Microinternships offer short-term, project-based work experiences that allow students to quickly gain industry-relevant skills and build professional networks. Co-op programs provide extended, paid work placements integrated into academic curricula, giving students in-depth exposure to their chosen field over multiple semesters. Explore the benefits and differences between microinternships and co-op programs to determine the best pathway for your career development.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between microinternships and co-op programs is crucial for navigating diverse employment opportunities effectively. Microinternships typically offer short-term, project-based work experiences that enhance specific skills and provide immediate resume boosts. Co-op programs involve extended, structured work placements integrated with academic curricula, offering deeper industry exposure and professional networking. Distinguishing these options helps students and job seekers align experiences with career goals and maximize employability.
Comparison Table
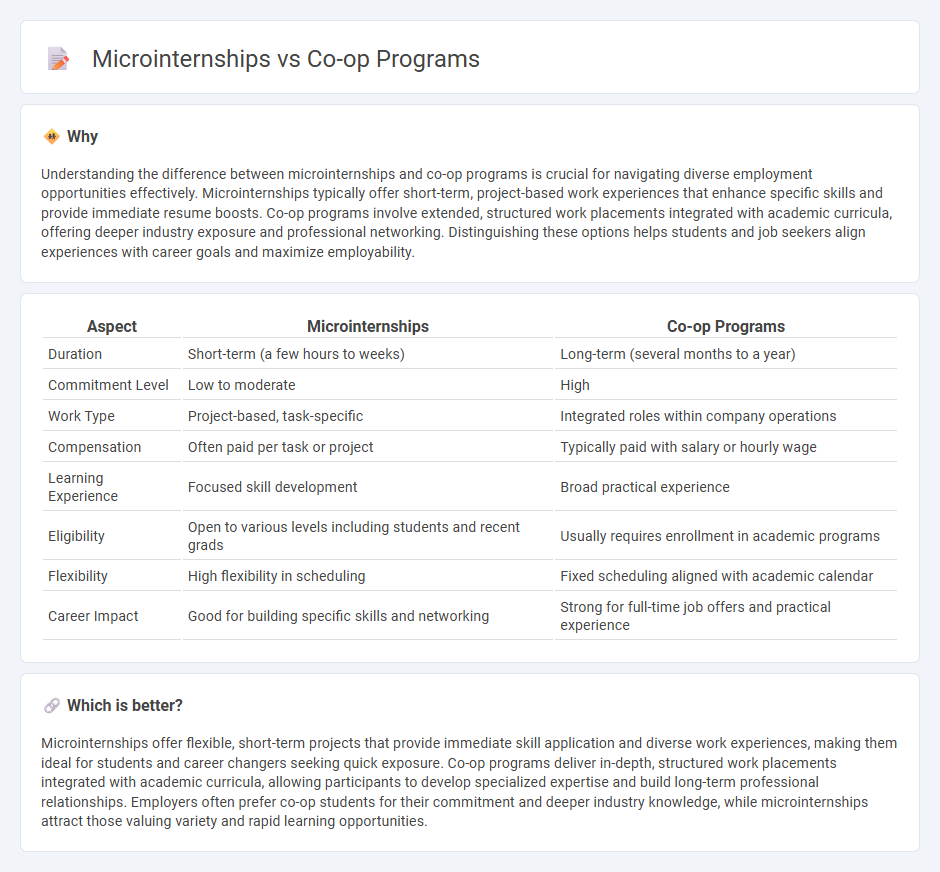
| Aspect | Microinternships | Co-op Programs |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Short-term (a few hours to weeks) | Long-term (several months to a year) |
| Commitment Level | Low to moderate | High |
| Work Type | Project-based, task-specific | Integrated roles within company operations |
| Compensation | Often paid per task or project | Typically paid with salary or hourly wage |
| Learning Experience | Focused skill development | Broad practical experience |
| Eligibility | Open to various levels including students and recent grads | Usually requires enrollment in academic programs |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in scheduling | Fixed scheduling aligned with academic calendar |
| Career Impact | Good for building specific skills and networking | Strong for full-time job offers and practical experience |
Which is better?
Microinternships offer flexible, short-term projects that provide immediate skill application and diverse work experiences, making them ideal for students and career changers seeking quick exposure. Co-op programs deliver in-depth, structured work placements integrated with academic curricula, allowing participants to develop specialized expertise and build long-term professional relationships. Employers often prefer co-op students for their commitment and deeper industry knowledge, while microinternships attract those valuing variety and rapid learning opportunities.
Connection
Microinternships and co-op programs both provide structured, short-term work experiences that connect students with employers, enhancing practical skills and improving job readiness. These experiential learning opportunities enable participants to apply academic knowledge in real-world settings while building professional networks and gaining insights into industry demands. Employers use these programs to identify and evaluate potential talent, streamlining recruitment and increasing workforce diversity.
Key Terms
Duration
Co-op programs typically span multiple months, often aligning with academic semesters and providing extended hands-on work experience, while microinternships are short-term, project-based assignments lasting from a few days to a few weeks. The longer duration of co-ops allows for deeper skill development and integration within the company culture, whereas microinternships offer flexible, rapid exposure to professional tasks. Explore more to determine which experience best aligns with your career goals.
Work Experience Type
Co-op programs offer extended, semester-long work placements integrated into academic curricula, providing in-depth industry experience and skill development. Microinternships consist of short-term, project-based assignments allowing students to gain diverse exposure and flexibility without long-term commitments. Explore how choosing between these work experience types can strategically enhance your career path.
Academic Integration
Co-op programs offer structured, semester-long work experiences deeply integrated with academic curricula, fostering practical application of classroom knowledge. Microinternships provide shorter, project-based tasks that complement academic learning but lack the extensive integration found in co-op programs. Explore how each option enhances academic growth and career readiness by learning more about their unique educational benefits.
Source and External Links
Cooperative education - Wikipedia - Co-op programs provide academic credit for structured work experiences combining classroom learning with paid work terms, commonly found in various universities with competitive entry and diverse academic fields including business, engineering, and science.
Top Schools for Co-Op Programs - Top Tier Admissions - Leading universities like Drexel, Georgia Tech, Northeastern, and University of Cincinnati have deeply integrated co-op programs into their curriculum, enhancing student employability and resulting in increased admissions.
Cooperative Education (Co-op) | Programs Overview - Co-op programs alternate academic study with full-time paid work, allowing students to maintain full-time status, earn competitive wages, receive academic credit, and gain professional experience under guided support.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com