Portfolio careers combine multiple part-time roles or projects, offering diverse income streams and skill development opportunities. The gig economy relies on short-term, freelance jobs often mediated by digital platforms, providing flexibility but less stability. Explore how these employment models impact work-life balance and financial security.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between portfolio careers and the gig economy is crucial for effective career planning and financial stability. Portfolio careers involve multiple part-time roles or projects with diverse skill development, while the gig economy consists of short-term, freelance jobs often lacking long-term security or benefits. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals optimize income streams and secure employment benefits. This knowledge enables better decision-making regarding work-life balance and career growth strategies.
Comparison Table
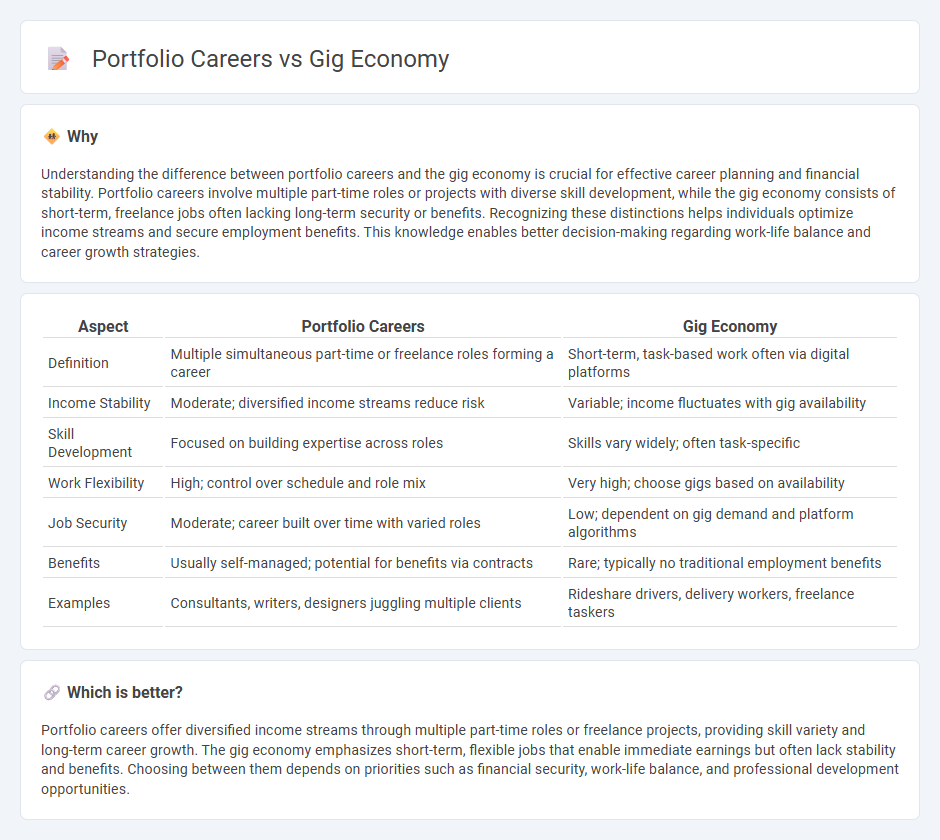
| Aspect | Portfolio Careers | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple simultaneous part-time or freelance roles forming a career | Short-term, task-based work often via digital platforms |
| Income Stability | Moderate; diversified income streams reduce risk | Variable; income fluctuates with gig availability |
| Skill Development | Focused on building expertise across roles | Skills vary widely; often task-specific |
| Work Flexibility | High; control over schedule and role mix | Very high; choose gigs based on availability |
| Job Security | Moderate; career built over time with varied roles | Low; dependent on gig demand and platform algorithms |
| Benefits | Usually self-managed; potential for benefits via contracts | Rare; typically no traditional employment benefits |
| Examples | Consultants, writers, designers juggling multiple clients | Rideshare drivers, delivery workers, freelance taskers |
Which is better?
Portfolio careers offer diversified income streams through multiple part-time roles or freelance projects, providing skill variety and long-term career growth. The gig economy emphasizes short-term, flexible jobs that enable immediate earnings but often lack stability and benefits. Choosing between them depends on priorities such as financial security, work-life balance, and professional development opportunities.
Connection
Portfolio careers thrive in the gig economy by enabling professionals to combine multiple freelance jobs, short-term contracts, or part-time roles to create diverse income streams. The gig economy provides the flexible platforms and opportunities that support portfolio workers in managing varied skillsets across industries. This connection fosters adaptability and resilience in employment, catering to evolving market demands and individual career goals.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Gig economy roles offer short-term, task-based flexibility, allowing workers to choose projects and hours independently, ideal for those seeking immediate, varied income streams. Portfolio careers involve managing multiple part-time jobs or freelance projects simultaneously, providing long-term career adaptability and skill diversification across industries. Explore the advantages of each to determine which pathway best suits your lifestyle and professional goals.
Income streams
The gig economy emphasizes short-term, task-based income streams from platforms like Uber or Fiverr, often leading to unstable earnings due to fluctuating demand. Portfolio careers combine multiple professional roles or projects, diversifying income sources across freelancing, consulting, and part-time jobs for greater financial resilience. Explore detailed comparisons and strategies to optimize your income streams in both models.
Job security
Gig economy roles often lack traditional job security due to their short-term, freelance nature and absence of employee benefits like healthcare and retirement plans. Portfolio careers, comprising multiple part-time or freelance positions, offer diversified income streams but still carry risks related to inconsistent earnings and limited job stability. Explore deeper insights into job security dynamics within gig economy and portfolio career models.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - A gig economy involves flexible labor exchange through digital platforms, hiring independent contractors for temporary work.
What is the Gig Economy? - The gig economy is a system where organizations hire workers for short-term commitments, often facilitated by digital platforms.
What is the gig economy and what's the deal for gig workers? - The gig economy uses digital platforms to connect freelancers with customers for short-term services, offering economic benefits but also raising worker protection concerns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com