Labor hoarding involves retaining excess employees during economic downturns to preserve skilled labor and avoid future recruitment costs, while restructuring focuses on workforce adjustment through layoffs or reallocation to improve organizational efficiency. Companies practicing labor hoarding aim to maintain operational stability and employee morale, whereas restructuring prioritizes cost reduction and strategic realignment. Explore deeper insights into how these contrasting approaches impact long-term business performance and workforce dynamics.
Why it is important
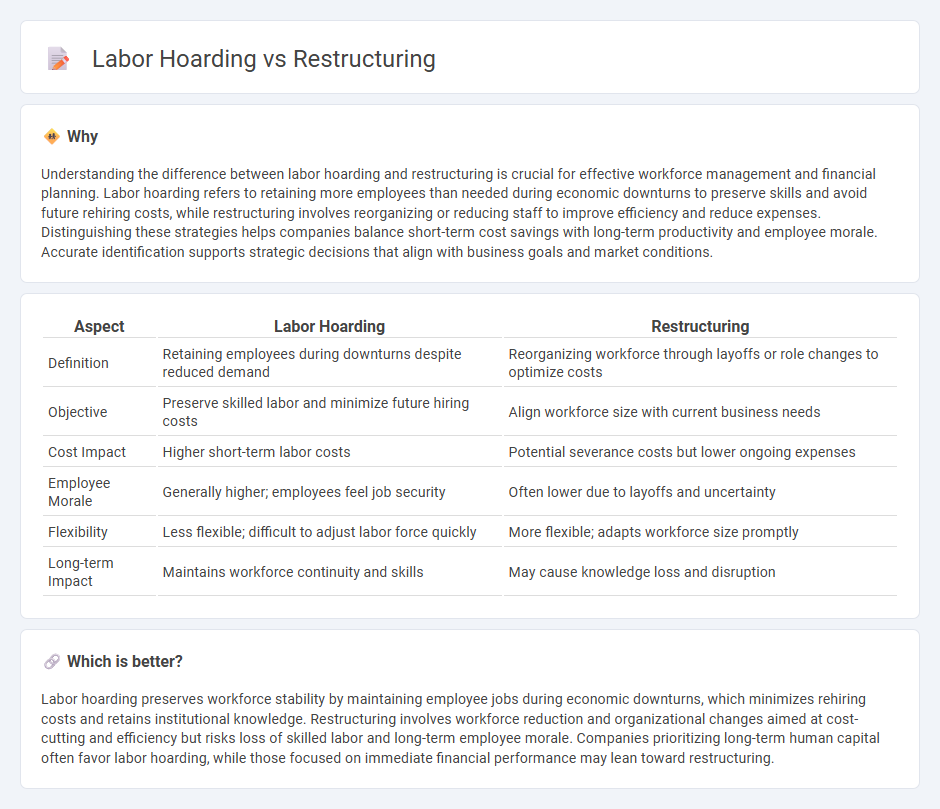
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and restructuring is crucial for effective workforce management and financial planning. Labor hoarding refers to retaining more employees than needed during economic downturns to preserve skills and avoid future rehiring costs, while restructuring involves reorganizing or reducing staff to improve efficiency and reduce expenses. Distinguishing these strategies helps companies balance short-term cost savings with long-term productivity and employee morale. Accurate identification supports strategic decisions that align with business goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Restructuring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during downturns despite reduced demand | Reorganizing workforce through layoffs or role changes to optimize costs |
| Objective | Preserve skilled labor and minimize future hiring costs | Align workforce size with current business needs |
| Cost Impact | Higher short-term labor costs | Potential severance costs but lower ongoing expenses |
| Employee Morale | Generally higher; employees feel job security | Often lower due to layoffs and uncertainty |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; difficult to adjust labor force quickly | More flexible; adapts workforce size promptly |
| Long-term Impact | Maintains workforce continuity and skills | May cause knowledge loss and disruption |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding preserves workforce stability by maintaining employee jobs during economic downturns, which minimizes rehiring costs and retains institutional knowledge. Restructuring involves workforce reduction and organizational changes aimed at cost-cutting and efficiency but risks loss of skilled labor and long-term employee morale. Companies prioritizing long-term human capital often favor labor hoarding, while those focused on immediate financial performance may lean toward restructuring.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than needed during economic downturns, anticipating future recovery or avoiding costly rehiring processes. This practice directly influences restructuring efforts by enabling smoother transitions when companies eventually realign their workforce to match new business strategies or market demands. Effective labor hoarding minimizes disruption during restructuring, preserving institutional knowledge and reducing long-term operational costs.
Key Terms
Workforce Adjustment
Workforce adjustment strategies such as restructuring involve the deliberate reorganization of a company's labor force to improve efficiency and reduce costs, often through layoffs or redeployment. Labor hoarding, in contrast, occurs when firms retain excess workers during downturns to avoid future recruitment costs and maintain employee morale. Explore the nuances of these approaches and their impacts on organizational performance and labor markets to understand optimal workforce management.
Job Retention
Restructuring involves organizational changes aimed at improving efficiency, often leading to layoffs, while labor hoarding refers to retaining employees despite reduced demand to preserve workforce stability. Job retention strategies during economic downturns emphasize labor hoarding to minimize rehiring costs and maintain institutional knowledge. Explore effective approaches to balance restructuring and labor hoarding to optimize job retention outcomes.
Organizational Flexibility
Organizational flexibility hinges on balancing restructuring efforts with labor hoarding practices to adapt efficiently to market changes. Restructuring optimizes workforce alignment and resource allocation, while labor hoarding preserves talent during downturns, enabling quicker recovery and sustained innovation. Explore the strategic impact of these approaches to enhance your organization's adaptability and long-term resilience.
Source and External Links
Restructuring - Wikipedia - Restructuring is the corporate management act of reorganizing legal, ownership, operational, or other structures to improve profitability, respond to crisis, or change ownership, including financial and corporate debt restructuring to ensure company viability.
What Is Corporate Restructuring? - IRIS Software Group - Corporate restructuring involves changes like debt restructuring, management reshuffles, and operational streamlining aimed at strengthening an organization's financial position and improving performance, especially during financial challenges.
What Is Corporate Restructuring? A Comprehensive Guide - Corporate restructuring can include organizational changes (hierarchy adjustment), operational streamlining (automation, outsourcing), and divestitures (selling non-core assets) to enhance efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com