Digital nomad visas enable remote workers to live and work legally in a foreign country while maintaining employment with their home-based company, offering flexibility and tax benefits. Expatriate contracts typically involve relocation with a formal employment agreement, providing local benefits and legal protections under the host country's labor laws. Explore the key differences to determine which option best supports your international career goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a digital nomad visa and an expatriate contract is crucial for legal compliance, tax obligations, and work rights. Digital nomad visas allow remote workers to legally reside in a foreign country while maintaining employment with an overseas company, typically for a limited time. Expatriate contracts usually involve direct employment by a foreign employer, including different labor laws, social security contributions, and relocation benefits. Knowing these distinctions ensures proper work authorization and optimizes financial and legal responsibilities during international employment.
Comparison Table
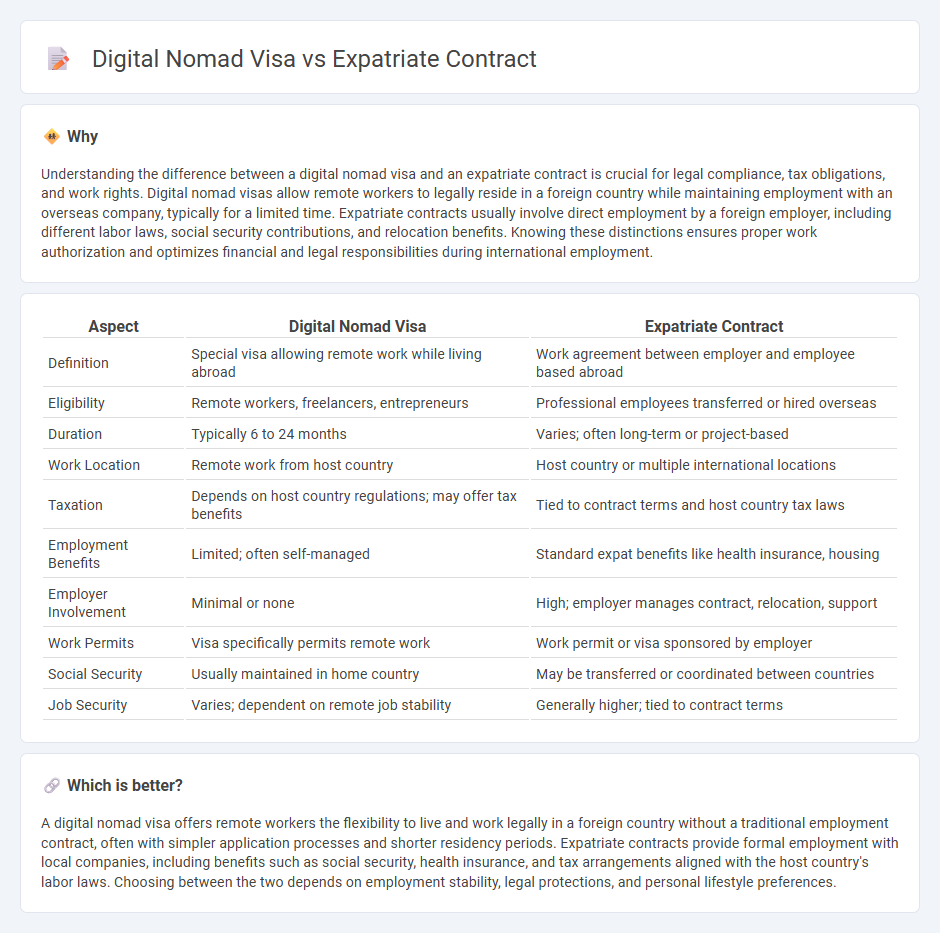
| Aspect | Digital Nomad Visa | Expatriate Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Special visa allowing remote work while living abroad | Work agreement between employer and employee based abroad |
| Eligibility | Remote workers, freelancers, entrepreneurs | Professional employees transferred or hired overseas |
| Duration | Typically 6 to 24 months | Varies; often long-term or project-based |
| Work Location | Remote work from host country | Host country or multiple international locations |
| Taxation | Depends on host country regulations; may offer tax benefits | Tied to contract terms and host country tax laws |
| Employment Benefits | Limited; often self-managed | Standard expat benefits like health insurance, housing |
| Employer Involvement | Minimal or none | High; employer manages contract, relocation, support |
| Work Permits | Visa specifically permits remote work | Work permit or visa sponsored by employer |
| Social Security | Usually maintained in home country | May be transferred or coordinated between countries |
| Job Security | Varies; dependent on remote job stability | Generally higher; tied to contract terms |
Which is better?
A digital nomad visa offers remote workers the flexibility to live and work legally in a foreign country without a traditional employment contract, often with simpler application processes and shorter residency periods. Expatriate contracts provide formal employment with local companies, including benefits such as social security, health insurance, and tax arrangements aligned with the host country's labor laws. Choosing between the two depends on employment stability, legal protections, and personal lifestyle preferences.
Connection
Digital nomad visas facilitate remote work by allowing employees to legally reside and work in foreign countries without traditional work permits, connecting closely with expatriate contracts that define the terms of employment for professionals working abroad. These visas support businesses by simplifying compliance with international labor laws, while expatriate contracts establish essential conditions such as duration, compensation, and tax obligations. Together, they streamline cross-border employment arrangements, enabling global mobility and flexible workforce management.
Key Terms
Work Authorization
Expatriate contracts typically provide a formal work authorization tied to a specific employer and country, ensuring compliance with local labor laws and tax regulations. Digital nomad visas grant remote workers legal permission to stay and work temporarily in a foreign country while maintaining employment with a company based elsewhere. Explore the key differences in work authorization requirements and benefits to determine the best option for your international career.
Tax Residency
Expatriate contracts often require employees to maintain tax residency in their home country while working abroad under specific international tax treaties, ensuring compliance with corporate taxation laws. Digital nomad visas allow remote workers to reside temporarily in a foreign country, often enabling favorable tax conditions or exemptions depending on local regulations and duration of stay. Explore deeper into tax residency rules related to these options to optimize your international work and tax planning.
Social Security Benefits
Expatriate contracts typically offer social security benefits aligned with the home country's system, ensuring contributions and coverage continuity during the assignment abroad. Digital nomad visas often require applicants to manage their own social security arrangements, as these visas do not automatically grant access to the host country's social security system. Explore the specific social security provisions linked to each option to make an informed decision about international work arrangements.
Source and External Links
What is an Expatriate Agreement? (Key Terms + Sample) - An expatriate agreement is a contract between a company and a foreign or migrant worker for an international job, outlining terms such as compensation, duration, and job conditions to govern the worker's relocation and work abroad.
Structuring Expatriate Arrangements - CM Murray LLP (PDF) - Expatriate contracts often include clauses suspending home country contracts and may require local contracts in host countries to comply with immigration and legal requirements, reflecting different pay and benefit structures.
Top 5 Tips on How to Negotiate an Expat Package - When negotiating an expatriate contract, it is critical to address tax responsibilities, reimbursement for housing costs, and to understand how foreign tax payments affect your overall compensation and US tax liabilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com