Digital nomad visas offer remote workers the opportunity to live and work legally in a foreign country without traditional employment restrictions, often for periods ranging from six months to two years. Temporary residence permits typically require sponsorship, provide broader rights to work locally, and are subject to more stringent application criteria and duration limits. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which option best suits your employment and residency goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a digital nomad visa and a temporary residence permit is crucial for employment compliance and legal residency status. Digital nomad visas specifically cater to remote workers, allowing them to legally work online without entering the local labor market. Temporary residence permits provide broader rights, enabling longer stays and possible access to local employment opportunities or social benefits. Accurate knowledge of these distinctions prevents legal issues and ensures optimal use of available immigration options for job security.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Nomad Visa | Temporary Residence Permit |
|---|---|---|
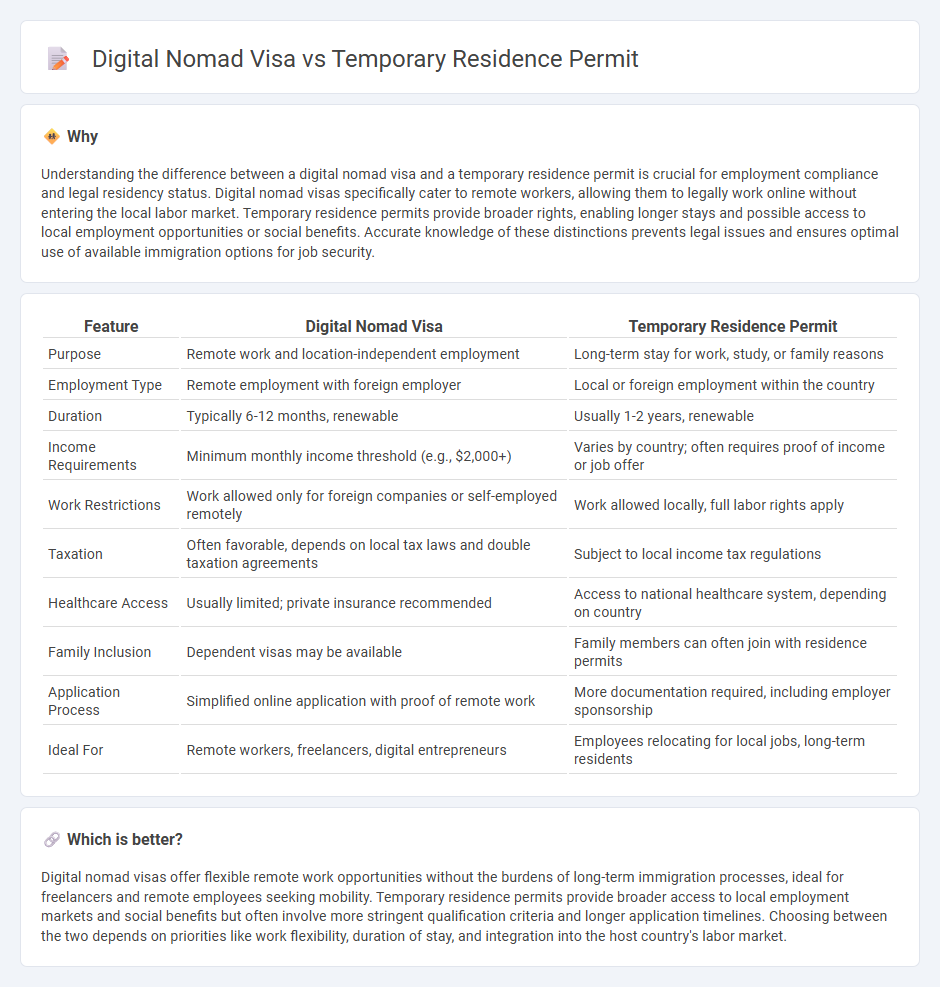
| Purpose | Remote work and location-independent employment | Long-term stay for work, study, or family reasons |
| Employment Type | Remote employment with foreign employer | Local or foreign employment within the country |
| Duration | Typically 6-12 months, renewable | Usually 1-2 years, renewable |
| Income Requirements | Minimum monthly income threshold (e.g., $2,000+) | Varies by country; often requires proof of income or job offer |
| Work Restrictions | Work allowed only for foreign companies or self-employed remotely | Work allowed locally, full labor rights apply |
| Taxation | Often favorable, depends on local tax laws and double taxation agreements | Subject to local income tax regulations |
| Healthcare Access | Usually limited; private insurance recommended | Access to national healthcare system, depending on country |
| Family Inclusion | Dependent visas may be available | Family members can often join with residence permits |
| Application Process | Simplified online application with proof of remote work | More documentation required, including employer sponsorship |
| Ideal For | Remote workers, freelancers, digital entrepreneurs | Employees relocating for local jobs, long-term residents |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer flexible remote work opportunities without the burdens of long-term immigration processes, ideal for freelancers and remote employees seeking mobility. Temporary residence permits provide broader access to local employment markets and social benefits but often involve more stringent qualification criteria and longer application timelines. Choosing between the two depends on priorities like work flexibility, duration of stay, and integration into the host country's labor market.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and temporary residence permits both facilitate legal employment and extended stays in foreign countries for remote workers. These permits provide authorization to engage in work activities while residing temporarily, ensuring compliance with local immigration and labor laws. By securing either document, digital nomads can maintain professional stability and access local services without violating visa restrictions.
Key Terms
Work Authorization
Temporary residence permits often provide comprehensive work authorization, allowing holders to engage in employment, freelance projects, or business operations within the host country, subject to specific national labor laws. Digital nomad visas typically grant permission to work remotely for foreign employers without entering the local labor market, limiting on-site employment but enabling legal remote work activities. Explore the detailed differences in work authorization frameworks between these two options to choose the best fit for your professional needs.
Duration of Stay
A temporary residence permit typically allows stays ranging from six months to a few years, depending on the issuing country's regulations. Digital nomad visas often grant shorter-term stays, commonly between six months and one year, with the possibility of renewal in some locations. Explore the specific duration conditions and renewal options to determine which suits your lifestyle best.
Remote Work Eligibility
Temporary residence permits often require proof of local employment or economic activity, limiting remote work options for digital nomads. Digital nomad visas specifically authorize remote workers to reside in a country while working for foreign employers, providing greater flexibility and legal clarity. Discover more about which option suits your remote work lifestyle best and the specific eligibility criteria involved.
Source and External Links
What is the difference between temporary and permanent ... - A temporary residence permit is a time-limited authorization allowing immigrants to stay in a country for a defined period, typically renewable and often serving as a pathway to permanent residence, but less secure due to the need for renewal and stricter eligibility requirements at each renewal.
Guide 5554 - Applying to remain in Canada as a temporary ... - In Canada, a Temporary Resident Permit (TRP) is issued to individuals who are otherwise inadmissible but are permitted to enter or stay for a limited time at the discretion of immigration authorities, with the permit subject to cancellation at any time and each family member requiring a separate TRP if also inadmissible.
Temporary Residence Permit of an EU Citizen's Family ... - In Czechia, a temporary residence permit for family members of EU citizens is granted to third-country nationals for stays longer than 90 days, provided they meet specific conditions related to their relationship with the EU citizen.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com