Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain employees during economic downturns to preserve skills and avoid future recruitment costs, despite reduced demand. In contrast, layoffs involve reducing the workforce to cut expenses quickly, often leading to short-term financial relief but potential long-term skill shortages. Explore the impact of these strategies on business resilience and workforce stability to understand their advantages and trade-offs.
Why it is important
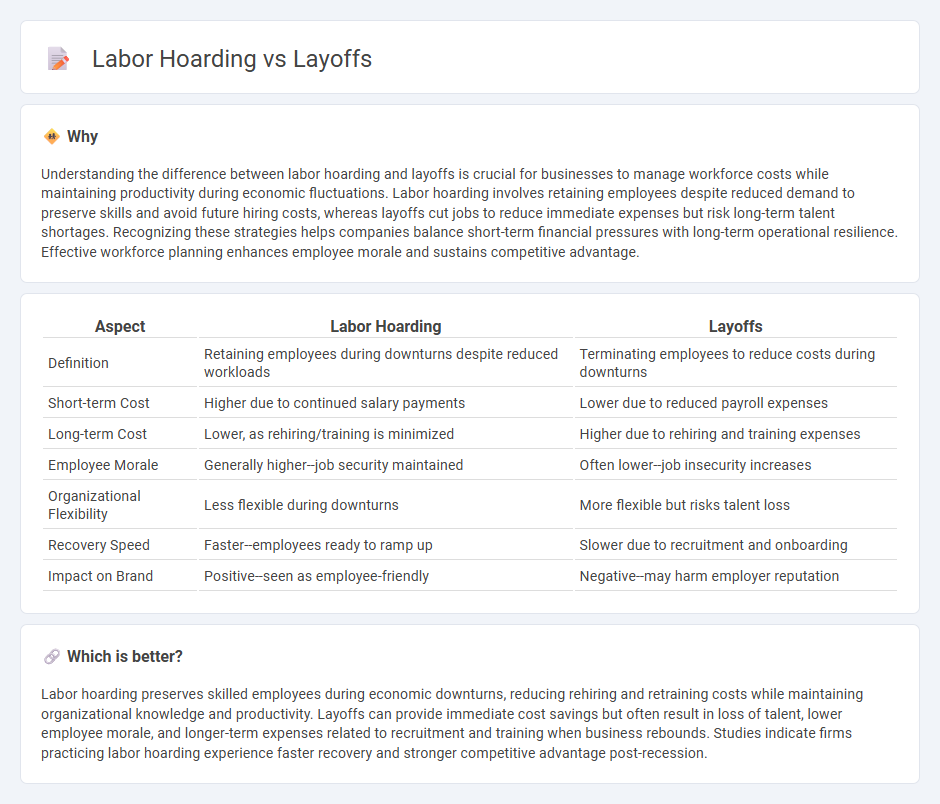
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and layoffs is crucial for businesses to manage workforce costs while maintaining productivity during economic fluctuations. Labor hoarding involves retaining employees despite reduced demand to preserve skills and avoid future hiring costs, whereas layoffs cut jobs to reduce immediate expenses but risk long-term talent shortages. Recognizing these strategies helps companies balance short-term financial pressures with long-term operational resilience. Effective workforce planning enhances employee morale and sustains competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Layoffs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during downturns despite reduced workloads | Terminating employees to reduce costs during downturns |
| Short-term Cost | Higher due to continued salary payments | Lower due to reduced payroll expenses |
| Long-term Cost | Lower, as rehiring/training is minimized | Higher due to rehiring and training expenses |
| Employee Morale | Generally higher--job security maintained | Often lower--job insecurity increases |
| Organizational Flexibility | Less flexible during downturns | More flexible but risks talent loss |
| Recovery Speed | Faster--employees ready to ramp up | Slower due to recruitment and onboarding |
| Impact on Brand | Positive--seen as employee-friendly | Negative--may harm employer reputation |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding preserves skilled employees during economic downturns, reducing rehiring and retraining costs while maintaining organizational knowledge and productivity. Layoffs can provide immediate cost savings but often result in loss of talent, lower employee morale, and longer-term expenses related to recruitment and training when business rebounds. Studies indicate firms practicing labor hoarding experience faster recovery and stronger competitive advantage post-recession.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than needed during economic downturns to preserve skills and avoid rehiring costs, which directly influences the timing and severity of layoffs. This practice delays layoffs by maintaining workforce stability, but prolonged labor hoarding can lead to increased operational expenses, eventually forcing firms to implement significant layoffs when financial pressures intensify. Understanding the balance between labor hoarding and layoffs is critical for optimizing workforce management and minimizing the negative impacts on productivity and employee morale.
Key Terms
Workforce Reduction
Workforce reduction through layoffs involves permanently terminating employees to cut costs and adjust to market demands, often leading to immediate savings but potential long-term skill shortages. Labor hoarding, by contrast, retains employees during downturns despite reduced demand, preserving institutional knowledge and enabling quicker recovery once conditions improve. Explore the strategic implications of layoffs versus labor hoarding to optimize workforce management.
Talent Retention
Talent retention strategies pivot between layoffs and labor hoarding, impacting workforce stability and long-term organizational growth. Layoffs reduce costs but risk losing valuable skills, while labor hoarding preserves talent but increases short-term expenses. Explore effective talent retention approaches to balance workforce management and sustain competitive advantage.
Productivity
Layoffs can lead to immediate cost reductions but often result in decreased productivity due to loss of skilled workers and lowered employee morale. Labor hoarding, where companies retain more employees than needed, can preserve organizational knowledge and maintain productivity levels during downturns, despite higher short-term costs. Explore how balancing layoffs and labor hoarding strategies impacts long-term productivity and business resilience.
Source and External Links
Mass layoffs continue across freight-related companies in the U.S. - Recent weeks saw 4,137 job cuts announced in sectors like transportation, manufacturing, and logistics, with major layoffs including Republic National Distributing Co. cutting 1,756 jobs due to rising operational costs and industry challenges.
How many people are laid off in the United States each month? - About 1.6 million people were laid off or discharged in May 2025, with layoffs 2.4% higher than May 2024, reflecting ongoing economic fluctuations and adjustments in the labor market.
Layoff - Wikipedia - Layoffs (temporary or permanent job terminations) are primarily business decisions driven by cost-cutting, organizational downsizing, or economic pressures, often resulting in collective employee displacement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com