The circular economy focuses on sustainable resource management by minimizing waste and promoting reuse, repair, and recycling processes to create a closed-loop system. The gig economy, by contrast, revolves around flexible, short-term jobs facilitated by digital platforms, emphasizing workforce agility and on-demand services. Explore the key differences and impacts of these economic models to understand their roles in shaping future markets.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular economy and gig economy is crucial for developing sustainable business models and labor policies. The circular economy focuses on resource efficiency by minimizing waste through reuse, recycling, and sustainable design. The gig economy emphasizes flexible, short-term employment often facilitated by digital platforms, impacting labor rights and income stability. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers balance environmental goals with economic and social workforce needs.
Comparison Table
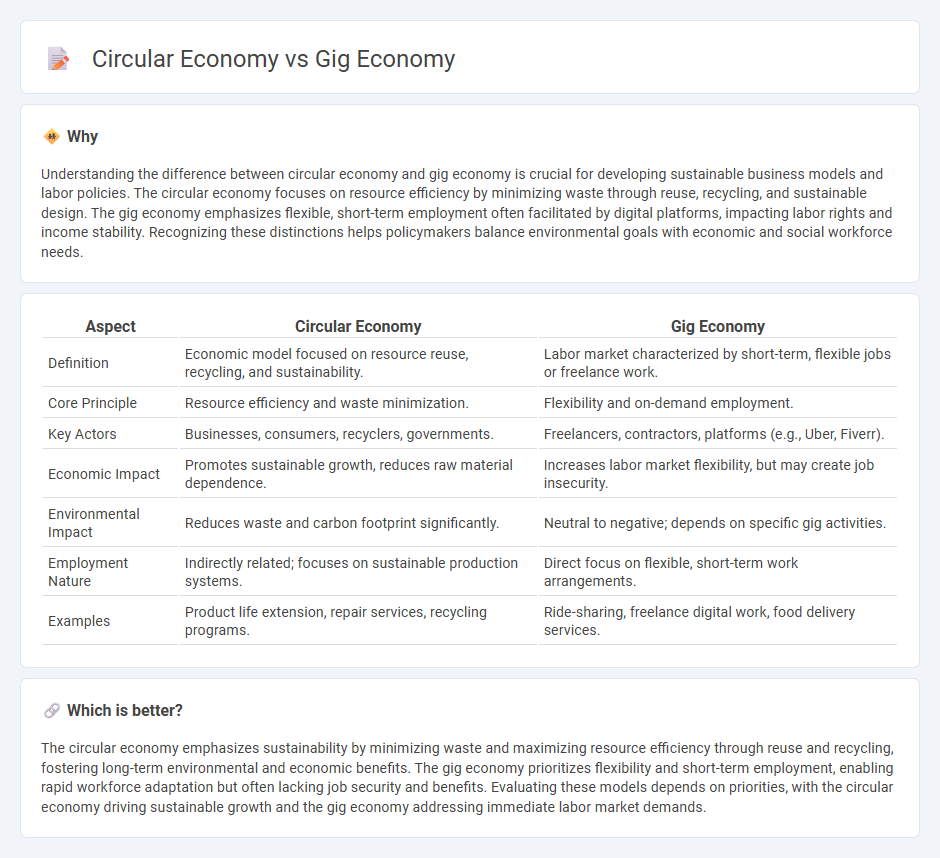
| Aspect | Circular Economy | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic model focused on resource reuse, recycling, and sustainability. | Labor market characterized by short-term, flexible jobs or freelance work. |
| Core Principle | Resource efficiency and waste minimization. | Flexibility and on-demand employment. |
| Key Actors | Businesses, consumers, recyclers, governments. | Freelancers, contractors, platforms (e.g., Uber, Fiverr). |
| Economic Impact | Promotes sustainable growth, reduces raw material dependence. | Increases labor market flexibility, but may create job insecurity. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and carbon footprint significantly. | Neutral to negative; depends on specific gig activities. |
| Employment Nature | Indirectly related; focuses on sustainable production systems. | Direct focus on flexible, short-term work arrangements. |
| Examples | Product life extension, repair services, recycling programs. | Ride-sharing, freelance digital work, food delivery services. |
Which is better?
The circular economy emphasizes sustainability by minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency through reuse and recycling, fostering long-term environmental and economic benefits. The gig economy prioritizes flexibility and short-term employment, enabling rapid workforce adaptation but often lacking job security and benefits. Evaluating these models depends on priorities, with the circular economy driving sustainable growth and the gig economy addressing immediate labor market demands.
Connection
The circular economy and gig economy intersect through their shared emphasis on resource efficiency and flexible labor markets, driving sustainable business practices and reducing waste. Circular economy models promote resource reuse and recycling, while the gig economy leverages independent contractors and freelance work to match supply with demand dynamically. Together, these economic systems enhance sustainability by optimizing asset utilization and minimizing environmental impact.
Key Terms
Flexibility (Gig Economy)
The gig economy emphasizes flexibility by offering workers the freedom to choose projects, set their schedules, and work from various locations, which enhances job autonomy and work-life balance. Unlike traditional employment, gig work allows rapid adaptation to market demands, fostering economic resilience through diversified income streams. Explore how this flexibility transforms labor markets and shapes future employment trends.
Resource Efficiency (Circular Economy)
The circular economy emphasizes resource efficiency by prioritizing the reuse, refurbishment, and recycling of materials to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. Unlike the gig economy, which focuses on flexible labor markets and on-demand services, the circular economy integrates systematic processes that extend product life cycles and promote sustainable resource management. Explore how adopting circular economy principles can drive long-term environmental and economic benefits.
Platform-based Labor (Gig Economy)
Platform-based labor in the gig economy revolutionizes workforce dynamics by enabling flexible, on-demand jobs through digital platforms like Uber and TaskRabbit, optimizing labor allocation and reducing unemployment. Unlike the circular economy, which emphasizes resource efficiency and waste reduction, the gig economy centers on service provision and labor market fluidity facilitated by technology. Explore how platform-based labor drives economic transformation and workforce innovation in today's digital landscape.
Source and External Links
What is the Gig Economy?| Definition from TechTarget - The gig economy is a free market system characterized by temporary positions where organizations hire independent workers for short-term commitments, enabled by digital platforms that connect freelancers globally across industries.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy allows individuals to work on short-term projects or gigs instead of full-time roles, with major growth reflecting a shift toward flexibility and autonomy in the workforce, reaching over 70 million freelancers in the U.S. and a global market valued at $556.7 billion in 2024.
Gig economy - Wikipedia - The gig economy involves freelance or side-employment jobs typically paid per task or project via digital platforms, providing workers greater schedule flexibility while enabling companies to reduce traditional employee costs like benefits and office expenses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com