Reverse recruiting leverages external talent to identify and attract niche candidates through proactive outreach and personalized engagement, often yielding faster placement for specialized roles. Internal recruitment focuses on promoting existing employees within the organization, capitalizing on their institutional knowledge and proven performance to fill vacancies quickly and cost-effectively. Explore the key differences between reverse recruiting and internal recruitment strategies to optimize your hiring process.
Why it is important
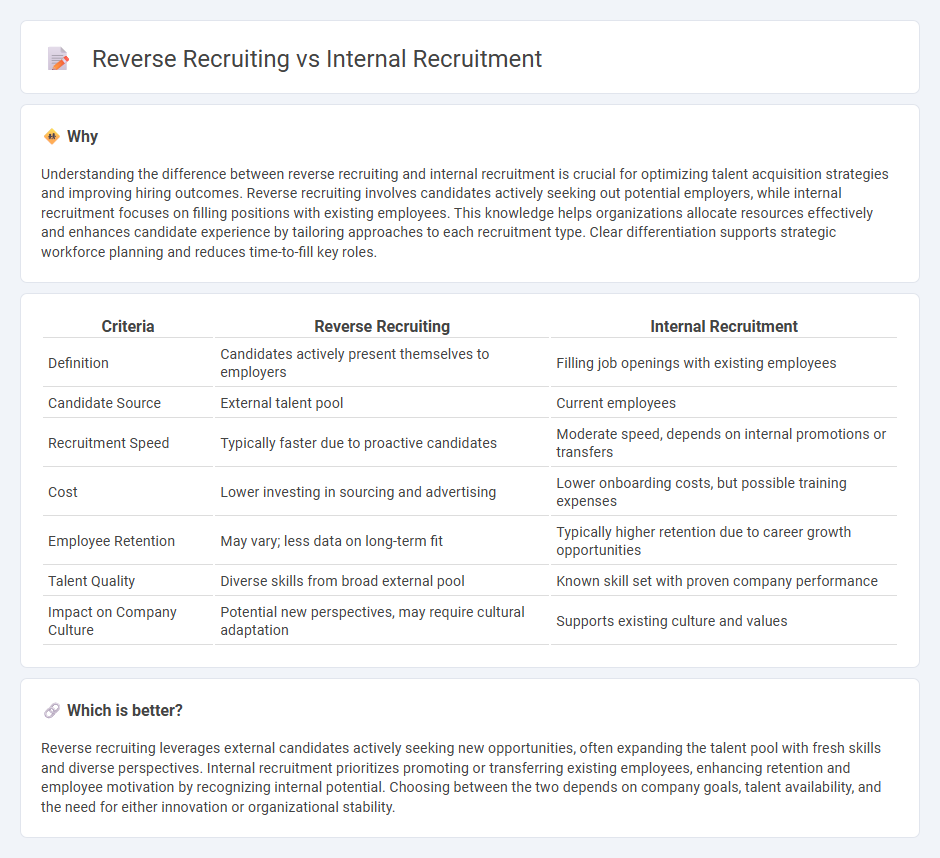
Understanding the difference between reverse recruiting and internal recruitment is crucial for optimizing talent acquisition strategies and improving hiring outcomes. Reverse recruiting involves candidates actively seeking out potential employers, while internal recruitment focuses on filling positions with existing employees. This knowledge helps organizations allocate resources effectively and enhances candidate experience by tailoring approaches to each recruitment type. Clear differentiation supports strategic workforce planning and reduces time-to-fill key roles.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Reverse Recruiting | Internal Recruitment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Candidates actively present themselves to employers | Filling job openings with existing employees |
| Candidate Source | External talent pool | Current employees |
| Recruitment Speed | Typically faster due to proactive candidates | Moderate speed, depends on internal promotions or transfers |
| Cost | Lower investing in sourcing and advertising | Lower onboarding costs, but possible training expenses |
| Employee Retention | May vary; less data on long-term fit | Typically higher retention due to career growth opportunities |
| Talent Quality | Diverse skills from broad external pool | Known skill set with proven company performance |
| Impact on Company Culture | Potential new perspectives, may require cultural adaptation | Supports existing culture and values |
Which is better?
Reverse recruiting leverages external candidates actively seeking new opportunities, often expanding the talent pool with fresh skills and diverse perspectives. Internal recruitment prioritizes promoting or transferring existing employees, enhancing retention and employee motivation by recognizing internal potential. Choosing between the two depends on company goals, talent availability, and the need for either innovation or organizational stability.
Connection
Reverse recruiting leverages employees' internal networks and knowledge to identify suitable candidates within the organization, making internal recruitment more efficient and aligned with company culture. This method enhances talent mobility by promoting existing staff to roles that fit their skills and career goals, thereby reducing external hiring costs and time. Integrating reverse recruiting with internal recruitment strategies supports workforce development and retention by valuing employee referrals and internal career progression.
Key Terms
Talent Pool
Internal recruitment leverages existing employee talent pools to fill vacancies quickly, reducing onboarding time and enhancing workforce retention. Reverse recruiting involves candidates actively seeking opportunities within a company's talent pool, enabling a proactive match between employee aspirations and organizational needs. Explore more about optimizing talent pool strategies to improve recruitment outcomes.
Candidate Experience
Internal recruitment enhances candidate experience by prioritizing employee career growth and leveraging existing organizational knowledge, which shortens onboarding time and boosts engagement. Reverse recruiting shifts the focus, with candidates actively approaching companies, leading to a more personalized and efficient hiring process that respects candidate preferences. Explore the unique advantages of both strategies to optimize your talent acquisition and improve overall candidate satisfaction.
Employer-Driven Process
Internal recruitment leverages existing employees to fill open positions, enhancing retention and reducing onboarding costs through a streamlined, employer-driven process. Reverse recruiting, meanwhile, involves employers actively marketing job opportunities to potential candidates, shifting the traditional dynamic by engaging talent proactively. Explore this strategic contrast further to optimize your hiring approach.
Source and External Links
What Is Internal Recruitment? 7 Internal Recruitment Methods - AIHR - Internal recruitment is the process of filling job openings within a company using current employees, with best practices including clear communication of opportunities, transparency, fair selection criteria, and support for employee development and transitions.
8 internal recruitment methods you need to know - Augeo - Effective internal recruitment methods include promotions, transfers, former employees, referrals, previous applicants, reorganizations, role changes, and converting contractors to full-time employees, aiming to motivate and retain employees through career growth.
Elevate Your Internal Recruitment Game - BambooHR - Internal recruitment involves hiring from within by understanding employee talent and career goals, establishing clear hiring policies, using internal communications for job postings, and providing fair screening and feedback to candidates.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com