Ghost work involves tasks completed by remote workers often unnoticed by end users, typically through digital platforms offering micro-tasks or content moderation. Flexible work encompasses various arrangements like remote work, freelance contracts, or adjustable hours, providing workers autonomy over their schedules. Explore the distinctions between ghost work and flexible work to understand the evolving landscape of modern employment.
Why it is important
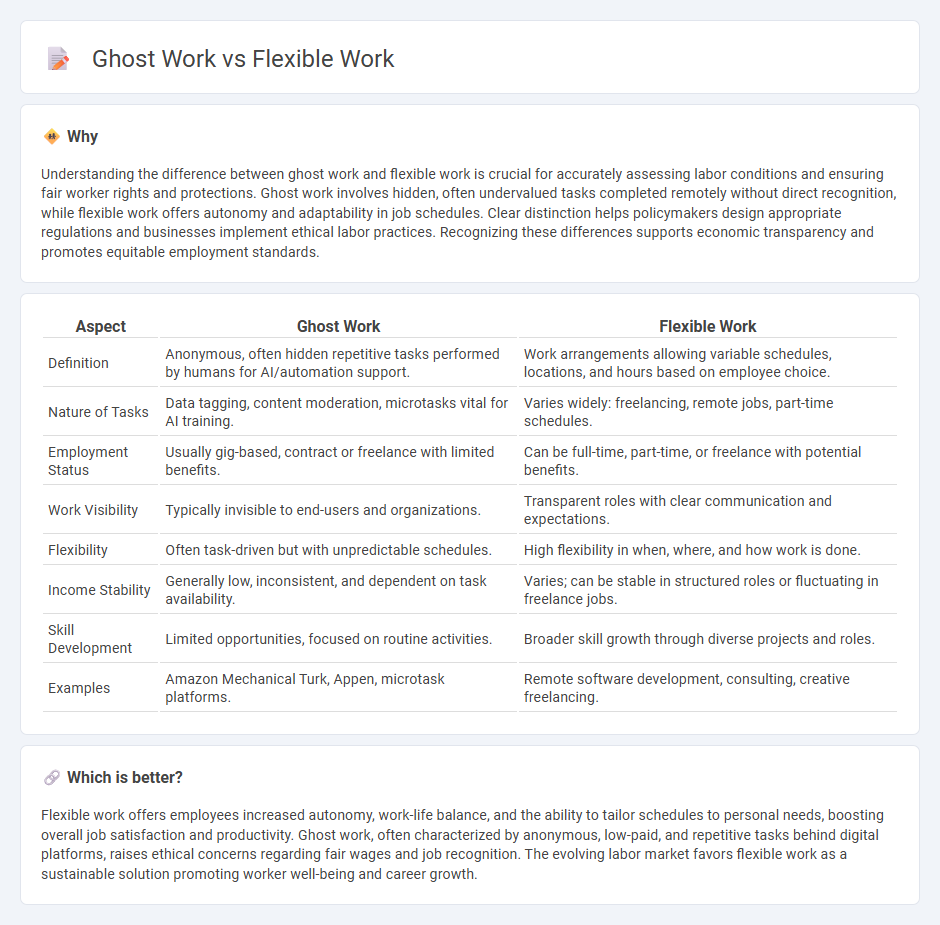
Understanding the difference between ghost work and flexible work is crucial for accurately assessing labor conditions and ensuring fair worker rights and protections. Ghost work involves hidden, often undervalued tasks completed remotely without direct recognition, while flexible work offers autonomy and adaptability in job schedules. Clear distinction helps policymakers design appropriate regulations and businesses implement ethical labor practices. Recognizing these differences supports economic transparency and promotes equitable employment standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Flexible Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Anonymous, often hidden repetitive tasks performed by humans for AI/automation support. | Work arrangements allowing variable schedules, locations, and hours based on employee choice. |
| Nature of Tasks | Data tagging, content moderation, microtasks vital for AI training. | Varies widely: freelancing, remote jobs, part-time schedules. |
| Employment Status | Usually gig-based, contract or freelance with limited benefits. | Can be full-time, part-time, or freelance with potential benefits. |
| Work Visibility | Typically invisible to end-users and organizations. | Transparent roles with clear communication and expectations. |
| Flexibility | Often task-driven but with unpredictable schedules. | High flexibility in when, where, and how work is done. |
| Income Stability | Generally low, inconsistent, and dependent on task availability. | Varies; can be stable in structured roles or fluctuating in freelance jobs. |
| Skill Development | Limited opportunities, focused on routine activities. | Broader skill growth through diverse projects and roles. |
| Examples | Amazon Mechanical Turk, Appen, microtask platforms. | Remote software development, consulting, creative freelancing. |
Which is better?
Flexible work offers employees increased autonomy, work-life balance, and the ability to tailor schedules to personal needs, boosting overall job satisfaction and productivity. Ghost work, often characterized by anonymous, low-paid, and repetitive tasks behind digital platforms, raises ethical concerns regarding fair wages and job recognition. The evolving labor market favors flexible work as a sustainable solution promoting worker well-being and career growth.
Connection
Ghost work, characterized by hidden or unseen digital labor, often overlaps with flexible work arrangements due to its reliance on remote, task-based employment facilitated by online platforms. Both types of employment emphasize autonomy, allowing workers to choose hours and projects while exposing them to inconsistent income and limited labor protections. This intersection highlights the evolving nature of employment, where technology enables flexibility but also challenges traditional job security and benefits.
Key Terms
Remote Work
Flexible work arrangements empower remote employees to tailor their schedules, enhancing productivity and work-life balance in various industries. Ghost work involves unseen digital labor performed remotely, often by gig workers, to manage AI training and content moderation, highlighting an evolving workforce dynamic. Discover more about how remote work trends reshape labor models and economic opportunities in the digital age.
Gig Economy
Flexible work in the gig economy offers autonomy over schedules and task selection, enabling workers to balance personal commitments with income generation. Ghost work involves invisible labor, such as data labeling and content moderation, often performed remotely without recognition or traditional employment benefits. Explore how these contrasting roles shape the evolving landscape of digital labor and worker rights.
Task-based Labor
Task-based labor, characterized by flexible work arrangements, allows employees to complete specific assignments on their own schedules, promoting autonomy and efficiency. Ghost work refers to invisible, often low-wage tasks performed behind the scenes, such as data labeling or content moderation, which are critical to AI and digital platforms yet lack formal recognition. Explore how understanding these distinctions can reshape labor policies and workforce management.
Source and External Links
6 Types of Flexible Work Arrangements with Examples - ActivTrak - Flexible work arrangements allow employees to choose how, when, and where they work, commonly including remote work, hybrid work, flexible hours, compressed schedules, part-time work, and freelance/contract options, all benefiting productivity and retention.
Workplace Flexibility - Employer Assistance and Resource Network - Workplace flexibility covers variations in when (schedules), where (remote or hybrid work), and how (methods or processes) work gets done, tailored to support employee needs and increase accessibility.
Flexible Work Schedules - OPM - Flexible work schedules include core hours plus flexible hours allowing employees to adjust their arrival and departure times to balance work and personal responsibilities within agency rules.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com