Digital nomad visas cater to remote professionals seeking location flexibility and extended stays in foreign countries without traditional work permits. Seasonal worker visas, conversely, target temporary laborers in agriculture, tourism, and hospitality sectors with specific time-bound employment permissions. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which visa aligns with your career goals and lifestyle preferences.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a digital nomad visa and a seasonal worker visa is crucial for complying with immigration laws and maximizing work opportunities abroad. A digital nomad visa allows remote professionals to live and work legally in a foreign country without engaging in local employment, whereas a seasonal worker visa is designed for individuals employed in temporary, location-specific jobs, often in agriculture or tourism. Choosing the correct visa ensures eligibility for benefits, tax obligations, and legal protections specific to the employment type. Misclassification can lead to visa denial, legal penalties, or deportation, impacting career and residency plans.
Comparison Table
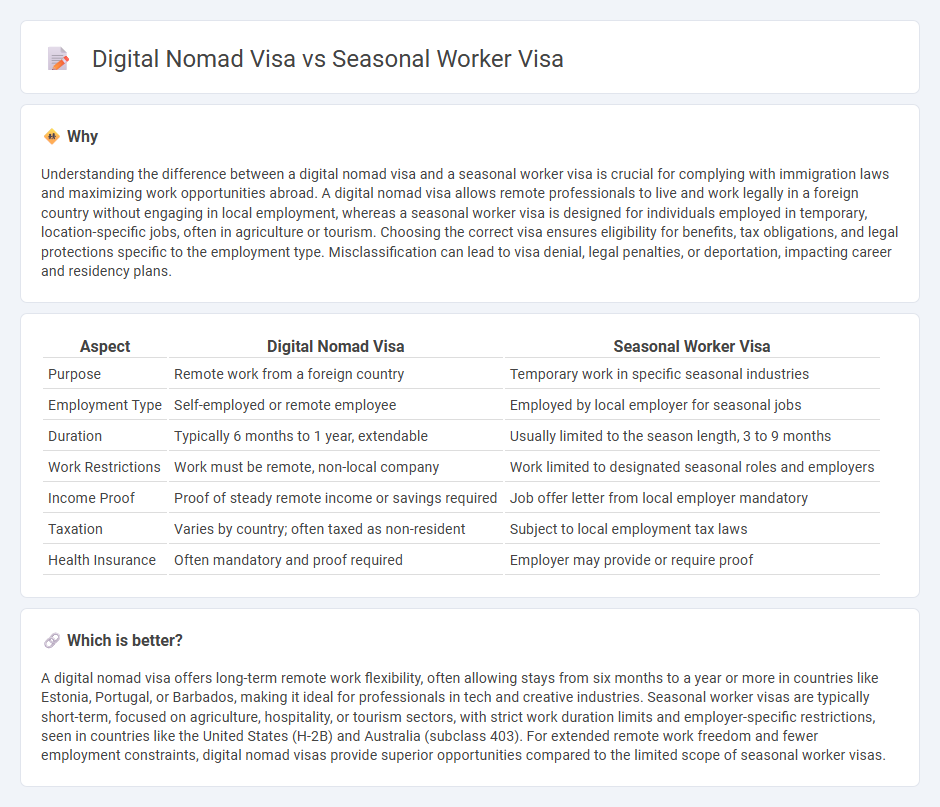
| Aspect | Digital Nomad Visa | Seasonal Worker Visa |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Remote work from a foreign country | Temporary work in specific seasonal industries |
| Employment Type | Self-employed or remote employee | Employed by local employer for seasonal jobs |
| Duration | Typically 6 months to 1 year, extendable | Usually limited to the season length, 3 to 9 months |
| Work Restrictions | Work must be remote, non-local company | Work limited to designated seasonal roles and employers |
| Income Proof | Proof of steady remote income or savings required | Job offer letter from local employer mandatory |
| Taxation | Varies by country; often taxed as non-resident | Subject to local employment tax laws |
| Health Insurance | Often mandatory and proof required | Employer may provide or require proof |
Which is better?
A digital nomad visa offers long-term remote work flexibility, often allowing stays from six months to a year or more in countries like Estonia, Portugal, or Barbados, making it ideal for professionals in tech and creative industries. Seasonal worker visas are typically short-term, focused on agriculture, hospitality, or tourism sectors, with strict work duration limits and employer-specific restrictions, seen in countries like the United States (H-2B) and Australia (subclass 403). For extended remote work freedom and fewer employment constraints, digital nomad visas provide superior opportunities compared to the limited scope of seasonal worker visas.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and seasonal worker visas both facilitate temporary international employment but target distinct workforce categories and durations. Digital nomad visas cater to remote professionals seeking flexibility without direct local employment, while seasonal worker visas authorize foreign labor for time-bound, industry-specific roles, often in agriculture or tourism. Both visa types reflect evolving labor mobility trends, responding to global workforce demands through legal frameworks encouraging cross-border economic participation.
Key Terms
Duration of Stay
Seasonal worker visas typically allow stays aligned with specific work periods, often ranging from three to nine months, depending on the country's agricultural or tourism calendar. Digital nomad visas generally offer longer durations, commonly from six months up to two years, designed for remote professionals who work independently of local employment. Explore visa options in detail to determine which duration best fits your work and lifestyle needs.
Work Restrictions
Seasonal worker visas typically impose strict work restrictions, limiting employment to specific industries such as agriculture or tourism and confining the duration of work to a defined season. Digital nomad visas offer more flexible work opportunities, allowing visa holders to perform remote work for foreign employers or their own businesses without location constraints. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which visa type best suits your professional needs and lifestyle.
Remote Work Eligibility
Seasonal worker visas are primarily designed for temporary employment in industries like agriculture or hospitality and often restrict the holder to specific job roles and locations, limiting remote work eligibility. Digital nomad visas offer broader eligibility for remote work, allowing visa holders to live in a country while working online for foreign employers or clients without local employment restrictions. Explore detailed visa requirements and benefits to determine which option best supports your remote work lifestyle.
Source and External Links
Seasonal Worker Visas: A Guide to Legal Navigation & ... - Seasonal worker visas in the U.S. include H-2A for temporary agricultural jobs and H-2B for non-agricultural seasonal work, requiring employers to prove insufficient U.S. workers and ensure no harm to local wages or conditions, with a multi-step application process involving labor certification and visa petitions.
H-2 Temporary or Seasonal Work Visa (H-2A & H-2B) - The H-2 visa allows temporary seasonal workers to enter the U.S. for agricultural work (H-2A) or other industries (H-2B) with employers filing a Temporary Labor Certification and petitioning USCIS to confirm the temporary need and wage parity for workers.
Temporary and Seasonal Workers (H-2A and H-2B) - H-2A visas have no annual cap and are for temporary agricultural labor; employers must show a shortage of U.S. workers and that hiring foreign workers won't negatively impact U.S. workers' wages or conditions; H-2B applies similarly for non-agricultural seasonal labor with employers required to provide legitimate job offers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com