Friendshoring reshapes global supply chains by prioritizing trade with allied nations to enhance economic security and reduce dependency on distant or hostile countries. This strategy contrasts with deglobalization, which involves a broader retreat from international trade and investment, leading to increased localization and self-sufficiency. Explore how these trends impact global economic dynamics and future trade policies.
Why it is important
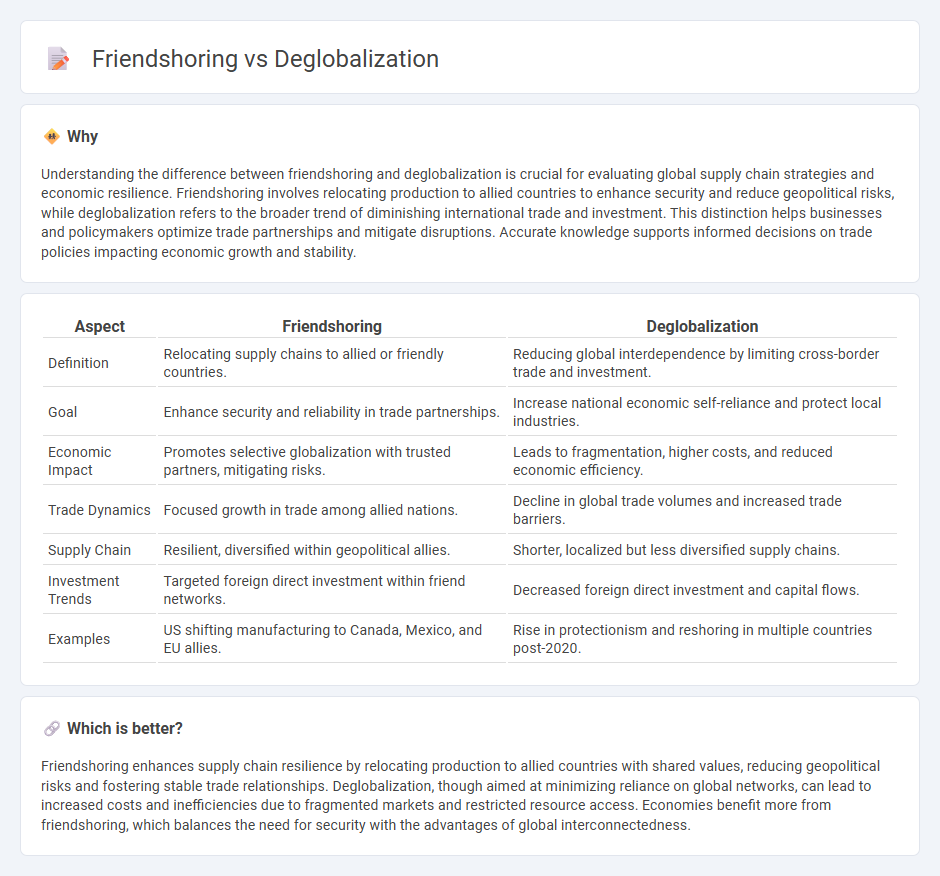
Understanding the difference between friendshoring and deglobalization is crucial for evaluating global supply chain strategies and economic resilience. Friendshoring involves relocating production to allied countries to enhance security and reduce geopolitical risks, while deglobalization refers to the broader trend of diminishing international trade and investment. This distinction helps businesses and policymakers optimize trade partnerships and mitigate disruptions. Accurate knowledge supports informed decisions on trade policies impacting economic growth and stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Friendshoring | Deglobalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating supply chains to allied or friendly countries. | Reducing global interdependence by limiting cross-border trade and investment. |
| Goal | Enhance security and reliability in trade partnerships. | Increase national economic self-reliance and protect local industries. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes selective globalization with trusted partners, mitigating risks. | Leads to fragmentation, higher costs, and reduced economic efficiency. |
| Trade Dynamics | Focused growth in trade among allied nations. | Decline in global trade volumes and increased trade barriers. |
| Supply Chain | Resilient, diversified within geopolitical allies. | Shorter, localized but less diversified supply chains. |
| Investment Trends | Targeted foreign direct investment within friend networks. | Decreased foreign direct investment and capital flows. |
| Examples | US shifting manufacturing to Canada, Mexico, and EU allies. | Rise in protectionism and reshoring in multiple countries post-2020. |
Which is better?
Friendshoring enhances supply chain resilience by relocating production to allied countries with shared values, reducing geopolitical risks and fostering stable trade relationships. Deglobalization, though aimed at minimizing reliance on global networks, can lead to increased costs and inefficiencies due to fragmented markets and restricted resource access. Economies benefit more from friendshoring, which balances the need for security with the advantages of global interconnectedness.
Connection
Friendshoring reshapes global supply chains by prioritizing trade partnerships among politically aligned countries, thereby reducing reliance on distant or adversarial nations. This strategic shift drives deglobalization by fragmenting international economic networks and fostering regionalized production hubs. As a result, friendshoring accelerates the retraction of globalization trends, emphasizing security and resilience over global integration.
Key Terms
Trade Barriers
Trade barriers shape the dynamics of deglobalization by increasing tariffs, quotas, and regulatory hurdles, which encourage nations to reduce dependency on global supply chains. Friendshoring, in contrast, strategically relocates production within allied countries, minimizing exposure to hostile trade barriers while maintaining access to stable markets. Explore the advantages and challenges of these trade strategies to understand their impact on global commerce.
Supply Chain Resilience
Deglobalization reduces supply chain risks by shortening global linkages and promoting local production, enhancing control over inventory and responsiveness to disruptions. Friendshoring strategically shifts supply chains to allied countries, balancing cost efficiency with political and economic stability to ensure continuity. Explore how integrating deglobalization and friendshoring strategies can optimize supply chain resilience in your business.
Geopolitical Alliances
Deglobalization shifts supply chains away from global networks to reduce dependency, emphasizing national interests and economic sovereignty amid rising geopolitical tensions. Friendshoring strengthens alliances by relocating production to trusted partner countries, leveraging geopolitical partnerships to ensure supply chain resilience and security. Explore how these strategies shape international trade and geopolitical alliances in today's dynamic global economy.
Source and External Links
Deglobalization - Wikipedia - Deglobalization is the process of reducing interdependence and integration between nations, often marked by declining international trade and investment, and stands in contrast to globalization's trend of increasing global connectivity.
The Specter of Deglobalization | Current History - Deglobalization refers to the reduction in interaction and integration among national economies, a process that intensified after the 2008 financial crisis and was further exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic's disruptions to global supply chains and rising protectionism.
Deglobalisation: what you need to know | World Economic Forum - Recent global shocks, such as the Ukraine war, COVID-19, and climate initiatives, are accelerating a shift toward deglobalization, with nations and corporations prioritizing security and resilience over the efficiency of global value chains.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com