Corporate venturing involves established companies investing in innovative startups to foster strategic growth and gain competitive advantage through collaboration. Private equity investment focuses on acquiring and restructuring mature companies to enhance their financial performance and generate high returns for investors. Explore the key differences and strategic benefits of corporate venturing and private equity investment to optimize your investment approach.
Why it is important
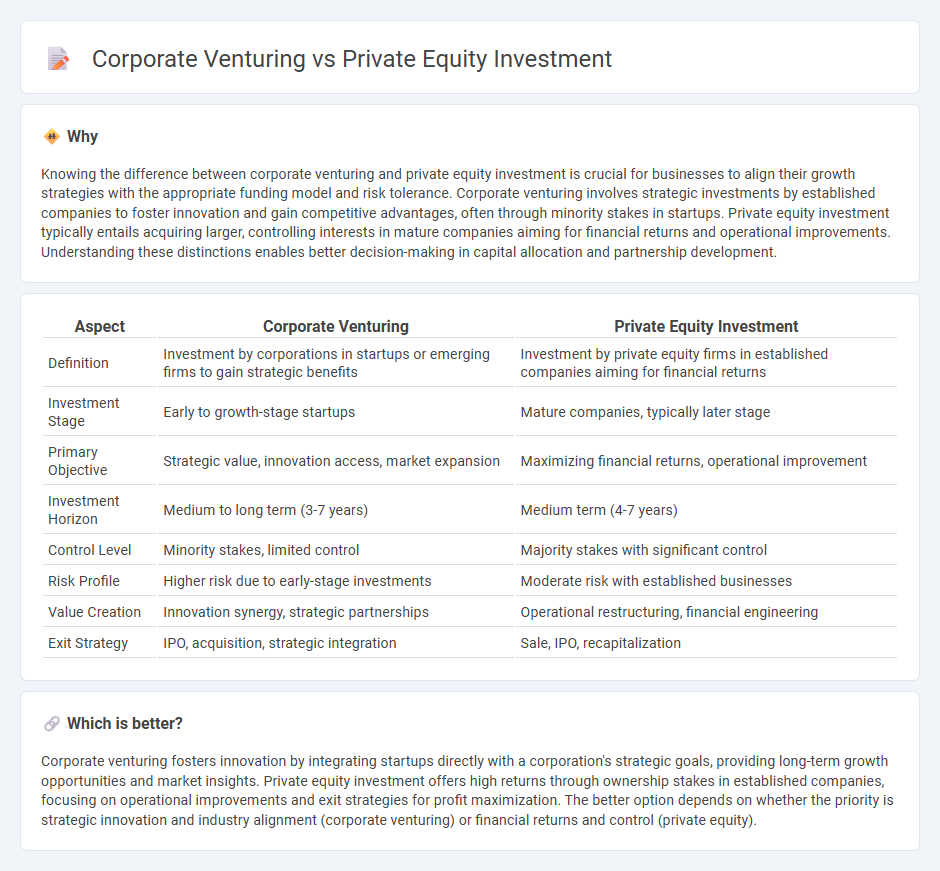
Knowing the difference between corporate venturing and private equity investment is crucial for businesses to align their growth strategies with the appropriate funding model and risk tolerance. Corporate venturing involves strategic investments by established companies to foster innovation and gain competitive advantages, often through minority stakes in startups. Private equity investment typically entails acquiring larger, controlling interests in mature companies aiming for financial returns and operational improvements. Understanding these distinctions enables better decision-making in capital allocation and partnership development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Private Equity Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment by corporations in startups or emerging firms to gain strategic benefits | Investment by private equity firms in established companies aiming for financial returns |
| Investment Stage | Early to growth-stage startups | Mature companies, typically later stage |
| Primary Objective | Strategic value, innovation access, market expansion | Maximizing financial returns, operational improvement |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long term (3-7 years) | Medium term (4-7 years) |
| Control Level | Minority stakes, limited control | Majority stakes with significant control |
| Risk Profile | Higher risk due to early-stage investments | Moderate risk with established businesses |
| Value Creation | Innovation synergy, strategic partnerships | Operational restructuring, financial engineering |
| Exit Strategy | IPO, acquisition, strategic integration | Sale, IPO, recapitalization |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing fosters innovation by integrating startups directly with a corporation's strategic goals, providing long-term growth opportunities and market insights. Private equity investment offers high returns through ownership stakes in established companies, focusing on operational improvements and exit strategies for profit maximization. The better option depends on whether the priority is strategic innovation and industry alignment (corporate venturing) or financial returns and control (private equity).
Connection
Corporate venturing and private equity investment intersect through their shared focus on fueling innovation and growth within companies. Corporate venturing arms invest in startups and emerging technologies to gain strategic advantages, while private equity targets mature businesses for operational improvements and value creation. Both approaches leverage capital infusion and strategic guidance to enhance portfolio company performance and drive long-term returns.
Key Terms
Deal Sourcing
Private equity investment relies heavily on extensive networks, market research, and intermediaries such as investment banks to source high-value deals, often targeting mature companies with stable cash flows. Corporate venturing emphasizes strategic alignment by leveraging internal innovation teams and partnerships with startups to identify disruptive technologies and early-stage opportunities. Explore more about optimizing deal sourcing strategies to maximize investment returns and strategic growth.
Value Creation
Private equity investment concentrates on acquiring substantial ownership stakes in mature companies to drive operational improvements and maximize financial returns through strategic restructuring and performance optimization. Corporate venturing targets early-stage startups, leveraging innovation and market disruption to foster long-term growth aligned with the parent company's strategic goals. Discover how these distinct approaches create value in diverse market environments and investment horizons.
Strategic Alignment
Private equity investment typically seeks financial returns through acquiring significant equity stakes in established companies, emphasizing value creation via operational improvements and market expansion. Corporate venturing aligns more closely with the strategic goals of the parent company by investing in innovative startups that can drive technological advancement or open new market opportunities. Discover how strategic alignment influences these investment approaches and their impact on business growth.
Source and External Links
An Introduction to Private Equity Basics | Morgan Stanley - Private equity involves investing in non-public companies or assets through strategies like buyout, growth equity, and venture capital, often requiring long-term capital commitments and access for qualified, institutional, or high-net-worth investors.
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity funds raise capital from institutional investors to acquire equity stakes in private companies, aiming to improve performance and generate returns over a multi-year horizon through strategies like revenue growth, cost reduction, and governance restructuring.
Private Equity: What You Need to Know - KKR - Private equity managers invest in privately held companies to enhance their value by strengthening management, pursuing acquisitions, optimizing operations, and refining business strategies during the holding period.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com