Diagnostic mapping identifies root causes of issues by analyzing data patterns and organizational processes, enabling targeted interventions. Problem structuring focuses on framing complex challenges, defining stakeholder perspectives, and clarifying objectives to facilitate collaborative decision-making. Explore more to understand how these approaches improve consulting outcomes.
Why it is important
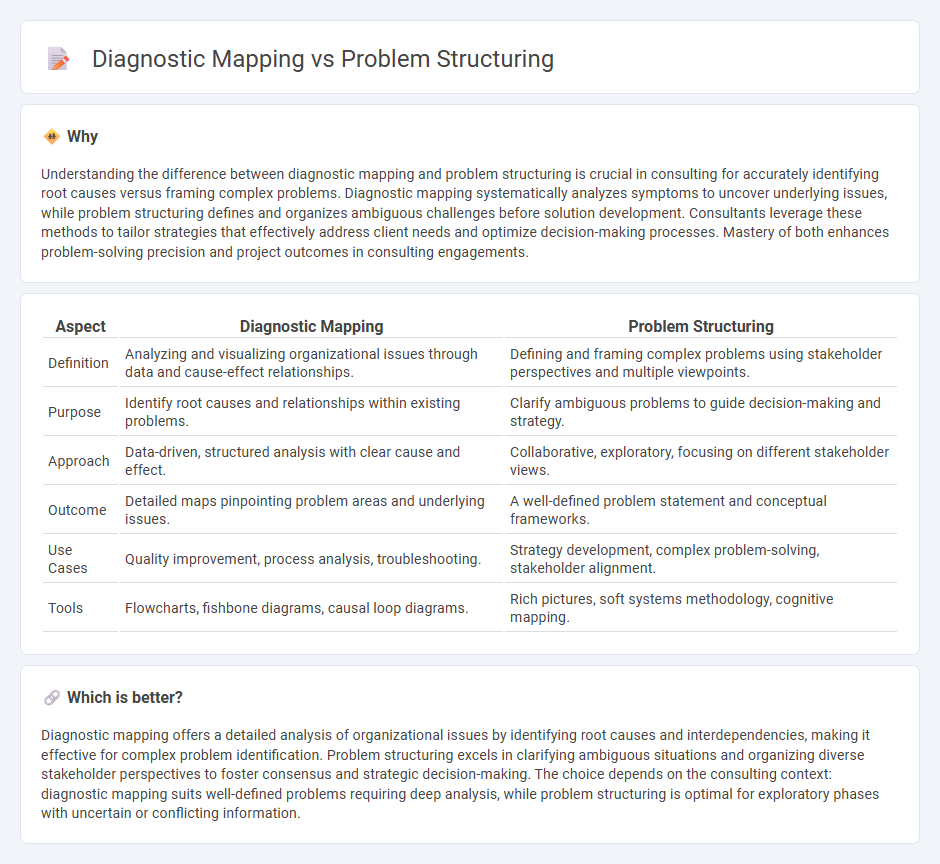
Understanding the difference between diagnostic mapping and problem structuring is crucial in consulting for accurately identifying root causes versus framing complex problems. Diagnostic mapping systematically analyzes symptoms to uncover underlying issues, while problem structuring defines and organizes ambiguous challenges before solution development. Consultants leverage these methods to tailor strategies that effectively address client needs and optimize decision-making processes. Mastery of both enhances problem-solving precision and project outcomes in consulting engagements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Diagnostic Mapping | Problem Structuring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzing and visualizing organizational issues through data and cause-effect relationships. | Defining and framing complex problems using stakeholder perspectives and multiple viewpoints. |
| Purpose | Identify root causes and relationships within existing problems. | Clarify ambiguous problems to guide decision-making and strategy. |
| Approach | Data-driven, structured analysis with clear cause and effect. | Collaborative, exploratory, focusing on different stakeholder views. |
| Outcome | Detailed maps pinpointing problem areas and underlying issues. | A well-defined problem statement and conceptual frameworks. |
| Use Cases | Quality improvement, process analysis, troubleshooting. | Strategy development, complex problem-solving, stakeholder alignment. |
| Tools | Flowcharts, fishbone diagrams, causal loop diagrams. | Rich pictures, soft systems methodology, cognitive mapping. |
Which is better?
Diagnostic mapping offers a detailed analysis of organizational issues by identifying root causes and interdependencies, making it effective for complex problem identification. Problem structuring excels in clarifying ambiguous situations and organizing diverse stakeholder perspectives to foster consensus and strategic decision-making. The choice depends on the consulting context: diagnostic mapping suits well-defined problems requiring deep analysis, while problem structuring is optimal for exploratory phases with uncertain or conflicting information.
Connection
Diagnostic mapping identifies key issues and data patterns within an organization, forming the foundation for effective problem structuring. Problem structuring then organizes these identified elements into coherent frameworks to facilitate targeted interventions and strategic decision-making. This connection ensures a systematic approach, enhancing clarity and precision in consulting solutions.
Key Terms
**Problem Structuring:**
Problem structuring involves identifying, defining, and breaking down complex issues into manageable components, enabling clearer understanding and strategic action. It emphasizes framing challenges to reveal underlying causes and interdependencies, which supports effective decision-making and solution development. Explore more to master problem structuring techniques and enhance organizational problem-solving capabilities.
Issue Tree
Problem structuring involves breaking down complex challenges into manageable components to identify root causes, while diagnostic mapping visually represents relationships between issues for clearer analysis. An Issue Tree is a key tool in problem structuring that hierarchically decomposes problems into smaller, logically connected sub-issues, enabling systematic exploration. Explore how mastering Issue Trees enhances problem-solving efficiency and decision-making clarity.
Hypothesis-Driven
Problem structuring emphasizes defining and framing complex issues without predefined solutions, enabling a clear understanding of underlying challenges. Diagnostic mapping, centered on hypothesis-driven analysis, systematically tests assumptions to identify root causes using data and evidence. Explore the detailed methodologies and benefits of hypothesis-driven diagnostic mapping to enhance problem-solving accuracy.
Source and External Links
Problem structuring - The Strategy Unit - Problem structuring involves understanding all causes and effects of a problem using tools like problem trees and driver diagrams to reveal complexity and guide the development of solutions and targeted interventions in a collaborative group setting.
problem structuring in public policy analysis - Problem structuring in public policy addresses ill-defined, complex problem situations by analyzing how humans interpret and define problems from indeterminate conditions to formulate actionable issues for decision-making.
Problem structuring methods - Wikipedia - Problem structuring methods (PSMs) are a family of facilitation techniques used to create data-populated models of complex situations, enhancing group productivity, managing power dynamics, and supporting participative decision-making through process and content skills.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com