Career lattice models promote employee growth through lateral moves and skill diversification, enhancing adaptability and long-term job satisfaction. Job rotation systematically exposes employees to different roles within the organization, improving expertise and cross-functional understanding. Explore more to discover how these strategies can optimize workforce development and retention.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between career lattice and job rotation is important because career lattice emphasizes lateral moves for skill development and long-term growth, while job rotation focuses on temporary assignments to improve job-specific skills. Employers use career lattice strategies to retain talent by providing diverse opportunities without requiring upward mobility. Job rotation helps employees gain experience in multiple roles, increasing flexibility and reducing burnout. Clarity on these concepts enables better career planning and organizational development.
Comparison Table
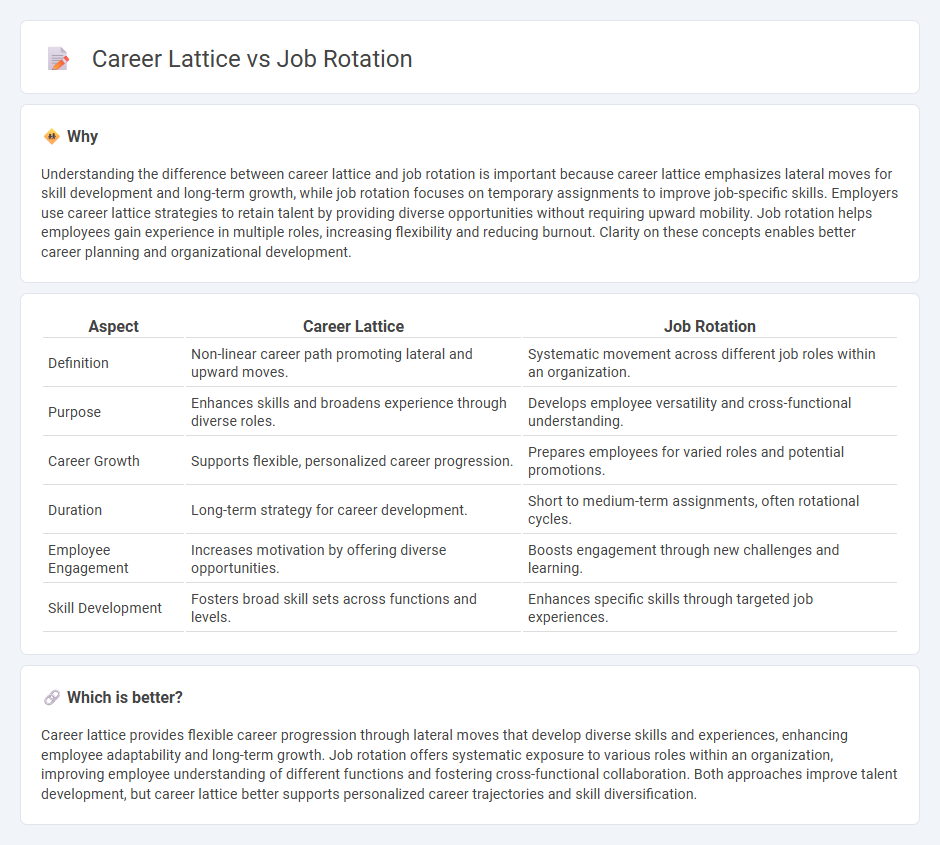
| Aspect | Career Lattice | Job Rotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-linear career path promoting lateral and upward moves. | Systematic movement across different job roles within an organization. |
| Purpose | Enhances skills and broadens experience through diverse roles. | Develops employee versatility and cross-functional understanding. |
| Career Growth | Supports flexible, personalized career progression. | Prepares employees for varied roles and potential promotions. |
| Duration | Long-term strategy for career development. | Short to medium-term assignments, often rotational cycles. |
| Employee Engagement | Increases motivation by offering diverse opportunities. | Boosts engagement through new challenges and learning. |
| Skill Development | Fosters broad skill sets across functions and levels. | Enhances specific skills through targeted job experiences. |
Which is better?
Career lattice provides flexible career progression through lateral moves that develop diverse skills and experiences, enhancing employee adaptability and long-term growth. Job rotation offers systematic exposure to various roles within an organization, improving employee understanding of different functions and fostering cross-functional collaboration. Both approaches improve talent development, but career lattice better supports personalized career trajectories and skill diversification.
Connection
Career lattice and job rotation are interconnected strategies that enhance employee development and organizational agility by promoting diverse skill acquisition and lateral career moves. Job rotation involves systematically shifting employees across different positions to build a broad skill set, supporting the flexible career pathways outlined in a career lattice. This approach fosters continuous learning, adaptability, and retention by enabling employees to explore various roles without traditional hierarchical constraints.
Key Terms
Skill diversification
Job rotation enhances skill diversification by systematically moving employees through different roles within the organization, allowing them to acquire a broad range of functional expertise. Career lattice expands this concept by offering both lateral and vertical career moves, emphasizing diverse skill development across various departments and job functions rather than a traditional upward trajectory. To explore how these strategies can boost your workforce's adaptability and career growth, learn more about job rotation and career lattice implementations.
Lateral movement
Job rotation involves systematically moving employees through different roles within an organization to develop diverse skills and broader business understanding. Career lattice emphasizes lateral movement along with vertical progression, enabling employees to gain experience in multiple functions or departments without necessarily moving up the hierarchy. Explore how lateral movement shapes career growth and flexibility in your professional development journey.
Career progression
Job rotation enhances career progression by exposing employees to diverse roles and skills within a company, fostering adaptability and broadening expertise. The career lattice model supports progression through lateral moves, skill development, and varied experiences, enabling nonlinear advancement and personalized career paths. Explore detailed strategies to leverage both frameworks for optimized career growth.
Source and External Links
Job rotation - Wikipedia - Job rotation is the lateral transfer of employees between jobs in an organization without a change in hierarchical rank or salary, used to motivate employees, manage fatigue, orient and develop careers, and increase flexibility and productivity.
Job rotation | EBSCO Research Starters - Job rotation is an HR strategy involving moving employees between jobs or departments to develop a broad range of skills, reduce monotony and burnout, enhance job satisfaction, and boost workforce flexibility.
Job Rotation: A Full Guide with 5 Examples - Job rotation involves temporary lateral moves between jobs, with examples from companies like The Slumber Yard and Heineken showing how it reduces turnover, broadens skills, and creates a flexible workforce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com