHA.com - Manual labor involves physical work typically done by "blue-collar" workers in fields such as construction, agriculture, manufacturing, and general industry, including jobs like plumbers, electricians, factory workers, farmers, and firefighters.
17 Manual Labor Jobs | Indeed.com - Manual labor jobs require physical effort and range from entry-level roles like housekeeping and custodial work to technical positions like emergency medical technicians and construction workers, often requiring training or certification.
What is manual labor? Simple Definition & Meaning - LSD.Law - Manual labor is work accomplished through physical strength and effort, with or without tools or machinery, exemplified by tasks such as lifting, digging, building, and farming.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com